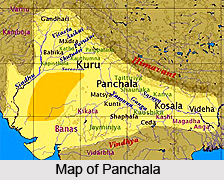
 Panchala is an important ancient Indian city. In the earlier days, it used to be the name of an ancient kingdom of northern India. It was situated in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the upper Gangetic plain surrounding the present-day states of Uttarakhand and western Uttar Pradesh. During Late Vedic times, Panchala enjoyed the position of being one of the most powerful states of South Asia, closely associated with the Kuru Kingdom.
Panchala is an important ancient Indian city. In the earlier days, it used to be the name of an ancient kingdom of northern India. It was situated in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the upper Gangetic plain surrounding the present-day states of Uttarakhand and western Uttar Pradesh. During Late Vedic times, Panchala enjoyed the position of being one of the most powerful states of South Asia, closely associated with the Kuru Kingdom.
The present Ruhelkhanda and some other districts comprised this state, which was divided in two parts. Aahi-chatra and Kampilya were its capitals of the northern and southern parts respectively. Panchala was divided into Uttara-Panchala and Dakshina-Panchala. Counted among the sixteen Mahajanapadas, the northern Panchala had Chhatravati as its capital and the south had its capital at Kampilya. In Panchala is situated the renounced city of Kanyakubja. Like many other kingdoms it was seen that the Panchals too had shifted to a republican form of government in sixth and fifth century BCE from being a monarchy.
Position of Panchala during Various Periods
Vedic period: During Vedic period, Panchala was the second political centre of Vedic civilization as its focus shifted east from the Punjab. This period is associated with the Painted Grey Ware culture. It started around 1100 BCE and declined from 600 BCE, with the end of the Vedic period. Panchala was home to the Shaunaka and Taittiriya Vedic schools.
It is believed that Panchalas probably comprised of five clans including Krivis, Turvashas, Keshins, Srinjayas and Somakas. It can be observed that the names of the last two clans, the Somakas and the Srinjayas are mentioned in the Mahabharata and the Puranas.
Draupadi who was the daughter of King Drupada of Panchala was married into the Pandavas, belonged to the Somaka clan. However, as per the Mahabharata and the Puranas, the ruling clan of the northern Panchala was an offshoot of the Bharata clan and Divodasa, Sudas, Srinjaya, Somaka, and Drupada were the most prominent rulers of this clan.
Magadhan Rule: Many historians opine that the Panchala was originally a monarchical clan and it appears that around 500 BCE it had switched to Republican Corporation. Then the Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya defines it as one of the sixteen mahajanapadas of the c. 6th century BCE. Panchala was annexed into the Magadha Empire at the time of Mahapadma Nanda regime in the mid-4th century BCE.
Post-Mauryan Period: The ancient coins found at Ahichatra and adjoining areas reveal the existence of independent rulers of Panchala during the post-Mauryan period. One side of these copper made coins which are generally in round shape depict the ruler`s name. The reverse side feature the depictions of the deities or sometimes of their attributes.
Shaunakayaniputra Vangapala who was the ruler of Ahichatra is identified with king Vangapala, known from the coins. After studying the coins, many historians have come to the conclusion that the last independent ruler of Ahichatra was probably Achyuta. He was defeated by Samudragupta, after which, Panchala was annexed into the Gupta Empire.



















