 Saran District is located in the southern post of the newly created Saran Division of North Bihar. This administrative district of Bihar has its headquarters located at Chhapra. Saran District is situated between 25 degree 36 minutes and 26 degree 13 minutes north latitude and 84 degree 24 minutes and 85 degree 15 minutes east longitude.
Saran District is located in the southern post of the newly created Saran Division of North Bihar. This administrative district of Bihar has its headquarters located at Chhapra. Saran District is situated between 25 degree 36 minutes and 26 degree 13 minutes north latitude and 84 degree 24 minutes and 85 degree 15 minutes east longitude.
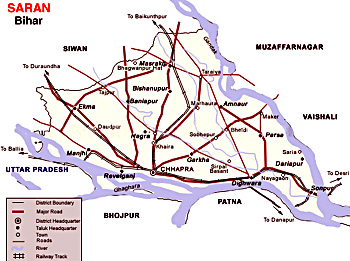
The Ganga River constitutes the southern boundary of the district beyond which lie Bhojpur District and Patna District. To the north of Saran lie Siwan District and Gopalganj District. The Gandak River forms the dividing line with Vaishali and Muzaffarpur district in the east. To the west of Saran lie the district of Siwan and the Ballia district of Uttar Pradesh, Ghaghara River constituting a boundary between Saran and Ballia.
History of Saran District
The historical background of the district as available in Ain-E-Akbari records Saran as one of the six Revenue Divisions constituting the province of Bihar. At the time of grant of Diwani to the British East India Company in 1765, there were eight Sarkars including Saran and Champaran. These two were later combined to form a single unit named Saran. Saran was included in the Patna Division when the Commissioner`s Divisions were set up in 1829. It was separated from Champaran in 1866 when it Champaran was constituted into a separate district. Saran was made a part of Tirhut Division when latter was created in 1908. By this time there were three subdivisions in this district namely Saran, Siwan and Gopalganj. In 1972 each subdivision of the old Saran District became an independent district. Present Saran District after separation of Siwan and Gopalganj District still has its headquarters at Chhapra.
Various hypotheses have been put forward about the origin of the name Saran. General Cunningham suggested that Saran was earlier known as Saran or asylum which was a name given to a Stupa (Pillar) built by emperor Ashoka. Another view holds that the name Saran has been derived from Saranga- Aranya or the deer forest, the district being famous for its wide expanses of forest and deer in prehistoric times.
Geography of Saran District
Geography of Saran District is shaped like a triangle with its apex at the confluence of boundary of Gopalganj district and Gandak-Ganga River. There are three rivers namely Ganga, Ghaghara River, Gandak which encircle the district from south, north, east and western side respectively. The district is entirely constituted of plains but there are quite a few depressions and marshes, which cause the formation of three broad natural divisions. Firstly, the alluvial plains along the big rivers which are subjected to periodic inundation and prone to floods, secondly the region of uplands away from the rivers and not subjected to floods and thirdly the diara areas in the beds of these great rivers. Out of 20 blocks in the districts, six blocks namely Sonepur, Dighwara, Revelganj, Chhapra, Manjhi and Dariyapur are affected by floods regularly. There are six partially flood affected blocks namely Garkha, Parsa, Marhoura, Amnaur, Jalalpur, and Ekma. The soil of the district is alluvial. No mineral of economic value is found in the district.
Tourism in Saran District
There are several places of interest in Saran District. Tourism in Saran District offers exploring opportunities of various ancient and religious sites like Aami, Sonepur (Princely State of Sonepur), Dhorh Ashram, Gautam Asthan, Silhauri and Chirand. Big fair are organized on several occasions like Shivaratri and Kartik Purnima. People from all parts of the country come for having a pleasurable traveling experience.






