 Many symptoms have been identified for an early detection of chicken pox. The common viral disease chicken pox is also known as Laghu Masurika in India and its symptoms have similarity with that of common cold and flu. The symptoms can be divided into a few sequences, according to their timings of appearance. Usually the symptoms of chicken pox or Laghu Masurika start to appear one or two days after the varicella zoster virus (VZV) enters the body.
Many symptoms have been identified for an early detection of chicken pox. The common viral disease chicken pox is also known as Laghu Masurika in India and its symptoms have similarity with that of common cold and flu. The symptoms can be divided into a few sequences, according to their timings of appearance. Usually the symptoms of chicken pox or Laghu Masurika start to appear one or two days after the varicella zoster virus (VZV) enters the body.
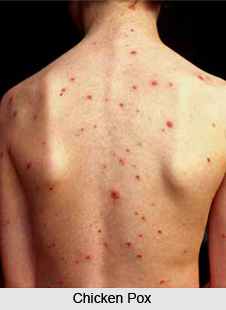
The very first symptom of chicken pox is that of a common cold. The affected person usually has a runny or stuffy nose and may have a burning sensation in the eyes. The eyes of the person may also water and become red, gradually. The second symptom is appearance of rash on the skin. The rash usually appear on the abdomen or back or face and then spread to almost everywhere on the body. The rash can be found on the organs like chest, arms, legs, scalp, mouth, nose, ears, genitals, etc. The rash appears as multiple small, red bumps that look like pimples or insect bites.
In the initial period, the rash is pinkish in colour; however, its colour deepens with time and eventually become red. Though, the rash is small in size initially, it becomes larger with time and they develop into thin-walled blisters filled with clear fluid, which becomes cloudy. The blisters usually have a width of less than a quarter of an inch. After a day or two, the blister wall of the rash breaks and leaves open sores that finally crust over to become dry, brown scabs. The blisters are reddish at base and generally appear in bouts over 2 to 4 days. The initial blisters usually disappear in a couple of days, but new spots appear. Hence, the blisters appear in cycles. Though, this cyclic formation of blisters may continue for up to two weeks, it may stop on the third day itself, in some cases.
 The extent of the rash that appears during chicken pox usually varies from person to person. Some patients have only a few spots; while others can have innumerous spots. The rash can become more extensive or severe among the kids suffering from skin disorders like eczema. Generally, the symptoms of chicken pox are found for a period of 10-21 days. Once, the rashes disappear, it takes another few days to clear the skin. However, one attack of the disease usually confers life-long immunity.
The extent of the rash that appears during chicken pox usually varies from person to person. Some patients have only a few spots; while others can have innumerous spots. The rash can become more extensive or severe among the kids suffering from skin disorders like eczema. Generally, the symptoms of chicken pox are found for a period of 10-21 days. Once, the rashes disappear, it takes another few days to clear the skin. However, one attack of the disease usually confers life-long immunity.
There are a few other symptoms of chicken pox, which can help in detecting the disease. These symptoms include fever, mild headache, abdominal pain, sore throat, or a vague sick feeling. These symptoms can be seen in some kids, generally a day or 2 before the rash appears. The fever usually remains low and all these symptoms may last for a few days. Another symptom of chicken pox is loss of appetite. In this case, the VZV affected person may feel less hunger than normal times. The VZV affected person may also develop serious bacterial infections involving the skin, lungs, bones, joints, and the brain (encephalitis). The VZV may remain inactively in nerve cells near the spinal cord of a person, after an infection, and may even reactivate later as shingles. Shingles is a disease similar to chicken pox and it can cause tingling, itching, or pain followed by a rash with red bumps and blisters. It is usually found in adults.
The symptoms of chicken pox are usually milder and the blisters are fewer among the younger kids, compared to the older children or adults. Though, it is a mild illness, chicken pox can affect infants, teens, adults, and people with weak immune systems more severely. The kids having normal immune systems can also occasionally develop complications, most commonly a skin infection near the blisters. The symptoms of chicken pox usually disappear without any treatment. Generally an infected child is advised to stay home and rest until the symptoms withdraws.




