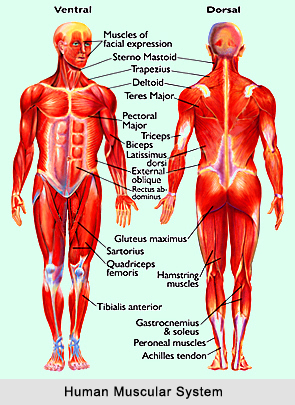
 Impact of Yoga on Muscular System of humans largely influences the strength and flexibility of an individual. Muscles are specialised tissues, which can convert chemical energy into the mechanical power and force. Practicing yoga can improve the muscular system in the human beings. Most of the yogic practices, especially Yoga Asanas, require fine control over the use of the muscles and the joints. The controlled use of specific group of muscles to bring about a particular movement, and the maintenance of the final position with minimum amount of muscle tone, are the two important factors in the performance of these asanas. Because of this, all the 3 features of muscular activity (skill, strength and stamina) are influenced by the Yogic practice. Additionally the gradual and sustained increase in the range of movements through various joints increases body flexibility.
Impact of Yoga on Muscular System of humans largely influences the strength and flexibility of an individual. Muscles are specialised tissues, which can convert chemical energy into the mechanical power and force. Practicing yoga can improve the muscular system in the human beings. Most of the yogic practices, especially Yoga Asanas, require fine control over the use of the muscles and the joints. The controlled use of specific group of muscles to bring about a particular movement, and the maintenance of the final position with minimum amount of muscle tone, are the two important factors in the performance of these asanas. Because of this, all the 3 features of muscular activity (skill, strength and stamina) are influenced by the Yogic practice. Additionally the gradual and sustained increase in the range of movements through various joints increases body flexibility.
All the muscles possess an amazing capacity for irritability, conductivity, extensibility and contractility. Irritability is the ability to respond to the stimulation. On stretching, the length of the muscle is increased. The muscle becomes thicker and shorter in length when it contracts. All the three types of muscles differ in their structure, nervous control, mode of contraction and location. The voluntary movements are finely controlled due to neuromuscular co ordination. The skeletal muscles move the joints with the help of the tendons. The most common types of movements in the human body are flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and rotation.
Voluntary Muscles in a human body include the following:
Skeletal Muscles
The skeletal muscles are attached with the bones and cartilages with the help of a tendon. Tendon is a strong band of fibrous tissue at the end of the muscle bundle. These muscles are controlled as per an individual`s desire and hence they are called voluntary muscles, like, muscles of the head, trunk, hands and legs, tongue, etc. Each muscle is composed of several elongated threadlike muscle fibers that are striated. Length of some of the fibers is about 12 centimeters.
Flexors
These muscles bring about the flexion and are located on the anterior surface of the joints or the body, for example, biceps muscles of arm on the front side.
Extensors
 These muscles are situated at the backside or behind the joints and cause extension, that is, the movement opposite to the flexion, like straightening of the bent knee.
These muscles are situated at the backside or behind the joints and cause extension, that is, the movement opposite to the flexion, like straightening of the bent knee.
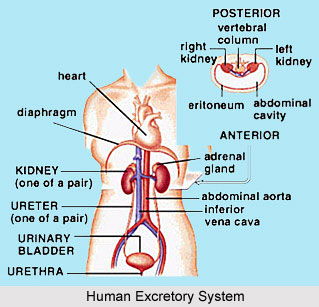
Diaphragm
It is one of the most important skeletal muscles in human body, which separates the thoracic, and the abdominal cavities, serving as a partition between these two cavities. It is a dome shaped sheet of voluntary muscle. Its convex surface touches the heart and the lungs. Its central part consists of a tendon, known as tendinous centre.
Abdominal Recti Muscles
These muscles are also known as Rectus Abdominus muscles. These are the skeletal muscles in the form of bands on the anterior side of the stomach, forming the abdominal wall. They are situated vertically on the right and left sides of the median line.
On the other hand cardiac muscle is an involuntary muscle, which works quite independently. The human beings cannot control them directly according to their wishes. Cardiac muscle normally initiates its own contractions and continues to contract rhythmically. It possesses characteristics of both the skeletal as well as smooth muscles. It is controlled by the autonomic nervous system and its own stretch reflex mechanism.
Different emotional states influence the muscle tone. Intense emotional excitement, fear, anxiety, happiness, confidence etc, can give rise to increased muscular tone or strength. This in turn would influence the posture. Emotions can interfere with the coordinated movements and render them disorganized. Emotions can also influence the cardiac and smooth muscles and change their tone.
Influence of Yoga Asanas
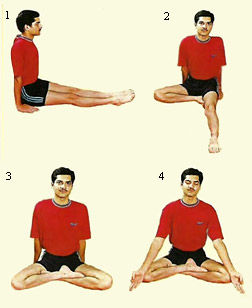
Yoga Asanas have variable impacts on the human body. Due to emotional impact muscle tone is affected which can disturb the functions of the body. To avoid such a state Yoga Asanas can be performed in a relaxed way for an increased coordination between the nervous and muscular systems, the muscle tone is also corrected and thus, the emotions are balanced. Moreover, if the muscle is stretched forcefully beyond its limits and such stretch is maintained, the muscle also tries to contract with force and shows its resistance. This tug-of-war gives rise to tremors in the muscles. With this increased muscular work, the breathing and circulation also increase. Hence Yoga Asanas should never be performed with a jerk.
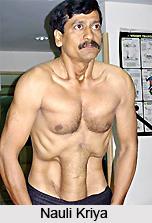
 When the muscles are relaxed, the muscle tone is reduced and at this moment there is no scope for worries and tensions. During Uddiyan and Nauli the diaphragm and the rectus abdominus muscles are contracted and therefore the positive or negative pressure is created in the abdomen. During Bandhas and Mudra, specific muscle sphincters are brought into action in order to stimulate related nerve plexuses, for instance, in Ashwini Mudra the anal sphincters are alternately contracted and relaxed.
When the muscles are relaxed, the muscle tone is reduced and at this moment there is no scope for worries and tensions. During Uddiyan and Nauli the diaphragm and the rectus abdominus muscles are contracted and therefore the positive or negative pressure is created in the abdomen. During Bandhas and Mudra, specific muscle sphincters are brought into action in order to stimulate related nerve plexuses, for instance, in Ashwini Mudra the anal sphincters are alternately contracted and relaxed.
Therefore it is due to the impact of the Yoga that the steadiness, flexibility and strength of the muscles can be improved. Besides this, the yogic practices also aid in improving the abdominal muscles. In addition to this, long term yoga training can help in the increase in the steadiness of the one particular part and also the coordination between two different parts of the body.