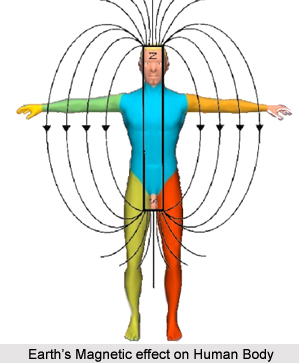
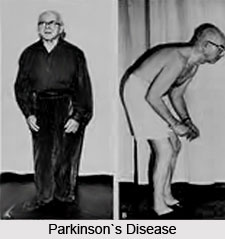
 Parkinson`s disease is a chronic disorder that requires broad-based treatment including patient and family education, support group services, general wellness maintenance, physiotherapy, exercise, and nutrition. Till date, no cure has been found for Parkinson`s disease, but medications or surgery can provide relief the patient.
Parkinson`s disease is a chronic disorder that requires broad-based treatment including patient and family education, support group services, general wellness maintenance, physiotherapy, exercise, and nutrition. Till date, no cure has been found for Parkinson`s disease, but medications or surgery can provide relief the patient.
Levodopa is the most widely used form of treatment, available in various forms. L-dopa is transformed into dopamine in the dopaminergic neurons by L-aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (often known by its former name dopa-decarboxylase). However, only 1-5% of L-dopa enters the dopaminergic neurons. The remaining L-dopa is often metabolised to dopamine somewhere else, thus causing a wide variety of side effects. Due to feedback inhibition, L-dopa results in a decrease in the endogenous formation of L-dopa, and thus ultimately becomes counterproductive.
Carbidopa and benserazide are dopa decarboxylase inhibitors that help to prevent the metabolism of L-dopa before it reaches the dopaminergic neurons and are generally given as combination preparations of carbidopa or levodopa. There are also controlled release versions of Sinemet and Madopar that extend out the effect of the L-dopa. Duodopa is a combination of levodopa and carbidopa, isolated as a thick gel. Using a patient-operated transportable pump, the drug is constantly delivered through a tube directly into the upper small intestine, where it is speedily absorbed.
Tolcapone inhibits the COMT enzyme, thus prolonging the effects of L-dopa, and so has been used to harmonize L-dopa. However, due to its probable side effects such as liver failure, it is restricted in its availability. A similar drug, entacapone has not been shown to cause noteworthy alterations of liver function and maintains adequate inhibition of COMT over time. The dopamine agonists bromocriptine, pramipexole, pergolide, ropinirole, apomorphine, cabergoline, and lisuride are fairly effective in the treatment of Parkinson`s disease. These have their own side effects including those mentioned above in addition to somnolence, hallucinations or insomnia.
Dopamine agonists can be useful for patients experiencing on-off fluctuations and dyskinesias as a result of high doses of L-dopa. Apomorphine can be administered via subcutaneous injection using a small pump, which is carried by the patient. A low dose is automatically administered throughout the day that reduces the fluctuations of motor symptoms by providing a steady dose of dopaminergic stimulation. After an initial "apomorphine challenge" in hospital to test its efficiency and brief patient and primary caregiver (often a spouse or partner), the latter of whom takes over safeguarding of the pump. The injection point must be changed daily and rotated around the body to avoid the development of nodules. Apomorphine is also available in a more acute dose as an autoinjector pen for crisis doses such as after a fall or first thing in the morning. Nausea and vomiting are common after effects of this kind of treatment of Parkinson`s disease, and may require domperidone (an antiemetic).
Selegiline and rasagiline reduce the symptoms of Parkinson`s disease by reducing monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B), thus inhibiting the breakdown of dopamine secreted by the dopaminergic neurons. Metabolites of selegiline include levoamphetamine and levomethamphetamine. This might result in side effects such as insomnia. A side effect of selegiline in combination with L-dopa can be stomatitis.
Surgery and deep brain stimulation is also a form of treatment of Parkinson`s disease. Treating Parkinson`s disease with surgery was once a common practice, but after the discovery of levodopa, surgery was restricted to only the severe cases. Studies in the past few decades have led to great improvements in surgical techniques of Parkinson`s disease, and surgery is again being used in people with advanced Parkinson`s disease for whom drug therapy is no longer sufficient. Deep brain stimulation is presently the most used surgical means of treatment of Parkinson`s disease, but other surgical therapies that have shown betterment including surgical lesion of the subthalamic nucleus and of the internal segment of the globus pallidus, a procedure known as pallidotomy.
Neurorehabilitation is carried out as treatment when there is partial evidence that speech or mobility problems can improve with rehabilitation although studies are still scarce and of low quality. Regular physical exercise or therapy can be beneficial to the patient for maintaining and improving mobility, strength, flexibility, movement speed, and quality of life; and speech therapy may improve voice and speech function. One of the most widely practiced treatments for the speech disorders associated with Parkinson`s disease is the Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT). LSVT focuses on increasing vocal loudness.
Through a combination of intensive research, Ayurvedic theory and the clinical experiences, many relieving processes have come up with formulas and drugs to cure Parkinson`s disease. The herbal medicines of Ayurveda have very minor effects like occasional constipation, and mild dizzy spells in the early phase of treatment. Unlike western medicine, Ayurvedic medicines have cured patients from this disease. These medicines can also be taken along with western medicines, with gradual phasing out of western medicine. First improvements in Parkinson`s disease are usually seen within 8 to 10 months and 1 to 4 years later, the disease disappears 90% to 99%.