Introduction
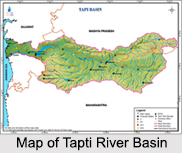 Tapti River is one of the major rivers in central India. It is one of the three rivers (the other two being, Narmada River and Mahi River), which flows in east to west direction. The Tapti River drains through the Gulf of Khambhat into the Arabian Sea. The river flows through the state of Surat, and is crossed by the Magdalla ONGC Bridge.
Tapti River is one of the major rivers in central India. It is one of the three rivers (the other two being, Narmada River and Mahi River), which flows in east to west direction. The Tapti River drains through the Gulf of Khambhat into the Arabian Sea. The river flows through the state of Surat, and is crossed by the Magdalla ONGC Bridge.
The Tapti River took birth in the Betul district from a place called Multai. The Sanskrit name of Multai is Multapi, meaning origin of Tapi Mata or the Tapti River. The Tapi River that flows in Thailand, was named after India`s Tapti River in August 1915. According to Hindu views, the Tapti River is the daughter of Lord Surya.  There is a Purana mentioning the virtues of Tapti extensively and it praises the river as more sacred than all other rivers including the Ganges.
There is a Purana mentioning the virtues of Tapti extensively and it praises the river as more sacred than all other rivers including the Ganges.
The Tapti purana says that "Ganga Snane, Narmada Darshane ch Tapti Smarane paapam nashyati". This saying means that by bathing in the Ganges, beholding Narmada and remembering Tapti, the devotee can be delivered from all sins.
History Of Tapti River
Tapti is a river of western India and the history of this river starts with its origin in the Betul district. It rises in Betul district of Madhya Pradesh and flows between two spurs of the Satpura Hills, across the plateau of Khandesh, and thence through the plain of Surat to the sea. It has a total length of around 724 km. and drains an area of 30,000 sq. m. For the last 32 m. of its course, it is a tidal flow, but is only navigable by vessels of small tonnage; and the port of Swally at its mouth. The history of this river is closely associated with the Anglo Portuguese history. The upper reaches of the river are now deserted, owing to silting at the outflow of the river. The waters of the Tapti are usually not used for irrigation.
 Tapti river is one of the major rivers in India and flows in the central part of India. The river originates from the Betul district of Madhya Pradesh in the Satpura range at an approximate height of about 752 meter above the sea level. The Tapti River flows through the Indian states of Maharashtra, Gujrat and Madhya Pradesh. Apart from the Narmada River, Tapi is the only river, which flows in the westward direction and empties into the Arabian Sea. The Tapi basin extends to the total area of 65, 145 sq km that is approximately 2.0% of the total geographical area of India. The main tributaries of the Tapi River are Purna, The Panjhra, The Vaghur, The Girna, the Bori and the Aner.
Tapti river is one of the major rivers in India and flows in the central part of India. The river originates from the Betul district of Madhya Pradesh in the Satpura range at an approximate height of about 752 meter above the sea level. The Tapti River flows through the Indian states of Maharashtra, Gujrat and Madhya Pradesh. Apart from the Narmada River, Tapi is the only river, which flows in the westward direction and empties into the Arabian Sea. The Tapi basin extends to the total area of 65, 145 sq km that is approximately 2.0% of the total geographical area of India. The main tributaries of the Tapi River are Purna, The Panjhra, The Vaghur, The Girna, the Bori and the Aner.
The historical importance of Tapti river dates back to the earlier times when Tapti river at Surat was used as the major ports for the purpose of exports of goods and also as an important halt destination for Muslim pilgrimage called Haj to Mecca. The river is also called by the names of Tapati, Tapee, Tapti and Taapi. Tapi river is been supporting the large number of population especially the aboriginal people such as Dhodia, and Bhils who are greatly dependent on it. The soil around the Tapi River is best for agriculture. The rural and tribal population around the Tapi River helps to harvest a large number of chief crops around it and sell it in the market to earn their livelihood. The water of the Tapi River is heavily used for the irrigation reasons. Tapi River is the home to the natural habitats of many wild animals including tigers, lions, snakes sloth bear and many more.
Origin Of Tapti River
The Tapti River originates in the Betul district from a place called Multai. The Sanskrit name of Multai is Multapi and the term means the origin of Tapi Mata or the Tapti River. The Tapi River in Thailand was named after India`s Tapti River on August 1915. According to Hindu values, the Tapi River is considered to be the daughter of Lord Surya. There is a Purana dedicated to the virtues of Tapi, which praises the river as holier than all other rivers including the Ganges. The Tapi purana has mentioned that bathing in the Ganges, beholding Narmada and remembering Tapi, any person can be delivered from all sins.
 The origin of Tapti River is at the Satpura range of Betul district in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is supposed to originating from small pond at a small town known as Multai, originally known as Multapi or the origin spot of Tapti. The Betul District encompasses an area of 10043 km² and population is around 13,95,175 as per 2001 census. The place Multapi has become a tourist spot and also a place for pilgrimage for the worshippers of Tapti River. Density of the population in this town is 138/km². Betul district is actually rich in tribal population. The tribal population of the district as per 2001 census is 5,49,907. The main tribes inhabiting the district are Gonds and Korkus. The other castes of tribe in this place include Kurmis, Bhoyars, Mehras, Kunbis, Chamars, Banias and Rajputs.
The origin of Tapti River is at the Satpura range of Betul district in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is supposed to originating from small pond at a small town known as Multai, originally known as Multapi or the origin spot of Tapti. The Betul District encompasses an area of 10043 km² and population is around 13,95,175 as per 2001 census. The place Multapi has become a tourist spot and also a place for pilgrimage for the worshippers of Tapti River. Density of the population in this town is 138/km². Betul district is actually rich in tribal population. The tribal population of the district as per 2001 census is 5,49,907. The main tribes inhabiting the district are Gonds and Korkus. The other castes of tribe in this place include Kurmis, Bhoyars, Mehras, Kunbis, Chamars, Banias and Rajputs.
The elevation of the origin of Tapti River above the sea is about 2000 ft. The area is essentially a highland tract, divided naturally into three distinct portions, differing in their superficial aspects, the character of their soil and their geological formation is similar throughout the upper course of the river. The northern part of the district forms an irregular plain of the sandstone formation. The area is a well-wooded tract, in many places stretching out in charming glades like an English park, but it has a very thin population and sparsely cultivated land.
In the extreme north of the originating point of River Tapti, a line of hills rises unexpectedly out of the great plain of the Narmada valley. The central tract alone is a concentrated region of rich soil, well watered by the Machna and Sampna rivers, almost entirely cultivated and studded with villages. To the south lies an undulating plateau of basaltic formation; along which rises the springs of the Tapti River at it`s highest point. These springs extend over the whole of the southern direction of the district, and finally merges with the wild and broken line of the Ghats, which goes down and meet with the plains. This tract comprises a sequence of stony ridges of trap rock, enclosing valleys or basins of fertile soil. Here cultivation is not done in most of the parts, except where the shallow soil on the tops of the hills has been turned to account.
 The climate of Betul or the place of Tapti River`s origin is fairly healthy. Its height above the plains and the neighborhood of widespread forests moderate the heat, and render the warmth pleasant throughout most of the part of the year. During the winter season the temperature at night falls below the freezing point. Rarely hot wind is felt before the end of April. The summer nights are comparatively cool and pleasant. During the monsoon the climate becomes very damp, and at times even cold and raw, bulky clouds and mist envelops the sky for many days together. The average annual rainfall of the place is 40 in.
The climate of Betul or the place of Tapti River`s origin is fairly healthy. Its height above the plains and the neighborhood of widespread forests moderate the heat, and render the warmth pleasant throughout most of the part of the year. During the winter season the temperature at night falls below the freezing point. Rarely hot wind is felt before the end of April. The summer nights are comparatively cool and pleasant. During the monsoon the climate becomes very damp, and at times even cold and raw, bulky clouds and mist envelops the sky for many days together. The average annual rainfall of the place is 40 in.
Betul district is rich in forests and biodiversity, specially the area of Multapi. Main timber species of Betul Forest is Teak. Many more types of trees including the Haldu, Saja, Dhaoda are also found in ample. Many medicinal plants are available in the forest areas of Betul. Huge amount of minor forest produce serve commercial purposes. The Tendu leaves, Chironji, Harra, Amla are also collected in huge quantity from the forests of Betul. Asia`s biggest wood depot is believed to be in Betul.
The major rivers flowing in the district are Ganjal River, which is a tributary of Tapti River, Morand River and Tawa River. These are the tributaries of Narmada River.
Geology Of Tapti River
The geology of Tapti River can be said as old and geologically stable region with an average elevation between 300 and 1,800 meters. The Vindhya Range constitutes the main separating line between the geological regions of the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Peninsular. This boundary range lies north of the Narmada River, and when viewed from there, it is possible to determine the high up escarpments that rise between 800 and 1,400 meters. The Vindhya Range includes the north central and northwestern boundary of the Peninsula and the Chota Nagpur Plateau of southern Bihar forms the northeastern boundary. The uplifting of the plateau of the central Peninsula and its eastward inclined formed the Western Ghats, a line of hills running from the Tapti River south to the tip of the Peninsula. The Eastern Ghats mark the eastern end of the plateau; they begin in the hills of the Mahanadi River basin and unite with the Western Ghats at the Peninsula`s southern tip.
The interior of the Peninsula lies south of the Narmada River. This zone is often termed the Deccan Plateau or simply the Deccan, featuring a series of plateaus with the summits of rolling hills and is intersected by many rivers. The plateau averages roughly 300 to 750 meters in elevation. Its major rivers--the Godavari, the Krishna, and the Kaveri--rise in the Western Ghats and flow eastward into the Bay of Bengal.
The coastal plain borders the plateau. On the northwestern side one can see tidal marshes, drowned valleys and estuaries, while on the south of this by lagoons, marshes, and beach ridges. Coastal plains on the eastern side of Tapti River are wider than those in the west; they are focused on large river deltas that are prime locations for human settlement.
Geography Of Tapti River
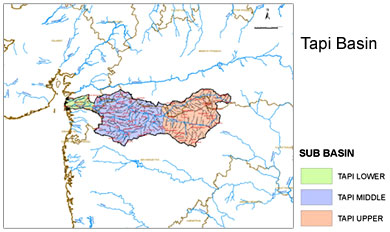 The Tapti River rises in Madhya Pradesh. The Vindhya Range includes the north central and northwestern boundary of the Peninsula; also the Chota Nagpur Plateau of southern Bihar forms the northeastern boundary of the Tapti River basin. The uplifting of the plateau of the central Peninsula and its eastward tilt formed the Western Ghats, a line of hills running from the Tapti River south to the tip of the Peninsula. The Eastern Ghats mark the eastern end of the Tapti plateau; the river begins in the hills Multapi and converges with the Western Ghats at the Peninsula`s southern tip.
The Tapti River rises in Madhya Pradesh. The Vindhya Range includes the north central and northwestern boundary of the Peninsula; also the Chota Nagpur Plateau of southern Bihar forms the northeastern boundary of the Tapti River basin. The uplifting of the plateau of the central Peninsula and its eastward tilt formed the Western Ghats, a line of hills running from the Tapti River south to the tip of the Peninsula. The Eastern Ghats mark the eastern end of the Tapti plateau; the river begins in the hills Multapi and converges with the Western Ghats at the Peninsula`s southern tip.
The interior of the Peninsula is mainly the area that lies south to the Narmada River, often termed the Deccan Plateau or simply the Deccan (from the Sanskrit daksina , meaning south), is a series of plateaus topped by rolling hills and intersected by many rivers. The plateau averages roughly 300 to 750 meters in elevation. The major rivers flowing in this plateau are Godavari, the Krishna, and the Kaveri--rise in the Western Ghats and flow eastward into the Bay of Bengal.
The coastal plain borders of the Tapti River the plateau. On the northwestern side, it features tidal marshes, drowned valleys, and estuaries; and in the south by lagoons, marshes, and beach ridges. Coastal plains on the eastern side of Tapti River are wider than those in the west; they are focused on large river deltas that serve as the concentrated zones of human settlement.
Tributaries of Tapti River
The Tapti River has many tributaries, the important tributaries of the river are Purna River, Girna River, Panzara River, Waghur River, Bori River and Aner River.
 The Tapti River basin covers an area of 65,145 km² that makes up almost two percent of the total area of India. The basin lies in the states of Maharashtra, coveri8ng an area about 51,504 km², Madhya Pradesh with 9,804 km² surface area and Gujarat covering 3,837 km² of land. The basin lies mostly in the northern and eastern districts Maharashtra state, including Amravati, Akola, Buldhana, Washim, Jalgaon, Dhule, Nandurbar, and Nashik districts, but also includes the Betul and Burhanpur districts of Madhya Pradesh and the Surat district of Gujarat.
The Tapti River basin covers an area of 65,145 km² that makes up almost two percent of the total area of India. The basin lies in the states of Maharashtra, coveri8ng an area about 51,504 km², Madhya Pradesh with 9,804 km² surface area and Gujarat covering 3,837 km² of land. The basin lies mostly in the northern and eastern districts Maharashtra state, including Amravati, Akola, Buldhana, Washim, Jalgaon, Dhule, Nandurbar, and Nashik districts, but also includes the Betul and Burhanpur districts of Madhya Pradesh and the Surat district of Gujarat.
The rivers of Tapti river basin include Shiva River, Gomai River, Vaki River, Arunavati River, Burai River, Panzara River, Bori River, Aner River, Girna River, Khandu River , Waghur River, Purna River, Nipani River, Mann River, Nesu River, Aas River, Umaa River and Shahanur River.
Tapti River Basin
The River basin of Tapti River is the vast fertile patch of land in central India. The river and its tributaries make up the Tapti River basin. The river basin encompasses an area of 65,145 km², which is nearly two percent of the total area of India. The basin lies in the Indian states of Maharashtra (around 51,504 km²), Madhya Pradesh (around 9,804 km²) and Gujarat (around 3,837 km²).
 The basin mostly lie in the northern and eastern districts Maharashtra state, including places like Amravati, Dhule, Akola, Washim, Buldhana, Nandurbar, Jalgaon and Nashik districts. However, the Betul and Burhanpur districts of Madhya Pradesh and the Surat district of Gujarat are the prime districts included in the Tapti River basin.
The basin mostly lie in the northern and eastern districts Maharashtra state, including places like Amravati, Dhule, Akola, Washim, Buldhana, Nandurbar, Jalgaon and Nashik districts. However, the Betul and Burhanpur districts of Madhya Pradesh and the Surat district of Gujarat are the prime districts included in the Tapti River basin.
The tributaries of Tapti River form a quality basin area that brings a vast geological change thus making it a highly fertile land. The principal tributaries of the Tapti River are the Purna River, Girna River, Panzara River, Waghur River, Bori River and Aner River. Other tributaries include Shiva River in Nandurbar district of Maharashtra State, Vaki River and Gomai River in Nandurbar, Burai River, Arunavati River, Kaan River and Panzara River in Dhule district of Maharashtra state. There are many more tributaries like the Bori River, Aner River, Girna River and Titur River Jalgaon districts of Maharashtra state. The Mausam River flows in Malegaon, while the Waghur River flows in Jalgaon, Aurangabad. The Purna River is a major tributary in this region, flowig in districts of Amravati, Akola, Buldhana and Jalgaon in Madhya Pradesh, it joins Tapti River at Changdev in Jalgaon.
The Nalganga River, Vishwaganga River, Nipani River, Mann River, Mas River are the tributaries that flow in the district of Buldhana. The Utawali River, Vishwamitri River, Nirguna River, Gandhari River and Aas River flow in Akola district. The Vaan River flows in Buldhana, Akola, Amravati districts of the Maharashtra state. The Morna River, Shahanur River, Bhavkhuri River, Katepurna River, Umaa River, Pendhi River in Akola, Amravati, Chandrabhaga River are some more prominent rivers in the Tapti River Basin.
The Tapti River Basin has some more important rivers used for irrigation purposes like the Bhuleswari Rive, Aarna River, Gadga Rive, Sipna River, Khapra Rive, Khandu River, Tigriy Rive, Surkhi Rive, Burshi River, Ganjal River and Nesu River.
Religious Importance of Tapti River
 According to the legends, Tapti River is the daughter of Surya or the Sun God. Some says that Surya has given birth to the Tapti River in order to save himself from his own intense heat. The river is also widely mentioned in the great Indian epic Mahabharata, according to which Tapti married Sanvaran, who is a legendary hero of the moon dynasty. Tapti and Sanvaran also had the son and named him Kuru. It was on his name only the Kuru dynasty started. Tapi is known as the Goddess among the Hindus and is worshiped religiously among them.
According to the legends, Tapti River is the daughter of Surya or the Sun God. Some says that Surya has given birth to the Tapti River in order to save himself from his own intense heat. The river is also widely mentioned in the great Indian epic Mahabharata, according to which Tapti married Sanvaran, who is a legendary hero of the moon dynasty. Tapti and Sanvaran also had the son and named him Kuru. It was on his name only the Kuru dynasty started. Tapi is known as the Goddess among the Hindus and is worshiped religiously among them.
Places of Interest along Tapti River
 The Tapti River, also known as Tapi River is located in central India and runs following an east to west itinerary, between two rivers namely, the Godavari and Narmada. It journeys through Surat and is crossed by the Magdalla ONGC Bridge. Along this river there are several places of interest. There are major towns along the river, which are situated in the Indian states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Gujarat. More specifically, these towns are Multai, Nepanagar and Burhanpur in Madhya Pradesh, Surat and Songadh in Gujarat and Bhusawal in Maharashtra.
The Tapti River, also known as Tapi River is located in central India and runs following an east to west itinerary, between two rivers namely, the Godavari and Narmada. It journeys through Surat and is crossed by the Magdalla ONGC Bridge. Along this river there are several places of interest. There are major towns along the river, which are situated in the Indian states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Gujarat. More specifically, these towns are Multai, Nepanagar and Burhanpur in Madhya Pradesh, Surat and Songadh in Gujarat and Bhusawal in Maharashtra.
Multai
Multai is located on the northern bank of the river Tapti. It is one of the southern cities of Madhya Pradesh. More specifically, it can be defined as a small town and a Nagar Palika in the district of Betul. Multai covers almost half of the Satpura plateau. Sanskrit word for Multai is Multapi, which stands for origin of Tapti River. Multapi is known to be the initial name of the city, Multai. It was therefore named after the river Tapti. It has an average elevation of about 749 meters (2457 feet). Forests lie to the west of the city between the districts of East Nimar and Amaraoti. Multai was one of the regional headquarters connecting the district headquarter in the north to the district headquarter, Nagpur in Maharashtra, during the Maratha regime and British rule in India.
Multai is a holy place and a home to two temples namely, Prachin (old) Mandir and Naveen (new) Mandir. Both these temples are dedicated to Mata Tapti. According to Hindu mythology, Mata Tapti is known to be the daughter of Surya, the Sun God. Akhad Saptami Tapti Janmotsav is known to be celebrated in this town. The Multai town is bedecked and an annual mela is also held on this occasion. This town is known for many ancient Hindu Temples, where Lord Shiva and Hanuman are worshipped.
The city has people belonging to different religions and following different traditions and cultural practices. Bundelkhandi language and culture has been identified in the northern part of the town. The southern part of the town is known for the presence of Marathi Language and Maharastrian culture. The rest of the town is prominently occupied by tribal population, known as the Gonds and Korkus. They believe in Bada Mahadev. They are known to also believe in superstitions and animal sacrifice as a ritual is associated with them. They depend on natural herbs for healthcare and medication.
Burhanpur
Burhanpur is situated on the north bank of the Tapti River, on the southwestern border of Madhya Pradesh. More specifically, it is about 340 kilometers (211 mi) southwest of Bhopal and about 540 kilometers (336 mi) northeast of Mumbai. It can be defined as a mid-size city and an administrative seat of Burhanpur district. It has a municipal corporation and also is one of the district headquarters of the state of Madhya Pradesh.
 Burhanpur is well known for textile industries. It is the largest hub for power loom industry in Madhya Pradesh. Burhanpur has several places capable of attracting a plethora of tourists. Asirgarh Fort, Jama Masjid, Swami Narayan Temple, Ganesh Temple, Dargah-e-Hakimi and Shahi Qila are some of the places attracting the attention of tourists.
Burhanpur is well known for textile industries. It is the largest hub for power loom industry in Madhya Pradesh. Burhanpur has several places capable of attracting a plethora of tourists. Asirgarh Fort, Jama Masjid, Swami Narayan Temple, Ganesh Temple, Dargah-e-Hakimi and Shahi Qila are some of the places attracting the attention of tourists.
Nepanagar
Nepanagar is an industrial township located in Burhanpur district. More specifically, this small township lies between Burhanpur and Khandwa and has many small villages in its surrounding. The name of this town is partially derived form the word "NEPA", which stands for National Environment Protection Authority.
A noteworthy attraction of this small town is the newsprint paper mill called the Nepa Mills Limited (earlier known as The National News Print Ltd). The Nepa Mill is known to occupy total land area of about 1869 acres. There are about 2164 residential quarters in the township, belonging to the Nepa Mills.
Surat
Surat is the administrative capital of the Surat district. The city centre is located about 22 km (14 mi) south of the Tapti River. The city is located about 284 kilometers (176 mi) south of the state capital, Gandhinagar; about 265 kilometers (165 mi) south of Ahmedabad; and about 289 kilometers (180 mi) north of Mumbai. Surat was earlier known as Suryapur. It has an elevation of about 13 m (43 ft). Surat has a tropical savanna climate moderated strongly by the sea to the Gulf of Cambay. Surat is well known for its relaxed lifestyle and its cuisine.
Surat itself has various centers of attraction for its visitors. Bank of River Tapi has a place of interest called the Tapi River Front at Adajan. The Sardar Patel Museum is a home to a collection of over 10,000 specimens of arts and crafts. It was established in the year 1998 and was originally called the Winchester Museum. Heritage Square and Surat Castle or Surat Fort is known to be a historical castle. It was planned and built between 1540 and 1546 by Khudawand Khan. Presently, it is located in the Chowk Bazar area in Surat. It is one of the chief ancient monuments of Surat. Chintamani Jain Temple is located in the Shahpor area. It is known to be constructed in the 15th century. Noteworthy features of this temple are wooden carvings, extremely rare paintings of the Jain monk, Acharya Hemachandra and of the Solanki King, Kumarpal. Blues Adventures is a recreational and adventure project, inaugurated in January 2013 by the then Chief Minister of Gujarat, Mr. Narendra Modi. It is known for water-sports activities, amusement park and restaurants. It is located at the basin of River Tapti (Tapi) on the Singanpore side of Weir-cum-Causeway in Surat. Jagdishchandra Bose Aquarium, also known as Surat Aquarium, Gavier Lake, Dr. Shyama Prasad Mukharjee Surat Municipal Zoo or Sarthana Nature Park Science Centre, the Dutch Cemetery, Navinchandra Mafatlal Garden are some of the other places of attraction in Surat.
Songadh
Songadh is a municipal corporation in the district of Tapi. The main town of Fort Songadh is situated on Highway 6 with Nandurbar district to its east and Vyara (district headquarters) to its west. More specifically this town is located at the foot of a solitary hill. Son stands for Gold and Gadh stands for fort. Thus, Songadh means the `Fort of Gold`. This main town is divided into two other towns called Junagam (old town) and Navagam (new town). It has an average elevation of 112 meters (367 feet).
Ukai Dam, Swarnim Tapi Van, Parshuram Temple, Hindustan Bridge, Rokadiya Hanuman Temple, Gaumukh, Dosvada Dam-Rani Mahal, the Central Pulp Mills, quarries located around Songadh and the TPS and Hydro power station are the places of interest in Fort Songadh.
Bhusawal
Bhusawal or Bhusaval is a city and a municipal council, established in 1882 in Jalgaon district. More specifically, this city is situated on National Highway 6. It is considered to be the biggest taluka of Jalgaon district. It has an average elevation of 209 meters (685 feet).
Bhusawal is well known for the cultivation of banana. This place is frequented by traders from various parts of the country for the purpose of buying raw bananas. There is also international export of these bananas. Bhusawal is also well known for its special white brinjals. Cultivation of these brinjals takes place in the nearby areas. They are a part of the delicacies in local marriages, apart from daal baati toop (a lentil dish served with ghee) and peanut garlic chutney. Bhusawal is also popular in whole of Jalgaon district for two items namely, Banducha Vada-Pav and Ghasilal Vada-Pav. Excursions in Bhusawal can be organized to the Thermal Power Station of Maharashtra State Electricity Board (Deepnagar), Orient Cement Grinding Unit, Ordinance Factory (Bhusawal and Varangaon), Indian Oil Corporation Limited Depot and Railway`s Zonal Training School.
Related Articles:
Water Resources in India
Indian Rivers
Dams in India
Lakes of India
Estuaries of India
Dams on Tapti River
Tapti River has several dams on it; the Hatnur Dam is located in Jalgaon district in Maharashtra. This earth fill dam has a height of about 25.5 m (84 ft) above the lowest foundation and a length of about 2,580 m (8,460 ft). Then there is the Ukai Dam located in Surat district and Tapi district in Gujarat. It is an earth-cum-masonry dam. The earth dam has a height of about 80.77 m whereas the masonry dam has a height of about 68.68 m. Some of the other dams are Nanduri Dam, Dehali Dam and Wadishewadi Dam.



















