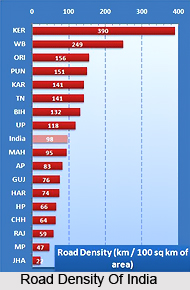
 The length of a road per 100 sq. km. is known as density of roads. In 1951 road density was 12, which had shot up to 63 by 1997-98. But it is highly irregular all through the country. The lowest density of below 10 is found in the precipitous states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Mizoram and Meghalaya. The next higher group with a density between 10 and 20 covers Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh. Orissa, Bihar, Sikkim, Assam, Manipur and Tripura. The next higher group with a density between 20 and 40, covers the states of Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Gujarat. Finally the group with a density of 40 and above comprises the states of Punjab and Haryana in the north and Tamil Nadu and Kerala in the south.
The length of a road per 100 sq. km. is known as density of roads. In 1951 road density was 12, which had shot up to 63 by 1997-98. But it is highly irregular all through the country. The lowest density of below 10 is found in the precipitous states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Mizoram and Meghalaya. The next higher group with a density between 10 and 20 covers Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh. Orissa, Bihar, Sikkim, Assam, Manipur and Tripura. The next higher group with a density between 20 and 40, covers the states of Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Gujarat. Finally the group with a density of 40 and above comprises the states of Punjab and Haryana in the north and Tamil Nadu and Kerala in the south.
The road density of Japan is 14 times higher, compared to India. And the ratio between the length of roads and total population is 33 times higher in the U.S.A., compared to India.
The socio-cultural implication of road density can be understood from the instance of Kerala. Easy accessibility of pastoral areas has ensued in fast increase of universal literacy, low infant mortality, higher longevity and a very low birth and growth rate of population. In fact in Kerala it is very tricky to find out exactly where occupancy of one village terminates and that of the other begins. They are almost linear and unbroken.
The Government of India is in charge for constructing and preserving national highways, because the state governments are responsible for state highways and district and village roads. However, Govt. of India has yet another very substantial task of building and maintaining border roads. India`s borders are located on the harshest territories, consisting of sublime mountains, deserts, swampy and rainy lands and impenetrable woods. It is only through these border roads that an uninterrupted supply route can be asserted for the jawans defending and safeguarding the international land frontiers. The country`s Border Road Organization (BRO) has built the Manali-Leh highway- the 2nd highest in the world. Its average height is a sublime 4,270 metres above sea level. It negotiates four precipitous passes, ranging between 4,875 and 5,485 metres above sea level.















