Introduction
Narmada River is a major riverpeninsular Indiawhich flows in east-west direction, along with two other rivers namely, the Tapti River and Mahi River. Reva is another name of Narmada River. It is one of the rivers in India which flows in a rift valley and acts as a divider between north India andsouth India. Narmada River can be used for navigation. At Hoshangabad, the river has some striking ghats on its banks.
History of Narmada River
 The history of Narmada River is closely associated with the place Amarkantak and Narmadakund. Amarkantak and rivers originating from it are hardly mentioned in Vedic literature, but these have been mentioned many a times in Puranas, Ramayana, Mahabharata, Vashishtha samhita and "Shatapatha Brahmana". After Mahabharata the history of a period of about 3000 years remains in dark. Professor Arjun Chaube Kashyap came to a conclusion that the Puranic name of Amarkantak was Riksh parvat. About 6000 years back the Suryavanshi samrat Mandhata established a town in the valley Riksh parvat and called it Mandhata. The queen of samrat Purukutsa, who was son of Mandhata, gave the title of Narmada to the river. Due to occupation of this area by Mandhata the descendents of Yayati migrated from this area to west of Madhya Pradesh and settled on the banks of Narmada River.
The history of Narmada River is closely associated with the place Amarkantak and Narmadakund. Amarkantak and rivers originating from it are hardly mentioned in Vedic literature, but these have been mentioned many a times in Puranas, Ramayana, Mahabharata, Vashishtha samhita and "Shatapatha Brahmana". After Mahabharata the history of a period of about 3000 years remains in dark. Professor Arjun Chaube Kashyap came to a conclusion that the Puranic name of Amarkantak was Riksh parvat. About 6000 years back the Suryavanshi samrat Mandhata established a town in the valley Riksh parvat and called it Mandhata. The queen of samrat Purukutsa, who was son of Mandhata, gave the title of Narmada to the river. Due to occupation of this area by Mandhata the descendents of Yayati migrated from this area to west of Madhya Pradesh and settled on the banks of Narmada River.
According to tradition, this Vindhyachal area, where the River Narmada flows was included in the Kingdom of Ayodhya, Bhrigu Rishi, Kapila Muni and Markandeya Rishi had ashrams here. It is also said that Pandavas resided along the riverbanks and gained spiritual benefits during their exile. After about 3000 years of Mahabharata the Adi Shankaracharya was born in 788 AD and sanctified on the banks of Narmada River. He established Pataleshwar Mahadev in Amarkantak at the origin of Narmada from the bamboo bunches. This place is known as Surajkund presently. There is no bamboo clumps here right now.
Ptolemy and the author of the Periplus have mentioned the river. The Ramayana, the Mahabharat and Puranas refer to it frequently. The Rewa Khand of Vayu Puran and the Rewa Khand of Skand Puran are full of references of the story of the birth and the importance of the Narmada River. It is said to have originated from the body of Lord Shiva. The river was created in the form of a lovely girl who enamored the Gods and hence the river was named by the Lord as Narmada, means delight giving.
It is also said to have been in love with the Sonbhadra, another river flowing on the Chhota Nagpur plateau. According to the Puranas the Narmada is also called the Rewa, from its middle course or the root through its rocky bed. To Shiva the river is especially sacred on the basis of its origin, and it is often called Shankari, i.e., daughter of Shankar. All the pebbles of the river were rolling on its bed are said to take the shape of his emblem with the saying - Narmada Ke Kanker utte Sankar. These lingam or the phallus shaped stones, called Banalinga are rare and in much demand for daily worship by the Hindus.
In the recent history, this area was offered in dowry to the Kalachuri King by the Chedi King of 10th to 11th century AD. The Kalchuri Maharaja Karnadeva (1042-1072 AD) had founded temples at Surajkund. In 1808 Amarkantak was reined by the King of Nagpur and later was taken under foreign rule. In the latest news, Amarkantak has been selected as the site for India`s first tribal university. UPA government decided to form a tribal university beside the banks of Narmada River.
Geology of Narmada River
 The Narmada Valley is a graben. A graben means a layered block of the earth`s crust that dropped down comparatively to the blocks on either side due to ancient spreading of the earth`s crust. Two normal faults, known as the Narmada North fault and Narmada South fault, parallel to the river`s course, and smear the boundary between the Narmada block and the Vindhya and Satpura blocks or horsts which rise relative to the Narmada Graben. The Narmada`s watershed includes the northern slopes of the Satpuras, and the steep southern slope of the Vindhya Range; however, not the Vindhyan tableland and the streams from which flow into the Ganges and Yamuna. The Narmada valley is considered very significant for paleontological studies in India. Several dinosaur fossils have been found in this area including the Titanosaurus indicus that was found in 1877 by Richard Lydekker and the recently discovered one is that of the Rajasaurus narmadensis.
The Narmada Valley is a graben. A graben means a layered block of the earth`s crust that dropped down comparatively to the blocks on either side due to ancient spreading of the earth`s crust. Two normal faults, known as the Narmada North fault and Narmada South fault, parallel to the river`s course, and smear the boundary between the Narmada block and the Vindhya and Satpura blocks or horsts which rise relative to the Narmada Graben. The Narmada`s watershed includes the northern slopes of the Satpuras, and the steep southern slope of the Vindhya Range; however, not the Vindhyan tableland and the streams from which flow into the Ganges and Yamuna. The Narmada valley is considered very significant for paleontological studies in India. Several dinosaur fossils have been found in this area including the Titanosaurus indicus that was found in 1877 by Richard Lydekker and the recently discovered one is that of the Rajasaurus narmadensis.
Geography of Narmada River
Geography of Narmada River relates to the features of Narmada River and the Narmada Valley. The length of Narmada River is approximately 1,315 km (817 mi). Valleys of Narmada River are historically as well as economically significant. The narrow valley of the Narmada lies below the Vindhyachal scarps. Narmada River flows across this narrow valley and the valley covers the southern region of Dhar District`s Manawar tehsil and the southeastern part of Kukshi tehsil. The height of the river ranges from about 275 meters to 150 meters. Its height in the northern part of Manawar tehsil and southwest low plain of Nisarpur varies. Westwards, Narmada Valley comprises of several hills that are the originating point of a number of streams. These streams join Narmada River resulting in a few stretches of alluvium deposit. Narmada River`s watershed consists of northern slopes of Satpura Mountain Range as well as the vertical southern slope of the Vindhya Mountain Range.
Origin of Narmada River
 The Narmada River is one of the 5 holy rivers of India and the origin of Narmada River is from Amarkantak, which is located near the border of the Indian states of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh, deep inside the dense forest of Maikal Mountain Range. The river actually originates from a small reservoir called the Narmadakund and rises from a height of 1057 m above sea level.
The Narmada River is one of the 5 holy rivers of India and the origin of Narmada River is from Amarkantak, which is located near the border of the Indian states of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh, deep inside the dense forest of Maikal Mountain Range. The river actually originates from a small reservoir called the Narmadakund and rises from a height of 1057 m above sea level.
The Narmada River flows through the Central India and being a peninsular river, the Narmada River receives water largely through rainfall. The Amarkantak region is actually one of the wettest regions of Central India and can actually be a source to Narmada as well as Son, Hasdeo, etc.
Religious Significance of Origin of Narmada River
The spot of the origin of Narmada River is considered to be a religious ground. The Narmadakund is an open reservoir, lying at the starting point of the Narmada River and has various temples of particular Hindu Gods and Goddesses encircling this place. The religious fervour of the tourists is easily satiated in this place. There are also numerous pilgrimage spots on the banks of the river, the most important among them are Mahewswar and Omkareshwar temples.
It is said that Lord Shiva gave matchless purifying powers to the Narmada River. The water of Narmada River purifies a man and helps him in attaining salvation. The Narmada finds mention in ancient texts of India as one of the seven most sacred rivers in India. The river is considered as the Goddess and is worshiped in India.
Course of Narmada River
 The course of River Narmada starts with its origin at a small tank called Narmada Kund located on the Amarkantak hill (at an height of 1057 m above sea level) in the Shahdol district of eastern Madhya Pradesh. The river flows down from the Amarkantak hill range at the Kapildhara falls over a high cliff and meanders down the hills flowing through a twisting course and crossing the rocks and islands up to the ruined palace of Ramnagar. The river flows further between Ramnagar and Mandla 25 km in the direction of southeast. The river course of Narmada is comparatively straight with deep water and there are hardly any rocky obstacles.
The course of River Narmada starts with its origin at a small tank called Narmada Kund located on the Amarkantak hill (at an height of 1057 m above sea level) in the Shahdol district of eastern Madhya Pradesh. The river flows down from the Amarkantak hill range at the Kapildhara falls over a high cliff and meanders down the hills flowing through a twisting course and crossing the rocks and islands up to the ruined palace of Ramnagar. The river flows further between Ramnagar and Mandla 25 km in the direction of southeast. The river course of Narmada is comparatively straight with deep water and there are hardly any rocky obstacles.
The Banger joins River Narmada from the left. The river then runs northeast in a narrow circle towards Jabalpur. Close to this city, Marble rocks stand as a popular tourist attraction. This river after a fall of some 9 metre called the Dhuandhara or the fall of mist, it flows for almost 3 km in a deep narrow channel across the magnesium limestone and basalt rocks called the Marble Rocks; from a width of around 90 metres above, it remains compressed in this channel of 18 meters only. After this point up to its emptying into the Arabian Sea, the Narmada enters three narrow valleys in between the Vindhyan Scarps in the north and the Satpura range in the South. The southern extension of the valley is much wider at certain places. The closely approaching line of the scarps and the Satpura hills separates these three valley sections.
Emerging from the Marble Rocks, river Narmada enters its first productive basin, this fertile land extends about 320 km with an average width of 35 km in the south direction. In the north the valley is limited to the Barna-Bareli plain, the execution of which is at Barkhara hills opposite to Hoshangabad. However, the hills again reduce in size and density at the Kannod plains. The fertile banks rise about to 12 metre high. It is in the first valley of the Narmada that many of its significant tributaries from the south join the river, and bring the waters of the northern slopes of the Satpura range. Among them, the prime tributaries are the Tawa (biggest tributary), the Sher, the Dudhi, the Shakkar and the Ganjal. The Hiran, the Choral, the Barna, the Karam and the Lohar are the main tributaries joining from the north.
Below Handia and Nemawar to Hiran fall (also called the deer`s leap) the river is surrounded by hills from both sides. In this stretch the character of the river often changes. The Omkareshwar Island, sacred to the Lord Shiva, is the most important river island in Madhya Pradesh. At first the descent is rapid and the stream, quickening in pace, rushes over a barrier of rocks. The Sikta and the Kaveri join it below the Khandwa plain. The Mandhar, about 40 km below Nemawar, and Dadrai, 40 km further down near Punasa are the two points where, the river falls over a height of about 12 m
A few kilometers further down near Bareli and the crossing ghat of the Agra to Mumbai road the Narmada enters the Mandleshwar plain. This convergence is on the National Highway No 3; the second basin is about 180 km long and 65 km wide in the south. The northern stretch of the basin is only 25 km. The second valley section is broken only by Saheshwar Dhara fall. The early course of about 125 km up to Markari falls is met with a succession of cataracts and rapids from the elevated table land of Malwa to the low-level of Gujarat plain. Approaching towards the west of this basin the hills draw very close but soon decline down.
Below Makrai, the river flows between Baroda and Nandod and then meanders through the rich plain of Bharuch district of Gujarat state. The banks are high between the layers of rich alluvial deposits, hardened mud, gravels like limestone and sand. The width of the river spans from 1.5 km at Makrai to 3 km near Bharuch. The width from this spot to the estuary is around 21 km at the Gulf of Cambay. An old channel of the river, 1 to 2 km south from the present one, is very clear below Bharuch. The Karanjan and the Orsing are the most significant tributaries in the original course. The former joins at Rundh and the latter at Vyas in Baroda district of Gujarat, opposite each other and form a Triveni (confluence of three rivers) on the Narmada. The Amaravati and the Bhukhi are more two tributaries of importance. A large drift called Alia Bet or Kadaria Bet, lie opposite to the mouth of the Bhukhi.
The tidal rise is felt up to 32 km above Bharuch, where the neap tides rise to about a metre and spring tide is almost 3.5 metre. The river is widely navigated for vessels of the burthen of 95 tonnes or 380 Bombay candies up to Bharuch and for vessels up to 35 tonnes (140 Bombay candies) up to Shamlapitha er Ghangdia. The small vessels that weigh around 10 tonnes, voyage up to Tilakawada in Gujarat. There are sand bases and shoals at mouth and also at Bharuch. The nearby island of Kabirwad, in the Narmada River, there is a gigantic Banyan tree, covering almost a hectare.
Tributaries of Narmada River
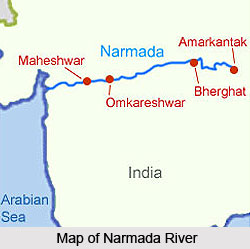 The tributaries of River Narmada are of great importance in Central India as they provide an important source of water, irrigation and other resource based activities. The Narmada River is one of the most important rivers situated in central India and the fifth largest river in the sub-continent. It forms a boundary between North and South India and flows in a westward direction for over a length of 1,312 kms before draining through the Gulf of Khambhat into the Arabian Sea. Among the major tributaries of the Narmada river are the Hallon River, Banjar River, Barna River and Tawa River. When river Narmada emerges from the Marble Rocks the river enters its first fertile basin. This basin extends about 320 km with an average width of 35 km in the south. The northern part of the valley is the Barna-Bareli plain, where the Barna River flows. The Tawa River flowing through central India is the longest tributary of the Narmada River. It originates in the Satpura Mountain Range of the Betul district and Chhindwara district of Madhya Pradesh.
The tributaries of River Narmada are of great importance in Central India as they provide an important source of water, irrigation and other resource based activities. The Narmada River is one of the most important rivers situated in central India and the fifth largest river in the sub-continent. It forms a boundary between North and South India and flows in a westward direction for over a length of 1,312 kms before draining through the Gulf of Khambhat into the Arabian Sea. Among the major tributaries of the Narmada river are the Hallon River, Banjar River, Barna River and Tawa River. When river Narmada emerges from the Marble Rocks the river enters its first fertile basin. This basin extends about 320 km with an average width of 35 km in the south. The northern part of the valley is the Barna-Bareli plain, where the Barna River flows. The Tawa River flowing through central India is the longest tributary of the Narmada River. It originates in the Satpura Mountain Range of the Betul district and Chhindwara district of Madhya Pradesh.
Banjar River
The Banjar River is the major tributary of the Narmada. It passes through the Mandla District in the state of Madhya Pradesh. The catchment area of the river contains some of the best Sal forests of the district. The Kanha National Park is situated in the upper courses of Narmada, along the banks of the Banjar River. It is almost 18 Kms from Mandla features several wild animals including the tiger.
 Tawa River
Tawa River
The longest tributary of the Narmada is the Tawa River. The river is one hundred and seventy two kilometers in length. It has its origins in the Satpura range of the Betul and Chhindwara districts of Madhya Pradesh. It continues to flow in a north-westerly direction from this point onwards and enters the village of Bandra Bhan in Hoshangabad district where it merges with the Narmada River.
Barna River
The Barna River flows along the Barna-Bareili plain. The banks of the river are about 12 metres high. The Hiran, the Barna, the Choral, the Karam and the Lohar are the significant tributaries joining Narmada from the north.
Halon River
The Halon valley falls in Balaghat district. The Halon River also flows across the Kanha National Park.
Thus discussed above are the important tributaries of the Narmada River.
Religious Significance of Narmada River
 The religious significance of Narmada River lies in its origin. The river is one of the most sacred of the five holy rivers of India; the other four sacred rivers of India are Ganga, Yamuna, Godavari and Kaveri. It is believed that a dip in any of these five rivers washes ones sins away. Ptolemy has mentioned the river in the 2nd century AD as Namade. The Ramayana, the Mahabharata and Puranas refer to it often. The Rewa Khand of Vayu Puran and the Rewa Khand of Skand Puran are completely devoted to the story of the birth and the significance of the River and hence Narmada is also called Rewa.
The religious significance of Narmada River lies in its origin. The river is one of the most sacred of the five holy rivers of India; the other four sacred rivers of India are Ganga, Yamuna, Godavari and Kaveri. It is believed that a dip in any of these five rivers washes ones sins away. Ptolemy has mentioned the river in the 2nd century AD as Namade. The Ramayana, the Mahabharata and Puranas refer to it often. The Rewa Khand of Vayu Puran and the Rewa Khand of Skand Puran are completely devoted to the story of the birth and the significance of the River and hence Narmada is also called Rewa.
There are many fables about the source of the Narmada. According to a myth, once, Lord Shiva, meditated so hard that he started perspiring. Shiva`s sweat gathered in a tank and started flowing in the form of a river - the Narmada. Another legend has it that two teardrops that fell from the eyes of Lord Brahma, the Creator of the Universe, yielded two rivers - the Narmada and the Son.
Legends also say that for Lord Shiva, the Hindu God, the river is particularly sacred on account of its origin, and it is often called Shankari or the daughter of Shankar. All the pebbles rolling on its bed are said to take the shape of his emblem with the saying - Narmada Ke Kanker utte Sankar that is a popular saying in the Hindi belt of India. This saying means that `pebble stones of Narmada gets a personified form of Shiva`. These lingam shaped stones are called Banalinga or Banashivalingas. These pebbles are much sought after for daily worship by the Hindus. The Brihadeeswara Temple in Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu is constructed by Rajaraja Chola and possesses one of the biggest Banalingas. Adi Shankara met his guru Govinda Bhagavatpada on the banks of river Narmada. Important places of pilgrimage along this river are Amarkantak, Omkareshwar, Maheshwar, Mahadeo temples, Nemawar Siddeshwar Mandir, Chausath Yogini, Chaubis Avatar Temple and others.
Ecology in Narmada River Valley
Stretching across approximately 169,900 square kilometers, the lower Narmada River Valley and its adjoining uplands are characterized by extensive dry deciduous forests. This unique ecoregion forms a transitional zone bordered by moister forest regions to the northeast, southeast, and southwest areas that benefit from higher rainfall during the southeast monsoon. To the south, west, and northwest lie the arid landscapes of the Deccan Plateau, Malwa, and Gujarat, creating a diverse ecological interface.
The region's natural vegetation forms a distinct three-tiered forest system. Teak dominates the upper canopy, accompanied by a variety of species such as Diospyros melanoxylon, Anogeissus latifolia (Dhaora), Lagerstroemia parviflora, Terminalia tomentosa, Lannea coromandelica, Hardwickia binata, and Boswellia serrata. The Indian teak trees along this river are much older as compared to the ones in the Himalayan Mountain Range. Along the riverbanks and perennial streams, moisture-rich zones support patches of moist evergreen forests. These riparian areas are typically home to species like Terminalia arjuna, Syzygium cumini (Jambul), Syzygium heyneanum, Salix tetrasperma, Homonoia riparia, and Vitex negundo.
This rich landscape supports diverse wildlife, including 76 species of mammals and 276 species of birds, though none are endemic to the area. Approximately 30% of the region retains relatively undisturbed forest cover, primarily within the Vindhya and Satpura mountain ranges. However, only about 5% of the land is officially protected, through reserves such as Bandhavgarh, Panna, and Sanjay National Parks.
Forests and Sanctuaries along Narmada River are quite rich and expansive. Some of the best hardwood Indian forests are found along this river. Several significant protected areas within the valley highlight the region's ecological richness. Kanha National Park, located in the upper Narmada basin, is one of India's most renowned wildlife sanctuaries. The park is nourished by the Sulkum and Banjar rivers, two tributaries of the Narmada, and is known for its population of Bengal tigers alongside other notable species.
Further west lies Satpura National Park, established in 1981 in the Narmadapuram district of Madhya Pradesh. Named after the Satpura (Mahadeo) hill range, the park forms part of a larger conservation landscape, along with the adjacent Bori and Panchmarhi Sanctuaries. Together, they preserve a vital portion of the Central Indian Highlands ecosystem. Satpura’s terrain supports an impressive range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, Indian bison (gaur), sloth bears, wild dogs, nilgai, four-horned antelope, mouse deer, and Indian giant squirrels. Birds such as hornbills and peafowl are frequently spotted. The flora includes sal, teak, tendu, bamboo, aonla, mahua, bael, and various medicinal plants and grasses.
Biodiversity is not limited to protected zones, many unprotected forests in the region are equally rich in plant and animal life, showcasing the ecological importance of the broader landscape. Adding a unique geological dimension to the region is the Mandla Plant Fossils National Park, located in the Dindori district of Madhya Pradesh. The park covers seven villages—Ghuguwa, Umaria, Deorakhurd, Barbaspur, Chanti Hills, Chargaon, and Deori Kohani.
Anthropological Sites along Narmada River
Anthropological Sites along Narmada River are considered to be of great interest among the tourists as well as historians. The extensive caves of Bhimbhetka are located in a dyke structure of the Narmada Valley, at about 45 km northeast of Bhopal. These caves lie between Bhopal and Hoshangabad highway and depict pre-historic rock shelter paintings. These paintings are considered to be a priceless chronicle in the history of India, which have been sculpted on the summit of the Vindhyas.
Narmada River Basin
Nestled between the Vindhya and Satpura mountain ranges, the Narmada basin spans approximately 98,796 square kilometers, marking the northern edge of the Deccan Plateau. This expansive basin stretches across a major portion of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, while also touching smaller sections of Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh.
Agriculturally rich, around 60% of the basin is comprised of cultivable land. Forests account for roughly 35%, with the remaining 5% consisting of grasslands, wastelands, and other landforms. The Narmada River itself is fed by 41 tributaries, 22 of which flow in from the Satpura range on the left bank, while the remaining streams originate from the Vindhya range on the right bank. Notably, Dhupgarh, located near Pachmarhi, stands as the basin’s highest elevation at 1,350 meters above sea level.
The basin is divided into five distinct physiographic regions based on its terrain and topography. These include:
Together, these regions form a diverse and ecologically significant landscape, supporting both natural habitats and human livelihoods across central India.
Development of the Basin of Narmada River
Development of Narmada River was planned for keeping the banks and water of the river clean and usable. The early background of Narmada River and the dispute related to it have led to the emergence of many advanced plans for the development of the Narmada River basin. Explorations for using the Narmada waters began around the time of independence, when Central Waterways, Irrigation and Navigation Commission (CWINC) came up with several storage schemes.
Mythological Significance of River Narmada
 The Narmada is one of the most sacred of the five holy rivers of India; the other four sacred rivers of India are Ganga, Yamuna, Godavari and Kaveri. It is believed that a dip in any of these five rivers washes ones sins away. Ptolemy has mentioned the river in the 2nd century AD as Namade. The Ramayana, the Mahabharata and Puranas refer to it often. The Rewa Khand of Vayu Puran and the Rewa Khand of Skand Puran are completely devoted to the story of the birth and the significance of the River and hence Narmada is also called Rewa.
The Narmada is one of the most sacred of the five holy rivers of India; the other four sacred rivers of India are Ganga, Yamuna, Godavari and Kaveri. It is believed that a dip in any of these five rivers washes ones sins away. Ptolemy has mentioned the river in the 2nd century AD as Namade. The Ramayana, the Mahabharata and Puranas refer to it often. The Rewa Khand of Vayu Puran and the Rewa Khand of Skand Puran are completely devoted to the story of the birth and the significance of the River and hence Narmada is also called Rewa.
There are many fables about the source of the Narmada. According to a myth, once, Lord Shiva, meditated so hard that he started perspiring. Shiva`s sweat gathered in a tank and started flowing in the form of a river - the Narmada. Another legend has it that two teardrops that fell from the eyes of Lord Brahma, the Creator of the Universe, yielded two rivers - the Narmada and the Sone.
Legends also say that for Lord Shiva, the Hindu God, the river is particularly sacred on account of its origin, and it is often called Shankari or the daughter of Shankar. All the pebbles rolling on its bed are said to take the shape of his emblem with the saying - Narmada Ke Kanker utte Sankar that is a popular saying in the Hindi belt of India. This saying means that `pebble stones of Narmada gets a personified form of Shiva`. These lingam shaped stones are called Banalinga or Banashivalingas. These pebbles are much sought after for daily worship by the Hindus. The Brihadeeswara Temple in Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu is constructed by Rajaraja Chola and possesses one of the biggest Banalingas. Adi Shankara met his guru Govinda Bhagavatpada on the banks of river Narmada. Important places of pilgrimage along this river are Amarkantak, Omkareshwar, Maheshwar, Mahadeo temples, Nemawar Siddeshwar Mandir, Chausath Yogini, Chaubis Avatar Temple and others.
Navigation Along The River Narmada
 The river is presently partially navigable in the estuary reach around Bharuch. However, the river has never been a transportation artery. The idea for inland navigation came from NWDT thus giving its award for the two main dams, namely the Sardar Sarovar in Gujarat, built 180 km from the coast and the Narmada Sagar in Madhya Pradesh. These two dams are separated by a river with a distance of about 900 km, and the plans to build two other dams in between of the main stem of the river. A practical survey has been carried out for navigating the Narmada from the sea up to Hoshangabad - a distance of 639 km. Another survey was upto Jubbulpore a further distance of 309 km upstream. The main objective in these studies was to check the arrangements needed to be planned to discuss the Maheswar, Omkareswar, Indira Sagar and Sardar Sarovar projects. As such, the navigation choice is still open and probably can only be tracked after all the above dams are completed and other implications executed.
The river is presently partially navigable in the estuary reach around Bharuch. However, the river has never been a transportation artery. The idea for inland navigation came from NWDT thus giving its award for the two main dams, namely the Sardar Sarovar in Gujarat, built 180 km from the coast and the Narmada Sagar in Madhya Pradesh. These two dams are separated by a river with a distance of about 900 km, and the plans to build two other dams in between of the main stem of the river. A practical survey has been carried out for navigating the Narmada from the sea up to Hoshangabad - a distance of 639 km. Another survey was upto Jubbulpore a further distance of 309 km upstream. The main objective in these studies was to check the arrangements needed to be planned to discuss the Maheswar, Omkareswar, Indira Sagar and Sardar Sarovar projects. As such, the navigation choice is still open and probably can only be tracked after all the above dams are completed and other implications executed.



















