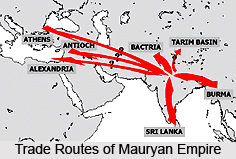
 Trade under Mauryan Administration indicate that Indians had developed an extensive system of inland trade which was borne along prominent trade-routes. The Khyber Pass became a strategically important port of trade and communication with the outside world. Greek states and Hellenic kingdoms became important trade partners of India. Trade extended through the Malay Peninsula into Southeast Asia. The export items included silk goods and textiles, spices and exotic foods. Scientific knowledge and technology with Europe and West Asia also took place.
Trade under Mauryan Administration indicate that Indians had developed an extensive system of inland trade which was borne along prominent trade-routes. The Khyber Pass became a strategically important port of trade and communication with the outside world. Greek states and Hellenic kingdoms became important trade partners of India. Trade extended through the Malay Peninsula into Southeast Asia. The export items included silk goods and textiles, spices and exotic foods. Scientific knowledge and technology with Europe and West Asia also took place.
Extensive trade took place during the rule of the Mauryas. The inland routes were marked by convenient stages and linked the most distant parts of the country with one another. Some of the important routes were:
East to west - This route ran mainly along the great rivers. From Champa boats plied up to Varanasi. Benares was the great industrial and trading centre of those times. From there they led up the Ganga River as far as Sahajati and up the Jumna as far as Kausambi.
North to south-west - This route extended from Saraswati, the capital of Kosala, to Pratishthana on the Godavari River and the stations lying on it in the reverse direction included Ujjayini, Vidisha, and Kausambi.
North to south-east - North-west route stretched along the land of the Five Rivers to the great highways of Central and Western Asia. The roads especially those passed through the forests infested by robbers against whom the merchants protected themselves by hiring the services of forest-guards. However the deserts had to be crossed at night with the help of land-pilots guiding the caravan by the stars. Some of the roads were considered as `royal` or `great` roads. The rivers had to be crossed by ferries as there were no bridges. The overland and over sea trade attracted the attention of Indian merchants.
The references in Kautilya`s Arthashastra speak of an advanced trade. Active encouragement of trade on the part of the State is spoken of. Constructions of wider roads that lead to market towns have been mentioned. Arthashastra gives us a valuable, though far from exhaustive, list of imports borne along routes markedly to the Ganges valley. The costlier merchandise that consists of elephants, horses, fragrant products, tusks, skins, gold and silver were more plentiful in the Himalayas. Among the products that was exported it included textiles of Bengal, Assam, Benares, the Konkan and Pandya, the silks of China, the woollens of Nepal, the skins of the Himalayan regions, the fragrant wood of Assam and the Himalayas.
The rule of the Mauryas helped to improve India`s inland and foreign trade. Chandragupta Maurya had a complete control over the coveted north-western route. With the conquest of the Deccan by Chandragupta Maurya, the possession of valuable western and southern routes was ensured to the Mauryas. When Ashoka conquered Kalinga the only possible rival for the mastery of the eastern trade was destroyed. The Mauryas brought all the great inland trade-routes under the control of a highly centralised and efficient administration. Their rule enhanced the growth of trade in other ways.
The Mauryas had a special department for the construction of roads that is indicated by Megasthenes` reference to the duties of officers called Agoranomoi. The wise policy of acquaintance with the Hellenistic powers started by Chandragupta Maurya after the repulse of Seleucus favoured the expansion of the Indian trade with West Asia and Egypt. The main trade between early Seleucid Empire and India was borne by land-route (the northern one passing through Bactria and the southern through Gedrosia and Garmania, Persis and Susiana) and by the sea-route (through Gerrha on the west coast of the Persian Gulf). In the light of this extensive commerce with western lands Ashoka`s attempted to extend the benefits of his religious and humanitarian propaganda to the Hellenistic kingdoms.



















