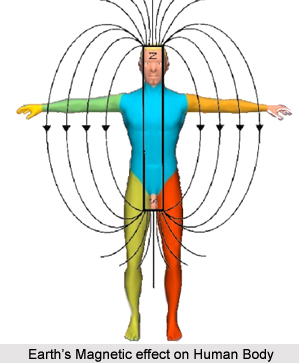
Cancer is usually named after the organ of the body affected by it, and also by its appearance under a microscope. There are around 200 types of cancer, identified so far. Most types of cancers start with a tumour, however; the cancers like Leukaemia do not form any tumour. Cancers can be classified according to the type of cells that has resemblance with the tumour. The cancers like Blood Cancer or Leukaemia, Breast Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Liver Cancer, Brain Cancer or Brain Tumour, Bladder Cancer, Bone Cancer, Lung Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Skin Cancer, etc. are most common all over the world. These cancers are considered the deadliest ones and cause maximum number of deaths.
Cancer is usually named after the organ of the body affected by it, and also by its appearance under a microscope. There are around 200 types of cancer, identified so far. Most types of cancers start with a tumour, however; the cancers like Leukaemia do not form any tumour. Cancers can be classified according to the type of cells that has resemblance with the tumour. The cancers like Blood Cancer or Leukaemia, Breast Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Liver Cancer, Brain Cancer or Brain Tumour, Bladder Cancer, Bone Cancer, Lung Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Skin Cancer, etc. are most common all over the world. These cancers are considered the deadliest ones and cause maximum number of deaths.
Groups of Cancer
Cancers can be divided into a few groups, namely Carcinoma, Sarcoma, Lymphoma and Leukaemia, Germ Cell Tumour, Blastic Tumour or Blastoma, etc.
•Carcinoma Group of cancers comprises some of the most commonly found cancers like breast, prostate, lung and colon cancer. The group includes the malignant tumours derived from epithelial cells.
•Sarcoma Group of cancers includes the cancers, in which the malignant tumours derive from the connective tissue or mesenchymal cells.
•Lymphoma or Leukaemia Group of cancers includes the malignancies, which derive from haematopoietic (blood-forming) cells.
•Another group of cancers is the Germ cell tumours, which derive from totipotent cells. These cancers are most found in the organs like testicle and ovary in adults; and on the body midline, particularly at the tip of the tailbone, in the foetuses, babies and young children. These cancers are also found at the base of the skull in horses.
•Blastic tumour or Blastoma is a group of cancers, where the tumour is usually malignant. This tumour resembles an immature or embryonic tissue and it is most commonly found in children.
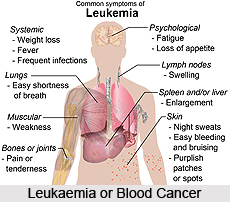
 Blood Cancer or Leukaemia
Blood Cancer or Leukaemia
Blood Cancer or Leukaemia is a cancer of the blood or bone marrow. Generally, it is characterised by an abnormal proliferation (production by multiplication) of blood cells; usually the white blood cells or leukocytes. Leukaemia belongs to the broad group of diseases called "Haematological Neoplasm". There are a few reasons identified for the development of blood cancer. These causes are natural or artificial ionising radiation, certain kinds of chemicals, certain viruses and genetic predispositions, exposure to electromagnetic fields etc.
Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer is worldwide considered as the 2nd most common type of cancer, only after the lung cancer. It is also considered as the 5th most common cause of cancer death. This type of cancer mainly affects the cells of breast in men and women. Breast cancer is found to be about 100 times as frequent among women as among men; however, the survival rates are equal in both sexes. The common causes of breast cancer include family history of breast cancer, previous incidence of uterine cancer, previous breast cancer, atypical changes and previous breast disease, genetic defects or changes, menstrual periods started before the age of 12, menopause ended after age 50, alcohol, high fat in diet, increased fibre diet, smoking, obesity, previous ovarian or Colon Cancer etc.
Cervical Cancer
Cervical Cancer is a type of malignant cancer that affects the cervix uteri or cervical area. The Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection is a major cause behind the development of cervical cancer. Though, primarily found in women, the men can also be affected by cervical cancer. Apart from HPV infection, some other factors like tobacco smoking, HIV infection, chlamydia infection, dietary factors, hormonal contraception, multiple pregnancies, exposure to the hormonal drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) and a family history of cervical cancer are also considered as causes of cervical cancer.
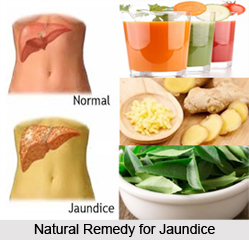
 Liver Cancer
Liver Cancer
Another common type of cancer is the Liver Cancer. This is the most common type of cancer worldwide. Mainly the liver is affected in this cancer and multiple types of tumours can develop in the liver due to liver cancer. Liver cancer is characterised by the presence of malignant hepatic tumours. These tumours can be found in patients as an abdominal mass, abdominal pain, jaundice or some other liver dysfunction. The main causes of liver cancer include hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection, alcohol, drugs, medications and chemicals like Aflatoxin B1, Hemochromatosis, Cirrhosis etc.
Brain Cancer
Brain Cancer also known as Brain Tumour is a common type of cancer that affects the most important parts of human body, the brain. The tumour mainly develops due to abnormal growth of cells within the brain or inside the skull. Brain cancer can develop in the lymphatic tissue, blood vessels, or in the cranial nerves of brain, and also in the skull, pituitary and pineal gland etc. Brain cancer is caused mainly due to radiation to the head; an inherited (genetic) risk and also due to HIV infection.
Bone Cancer
Bone Cancer is another common type of cancer that affects the cells of bone. The major types of bone cancer include osteosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, malignant fibrous histiocytoma and chondrosarcoma. Bone cancer can spread to the other parts of the body like prostate, breast or lung. Many factors are identified as causes of bone cancer and they include being a child of young adult, previous radiation or chemotherapy, history of Paget`s disease, family history of bone cancer, having hereditary retinoblastoma etc.
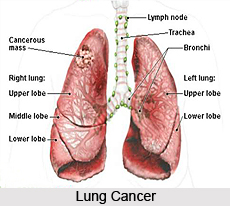
Lung Cancer
Another severe type of cancer is the Lung Cancer. This is mainly caused for uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. This uncontrolled growth may lead to metastasis that is the invasion of adjacent tissue and infiltration beyond the lungs. Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer-related death in men and the 2nd most common in women, all over the world. Tobacco smoking, radon gas exposure, asbestos, viral infections etc. are the major causes behind developing lung cancer. The most common symptoms of lung cancer include shortness of breath, coughing, weight loss etc.
Other Types of Cancer
Apart from the above mentioned cancers, there are also several other types of cancers. These include Adrenocortical Carcinoma, Aids Related Lymphomas, Anal Cancer, Carcinoma Of Unknown Primary (CUP), Colorectal Cancer, Coetaneous T-Cell Lymphoma, Endometrial Cancer, Oesophageal Cancer, Ewing`s Tumours, Extra Hepatic Biliary Tree Cancers, Gall Bladder Cancer, Gastrointestinal Carcinoids, Gestational Trophoblastic Tumours, Hypo Pharyngeal Cancer, Kaposi`s Sarcoma, Larynx Cancer, Malignant Melanoma, Mesothelioma, Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Nasopharyngeal Cancer, Nasal and Paranasal Sinus Cancers, Ovarian Cancer, Oral Cancer, Parathyroid Cancer, Pheochromocytoma Cancer, Pituitary Tumours, Prostatic Cancer, Renal Cell Cancer (RCC), Salivary Gland Cancer, Stomach Cancer (Gastric Cancer), Testicular Cancers, Thyroid Cancers, Ureter and Renal Pelvis Cancers, Vulval Cancer etc.
Cancers are usually treated following the conventional Cancer treatment methods. In most types of cancers, total cure can be achieved if the tumour is identified when it is small and has not spread at all. However, cancers become incurable when they reach an advanced stage; have grown to a large size; and have already sent seedlings to other parts of body.