 Penna River is a river of Southern India in Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. The Penna River rises in Nandi Hills in Chikballapur District of Karnataka, and runs north and east through the states of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh to empty into the Bay of Bengal. The river basin lies in the rain shadow region of Eastern Ghats and receives 500 mm average rainfall annually.
Penna River is a river of Southern India in Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. The Penna River rises in Nandi Hills in Chikballapur District of Karnataka, and runs north and east through the states of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh to empty into the Bay of Bengal. The river basin lies in the rain shadow region of Eastern Ghats and receives 500 mm average rainfall annually.
Etymology of Penna River
The name of the river Penneru is derived from Telugu words "penu" meaning grand and "yeru" meaning river, stream, or a rivulet. It also called as "Utthara Pinakini" in Kannada. The name Pinakini refers to Pinaka bow of the Nandhiswara, the presiding deity of the Nandi hills at the origin of the river.
Tributaries of Penna River
Penna River has a few tributaries. Its main tributaries are the Jayamangali, Kunderu and Sagileru from the north and Chitravathi, Papagni and Cheyyeru from the south.
 Course of Penna River
The Penna River has several sources and mouths but the main source of the water is from rains. The river is seasonal and appears like small stream during dry periods. The main stream starts in Nandi Hills in of Karnataka, flows for 597km in north and east directions through several mountains and plains, and joins the Bay of Bengal in Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh. It is 597 kilometres (371 mi) long, with a drainage basin covering 55,213 sqkm in Karnataka and 48,276 sqkm in Andhra Pradesh.
Course of Penna River
The Penna River has several sources and mouths but the main source of the water is from rains. The river is seasonal and appears like small stream during dry periods. The main stream starts in Nandi Hills in of Karnataka, flows for 597km in north and east directions through several mountains and plains, and joins the Bay of Bengal in Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh. It is 597 kilometres (371 mi) long, with a drainage basin covering 55,213 sqkm in Karnataka and 48,276 sqkm in Andhra Pradesh.
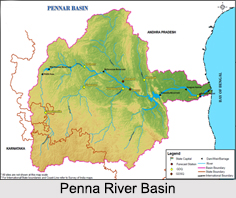
Penna River Basin
The watershed of the Penna River and its tributaries covers part of the southern Deccan plateau, including most of the Rayalaseema region of Andhra Pradesh and part of Karnataka. The Kolar Plateau forms the divide between the Penna watershed and those of the Kaveri, Ponnaiyar and Palar rivers to the south. The Penna drains the northern portion of the plateau, which includes parts of Kolar and Tumkur districts in Karnataka. The upper watershed of the Penna includes Cuddapah District, central and eastern Anantapur District, the southern part of Kurnool District, north-western of Chittoor District.
Estuary of Penna River
The estuary of the Penna River extends 7 km upstream from the Bay of Bengal. Upputeru tidal creek and Isakapalli lagoon form the main coastal wetlands in the Penna River.















