 The United Provinces of Agra and Oudh was one of the former provinces of British India that was under the rule of the British Empire in India. The territory existed from the year 1902 until the Indian independence in 1947. The official name of the region was shortened to United Provinces by the Government of India Act 1935. United Provinces was also one of the provinces of independent India till the year 1950. The province matched roughly with the modern day state of Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand state. The United Provinces of Agra and Oudh existed as 2 distinct provinces, namely Oudh and North Western Provinces from the year 1856 to 1902.
The United Provinces of Agra and Oudh was one of the former provinces of British India that was under the rule of the British Empire in India. The territory existed from the year 1902 until the Indian independence in 1947. The official name of the region was shortened to United Provinces by the Government of India Act 1935. United Provinces was also one of the provinces of independent India till the year 1950. The province matched roughly with the modern day state of Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand state. The United Provinces of Agra and Oudh existed as 2 distinct provinces, namely Oudh and North Western Provinces from the year 1856 to 1902.
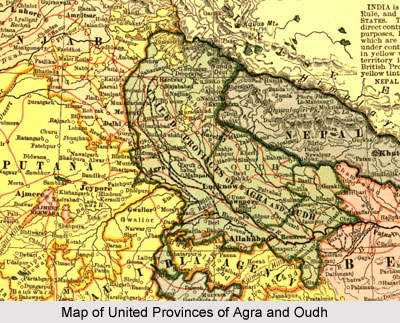
Location of United Provinces of Agra and Oudh
The United Provinces of Agra and Oudh was bordered by China in the north; by Nepal in the north east; by the Shahabad, Saran, Champaran and Palamau districts of Bengal in the south east; by 2 of the Chota Nagpur States in the Central Provinces, Saugor District in the Central Provinces, Rewa and few minor states in the Central India Agency in the south; and by the states of Bharatpur, Dholpur, Gwalior, the districts of Karnal, Delhi, Gurgaon and Ambala in the Punjab, as well as the Punjab States of Jubbal and Sirmur in the west. The Jumna River formed a part of the border in the west, the Ganga River formed part of the southern boundary, and the Gandak River was part of the eastern border.
The province of Agra covers a total area of 83,198 sq miles, where as the Oudh province was scattered over an area of 23,966 sq miles. The total area covered by the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh was 107,164 sq miles. The area of the 2 princely states of Tehri and Rampur in the Provinces was 5,079 sq miles. In the year 1834, the Presidency of Agra was formed, after which the area was included in the Bengal Presidency, which was also known as the Western Provinces. The United Provinces of Agra and Oudh included 4 separate tracts of realm, like the parts of the Himalayas, the great Gangetic plain, the sub-Himalayan tracts, and parts of the hill systems of Central India.
History of United Provinces of Agra and Oudh
During the 18th century, the Mughal Empire was declining as a result of the internal conflict, development of the Maratha forces and the expansion of the British Empire in India. By the mid-eighteenth century, the modern territory of Uttar Pradesh was split between various states such as Oudh or Awadh in the centre and east that was administered by a Nawab; Rohilkhand in the north that was ruled by the Afghans; the Marathas controlled the Bundelkhand region in the south; and the Mughal Empire that controlled the whole Doab and the Delhi region. The forces of Awadh and the Mughal Emperor fought against the British army in the Battle of Buxar. After the British won, the entire territory of Awadh was restored to the Nawab. Later Governor General Warren Hastings promoted the region of Awadh by providing the Nawab the British forces to defeat Rohilkhand in the Rohilla War. Moreover, Kora and Allahabad were given to Awadh as Shah Alam surrendered to the authority of the Marathas. The British administration received the Benares province from Awadh in return.
Later Lord Wellesley obtained the cession of Rohilkhand, lower Doab and Gorakhpur division from the Nawab of Oudh in 1801. This bounded the province of Awadh from all sides except north. After the victory of Lord Lake in the Second Anglo Maratha War in 1804, a portion of Bundelkhand and the rest of the Doab, and also included Agra and Delhi, were acquired from Scindia. Later the Kumaon Division was obtained after the Gurkha War in 1815 and a portion of Bundelkhand was obtained in 1817 from the Maratha Peshwa. Thus the new territories that were acquired were known as the Ceded and Conquered Provinces and were administered by the Governor General. In the year 1833 an act of Parliament was passed to constitute a new province with Agra as its capital. But the scheme was not successfully carried out. In 1835, another statute authorized the appointment of a Lieutenant Governor for the North Western Provinces.
The North Western Provinces incorporated the territories of Delhi and Gurgaon, which were later transferred to Punjab after the great revolt of 1857. After 1853, the territories of Saugor and Nerbudda were also reassigned which were included into the Central Provinces. The region of Awadh was still maintained by the native ruler known as Nawab and in the year 1819, the ruler was granted the title of king. In 1856, Awadh was annexed and comprised of a separate chief commissionership. In the year 1877, the offices of Lieutenant Governor of the North Western Provinces and Chief Commissioner of Oudh were united with the same individual.
Later in the year 1902, the new name of United Provinces of Agra and Oudh was launched and the title of Chief Commissioner was abolished. In 1935, the official name of the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh was shortened by the Government of India Act 1935 to the United Provinces. After the withdrawal of the British and the independence of the nation, the United Provinces became a province of the newly formed Union of India. After the adoption of the new Constitution of India on 26 January 1950, the region became the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. In the year 2000, a portion of the Uttar Pradesh state was separated in order to create the new Indian state of Uttaranchal, which is now known as Uttarakhand.






































