Glaucoma should be treated as soon as possible. The damage that has already occurred from glaucoma cannot be repaired-it will either stay the same or get worse. Catching glaucoma at its earliest stages demands treatment of Glaucoma as soon as possible to revive one`s normal vision.
Glaucoma should be treated as soon as possible. The damage that has already occurred from glaucoma cannot be repaired-it will either stay the same or get worse. Catching glaucoma at its earliest stages demands treatment of Glaucoma as soon as possible to revive one`s normal vision.
All of the various glaucoma treatments and procedures are aimed at reducing eye pressure. Eye pressure does not necessarily cause glaucoma, but once it develops, eye pressure speeds up the destructive process. There are a number of different treatments for glaucoma like eye drops, oral medication and surgery. The type of treatment depends upon individual conditions. Eye drops are used to reduce eye pressure by either increasing the eye`s ability to drain or by lessening the amount of fluid it produces. If one notices any side effects from any eye drops used, one should contact the doctor. If a particular medication is causing problems, there are usually others that can be used.
The process of applying eye drop in case of glaucoma is also important to be noted. Firstly, the eyes should be closed after putting in the drops and the face should be turned up so the drop is more likely to stay on the eye. Finally, gentle pressure should be applied on the skin between the eye and nose. Medications that are applied directly to the eye are usually in the form of eye drops, but sometimes ointments are also prescribed.
There are six different types of medications that are administered to the eye to treat glaucoma. Beta-blockers cause little discomfort and work by decreasing the production of watery fluid. However, they can make breathing and heart problems worse in people with heart or lung conditions. Prostaglandins increase drainage can cause blue and green eyes to become darker. Alpha-stimulators are used with other medications to lower eye pressure, which can cause allergic reactions in and around the eyes. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors decrease fluid production. Because they are sulfa based, people allergic to sulfa should not use them. Miotics increase fluid drainage and they can, however, cause headaches while initial usages. Epinephrine increases fluid drainage. Even though there are not usually any major complications, it can cause momentary redness of the eye and hazy vision.
Pills are usually used to decrease fluid production and treat glaucoma. They can be very effective in lowering eye pressure, but they also bring about side effects in about half of the people who take them. Possible side effects of glaucoma pills include tingling in the fingers and toes, fatigue, loss of appetite, mood changes, blood chemistry imbalance, kidney stones, aplastic anemia, which is an extremely rare but possibly life-threatening condition in which the bone marrow no longer produces blood cells. Surgery is also a form of treatment of glaucoma. Conventional surgery to treat glaucoma makes a new opening in the meshwork. This new method helps fluid to leave the eye and lowers intraocular pressure. Both laser and conventional surgeries are performed to treat glaucoma. Surgery is the primary therapy for the patients with congenital glaucoma. Generally, these operations are a momentary solution, as there is not so far a cure for glaucoma.
Canaloplasty is a nonpenetrating procedure using microcatheter technology. To perform a canaloplasty, a slit is made into the eye to gain access to Schlemm`s canal in a similar fashion to a viscocanalostomy. A microcatheter will revolve the canal around the iris, enlarging the main drainage channel and its smaller collector channels through the injection of a sterile, gel-like substance called viscoelastic. The catheter is then detached and a suture is placed within the canal and tightened. By opening the canal, the pressure inside the eye may be comforted, although the reason is uncertain since the canal (of Schlemm) does not have any noteworthy fluid resistance in glaucoma or healthy eyes. Long-term results are not available.
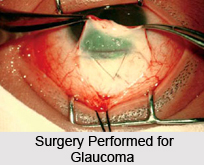
Laser trabeculoplasty may be used to treat open angle glaucoma. It is a temporary solution, not a cure. A 50 ?m argon laser spot is intended at the trabecular meshwork to motivate opening of the mesh to allow more outflow of aqueous fluid. Usually, half of the angle is treated at a time. Traditional laser trabeculoplasty utilizes a thermal argon laser. The procedure is called Argon Laser Trabeculoplasty or ALT. A newer type of laser trabeculoplasty is invented that uses a "cold" (non-thermal) laser to stimulate drainage in the trabecular meshwork. This newer procedure which uses a 532 nm frequency-doubled, laser which selectively targets melanin pigment in the trabecular meshwork cells, called Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty or SLT. Studies show that SLT is as effective as ALT at lowering eye pressure. In addition, SLT may be repetitive for three to four times, whereas ALT can usually be repeated only once.
Nd:YAG Laser peripheral iridotomy may be used in patients susceptible to or affected by angle closure glaucoma or pigment diffusion syndrome. During laser iridotomy, laser energy is used to make a small full-thickness opening in the iris. This opening equalizes the pressure between the front and back of the iris correcting any abnormal bulging of the iris. In people with narrow angles, this can expose the trabecular meshwork. In some cases of irregular or short-term angle closure this may lower the eye pressure. Laser iridotomy reduces the risk of developing an assault of acute angle closure. In most cases it also reduces the risk of developing continual angle closure or of adhesions of the iris to the trabecular meshwork.
Trabeculectomy is another method of treatment of glaucoma. The most common conventional surgery performed for glaucoma is the trabeculectomy. Here, a partial thickness flap is made in the scleral wall of the eye, and a window opening made under the flutter to remove a portion of the trabecular meshwork. The scleral flap is then sutured freely back in place. This allows fluid to flow out of the eye through this opening, resulting in lowered intraocular pressure and the formation of a bleb or fluid bubble on the surface of the eye. Scarring can occur around or over the flap opening, thus causing it to become less effective or lose efficacy altogether. One person can have multiple surgical procedures of the same or different types.
Glaucoma drainage implants include the original Molteno implant or the valved implants, such as the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant or the ExPress Mini Shunt and the later generation pressure ridge Molteno implants. These are indicated for glaucoma patients not responding to maximal medical therapy, with previous failed guarded filtering surgery (trabeculectomy). The flow tube is inserted into the anterior chamber of the eye and the plate is fixed underneath the conjunctiva to allow the flow of watery fluid out of the eye into a chamber called a bleb.
Since glaucoma is one of the most common diseases, the methods of treatments have also been in abundance. The situation of the patient and his troubles can be taken care of through various kinds of methods to treat glaucoma.