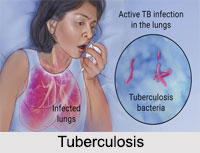
 Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that enters into the body through nose, mouth and windpipe and settles down in the lungs. A tiny germ called Tubercle Bacillus enters into the body and later on it multiplies by millions and produces small raised spots called Tuberculosis. Those suffering from the disease for a considerable time eject living germs while coughing or spitting and when these enter the nose or mouth of healthy persons, they contract the disease.
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that enters into the body through nose, mouth and windpipe and settles down in the lungs. A tiny germ called Tubercle Bacillus enters into the body and later on it multiplies by millions and produces small raised spots called Tuberculosis. Those suffering from the disease for a considerable time eject living germs while coughing or spitting and when these enter the nose or mouth of healthy persons, they contract the disease.
Types of Tuberculosis
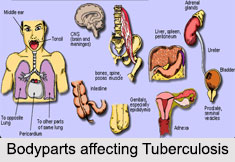
Tuberculosis is a complex disease. It can affect different areas of the human body, such as the lungs, lymph nodes, skeletal system or brain. Different types of Tuberculosis exist, which can be completely curable, but some forms could also lead to death. Tuberculosis may be regarded in two categories namely;
•Latent Tuberculosis: It refers to the condition when the bacteria remains inactive in the body and causes no symptoms while suffering from Tuberculosis.
•Active Tuberculosis: This is when the Tuberculosis bacteria multiply in the body, causing to develop the symptoms of tuberculosis.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
 Tuberculosis tends to consume the body and the patient loses strength, colour and weight. Other symptoms raise in temperature especially in the evening, a persistent cough and hoarseness, difficulty in breathing, pain in the shoulders, indigestion, chest pain and blood in the sputum.
Tuberculosis tends to consume the body and the patient loses strength, colour and weight. Other symptoms raise in temperature especially in the evening, a persistent cough and hoarseness, difficulty in breathing, pain in the shoulders, indigestion, chest pain and blood in the sputum.
Causes of Tuberculosis
Lowered resistance and calcium deficiency are the chief causes of this disease. A variety of other factors such as suppression of the disease by drugs and medication, use of stale and acid forming foods, eating wrong combination of foods, such as taking fruits with starchy foods at one meal, causing fermentation in the stomach; wasting of energy through excessive loss of semen and living in ill-ventilated houses.
Other causes include exposure to cold, loss of sleep, impure air, a sedentary life, overwork, contaminated milk, use of tobacco in any form, liquor of all kinds, tea, coffee and all harmful drinks. The factors prepare the ground for the growth of germs of various kinds, including Tubercle Bacillus.
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
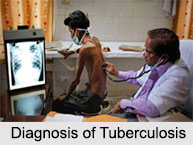 The first step to diagnosing Tuberculosis is thorough physical examination wherein the doctor checks the lymph nodes for swelling and lung sounds are carefully checked using a stethoscope. Blood and sputum tests may also be taken for laboratory examination.
The first step to diagnosing Tuberculosis is thorough physical examination wherein the doctor checks the lymph nodes for swelling and lung sounds are carefully checked using a stethoscope. Blood and sputum tests may also be taken for laboratory examination.
Treatment of Tuberculosis
The patient should be put on an exclusive fresh fruit diet for 3 or 4 days. However, fruits like Bananas and dried or tinned fruits should not be taken. After the all-fruit diet, the patient should adopt a fruit and milk diet and continue the same for about 4 to 6 weeks. The patient should avoid all devitalised foods such as white bread, white sugar, refined cereals, tinned, canned and preserved foods.
Regular use of radish and Indian gooseberry juice with honey has proved to be an effective remedy for tuberculosis. Its regular use will promote vigour and vitality in the body within a few days. The patient"s vital resistance can be built up by water treatment twice a day. A short hot fomentation with alternate short cold application to the chest, back, and in the stomach region or a neutral immersion bath for an hour just before retiring at night is also beneficial.
The patient should take complete rest of both mind and body. Other beneficial steps towards curing the disease are avoidance of strain, slow massage, deep breathing and light occupation to ensure mental diversion.
Yoga Asanas for Tuberculosis
Certain yoga practices are beneficial in the treatment of tuberculosis in its early stages. These include asanas like Viparitakarani, Sarvangasana and Shavasana and Jalneti Kriya and Anuloma-Viloma Pranayama.




