 Sikkim is bordered with the snow capped mountains, hill stations, mountain forests, lakes and mountain passes. It lies just to the south of Tibet, sandwiched between Nepal to the west and Bhutan to the east.
Sikkim is bordered with the snow capped mountains, hill stations, mountain forests, lakes and mountain passes. It lies just to the south of Tibet, sandwiched between Nepal to the west and Bhutan to the east.
Naming of Sikkim
The word `Sikkim` combines of two words "Su" and "Khyim". Su means "new" and Khyim, means "palace" or house. Therefore the word means new palace or house, in reference to the palace built by the state`s first ruler, Phuntsok Namgyal. The Tibetan name for Sikkim is `Denjong` which means the "Valley of Rice."
History of Sikkim
History of Sikkim traced back from 14th Century. Lepchas are the original inhabitants of Sikkim from the ancient era. In Buddhist literature, the early history of Sikkim was recorded. Later in 1642, Phintsok Namgyal (1604-1670) became the first Chogyal (King). His descendents ruled Sikkim for more than 330 years. During the 1700`s Sikkim suffered massive invasion from Nepal and Bhutan and lost much territory as a result. The Nepalese also migrated to Sikkim and settled as farmers. Sikkim assisted the British East India Company in a successful war against Nepal and after that Sikkim became an integral part of Sikkim.
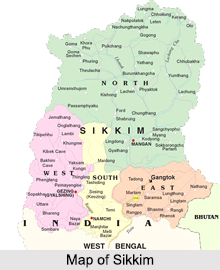
Geography of Sikkim
Sikkim is a gorgeous and beautiful Indian state nestled in the Himalayan Mountain Range. Sikkim is thumb-shaped and has a mountainous terrain. Kanchenjunga peak is the highest point in Sikkim. Teesta River is the major lifeline of Sikkim.
Demography of Sikkim
According to the Population Census in the year 2011, Sikkim is populated with 610,577 people. The majority of the people living in Sikkim are of Nepali origin. The native Sikkimese is the Bhutias, who migrated from the Kham district of Tibet in the 14th Century and the Lepchas migrated from the Far East.
Culture of Sikkim
Culture of Sikkim is completely based on Buddhism origin. The people of Sikkim celebrate the regional festivals like Diwali, Dusshera, Losar, Makar Sankranti and Bhumchu. Here the Muslims celebrate the Eid ul-Fitr and Muharram.
Education of Sikkim
Sikkim is developed with education and arts. Here the literacy rate was 82.2 percent, out of which 87.29 percent are the male percentage and 76.43 percent for females.
 Administration in Sikkim
Administration in Sikkim
Sikkim is governed by the Governor, who is appointed by the Central Government. His main role is to oversee the swearing in of the Chief Minister. The governor appoints the cabinet ministers on the advice of the Chief Minister. Sikkim has a unicameral legislature. Sikkim is allocated one seat in each of both chambers of the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha.
The districts are headed by the District Collector/ District Magistrate. He is responsible for maintaining law and order in the State. Sikkim has four districts namely East Sikkim, West Sikkim, North Sikkim and South Sikkim. The district capitals are Gangtok, Geyzing, Mangan and Namchi respectively. These four districts are further divided into Sub-Divisions. "Pakyong" is the sub-division of East District. "Soreng" is the sub-division of West District. "Chungthang" is the sub-division of North District and "Ravongla" is the sub-division of South District.
Economy of Sikkim
The economy of Sikkim is dependent on agriculture. Rice is grown on the hillsides of the southern areas of Sikkim. Sikkim is the biggest producer of greater cardamom in India. The minerals mined in Sikkim are copper, dolomite, limestone, graphite, mica and coal.
Tourism of Sikkim
Sikkim is known for the lofty snow capped Kanchenjungha and the pea green woodlands. Sikkim is the land of colours, lakes and flowers. Tsomgo Lake, Baba Mandir, Nathula Pass, Enchey Monastery, Hanuman Tok, Tashi View Point, Ganesh Tok, Do - Drul Chorten, Rumtek monastery, Lachung, Yumthang, and Gurudongmar Lake are popular places of tourist attraction in Sikkim






