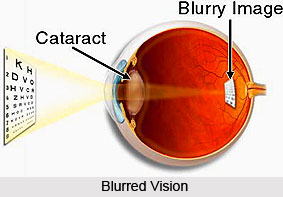
 Cataract can be defined as an eye disorder that leads to the changes in clarity of the natural lens inside the eye. This change gradually degrades visual quality of the affected person. The natural lens plays a crucial role in focusing unimpeded light on the retina at the back of the eye. The retina transforms light to a neurological signal that the brain interprets as vision. Cataracts when caused block and distort light passing through the lens, causing visual symptoms and complaints. Cataract development is usually a gradual process of normal aging but can occasionally occur rapidly. The gradual change in vision is so rapid that it cannot be determined as Symptoms of Cataract.
Cataract can be defined as an eye disorder that leads to the changes in clarity of the natural lens inside the eye. This change gradually degrades visual quality of the affected person. The natural lens plays a crucial role in focusing unimpeded light on the retina at the back of the eye. The retina transforms light to a neurological signal that the brain interprets as vision. Cataracts when caused block and distort light passing through the lens, causing visual symptoms and complaints. Cataract development is usually a gradual process of normal aging but can occasionally occur rapidly. The gradual change in vision is so rapid that it cannot be determined as Symptoms of Cataract.
Cataracts usually affect both eyes; however, it is also caused in one eye that advances more rapidly. Cataract is a very common disease that affects people at an old age. It develops usually without any pain and is associated with any eye redness. Various kinds of Symptoms of Cataract are seen as the eye disorder reaches its advanced stage. Major symptoms of the cataract include blurred vision, difficulty with glare, dulled colour vision, increased nearsightedness accompanied by frequent changes in eyeglass prescription, and occasionally double vision in one eye.
Moreover, certain Symptoms of Cataract comprise a phenomenon called "second sight" in which one`s reading vision improves as a result of their increased nearsightedness from swelling of the cataract. Furthermore, cataracts continue progress and opacify, vision becomes cloudy. Thus, the symptoms in the early stages of cataracts provide little effect on vision. Symptoms of cataracts depend on the type of cataract. Each type has its particular sign. Though, the common symptoms of a cataract may include cloudy vision or double vision. A person affected with cataract may see images that take on a yellowish tint as colour vibrancy diminishes. Reading becomes difficult over time because of a reduced contrast between letters and their background. People who have diffuse cataracts in the rear walls of their lenses are particularly prone to glare sensitivity because bright light tends to scatter in their lenses.
Symptoms of Cataract change with advanced cases, the pupil, which is normally black, looks milky or yellowish. The person diagnosed with the eye disorder has vision which is reduced. The person can only distinguish between light from dark. In addition to that symptoms may vary depending on the part of the lens that is affected.
The types of cataracts and their related symptoms include
•Nuclear Cataracts: Cataracts of the lens nucleus are most commonly associated with aging. The symptoms of these kinds of cataracts include hazy distance vision and increasing glare. Moreover, persons affected with this type of cataracts experience progressive nearsightedness. This effect may even temporarily counteract age-related farsightedness and provide a temporary improvement in overall vision in some people. Furthermore, the improvement fades when the cataract advances sufficiently to engulf the inherent farsightedness
•Cortical Cataracts. Cortical cataracts usually start on the outside of the cortex which is the outer area of the lens. In this type of cataract, there is very little initial effect on vision. Glare develops as these cataracts increase and approach the center of the lens. The common of symptoms of these Cataracts include problems with distance vision, contrast sensitivity, and clarity may occur as the cataracts progress further
•Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts. Posterior subcapsular cataracts typically start near the center of the back part of the capsule surrounding the lens. These cataracts often advance rapidly. In certain cases patients suffer from major impairment of eyesight, including near-vision problems and glare, develops within several months. When the cataract becomes more opaque, clear vision is compromised. A loss of visual acuity is seen as well as contrast sensitivity is also lost. Thus, the contours, shadows and colour vision become less vivid.
Thus, common Symptoms of Cataracts noticeable in a person is blurring and worsening of vision. Other symptoms include the dimming and fading of colours, decreased night vision, problems with bright lights and sunshine. Most importantly eyesight of an individual may also progressively grow worse.