 Mountbatten Plan was a plan for the Partition of India into two dominions, India and Pakistan which was declared by Lord Mountbatten. Lord Mountbatten came to India with an aspiration to the partition of India and the speedy transfer of responsibility, initially in the form of Dominion Status, to Indian Governments for the sections of a divided India. Lord Mountbatten replaced Lord Wavell as Viceroy of India in 1947. He was the 34th and last of the British Governors-General of India.
Mountbatten Plan was a plan for the Partition of India into two dominions, India and Pakistan which was declared by Lord Mountbatten. Lord Mountbatten came to India with an aspiration to the partition of India and the speedy transfer of responsibility, initially in the form of Dominion Status, to Indian Governments for the sections of a divided India. Lord Mountbatten replaced Lord Wavell as Viceroy of India in 1947. He was the 34th and last of the British Governors-General of India.
Background of Mountbatten Plan
Lord Mountbatten wanted to bring about a truce between the two major communities, the Hindus and the Muslims. This peaceful settlement between the two communities was vital for a peaceful transfer of power. The two leaders Mahatma Gandhi and Mohammad Ali Jinnah both signed a joint appeal for peace to the Viceroy and pointed out the recent acts of lawlessness and violence that had brought the utmost disgrace on India.
 However, this appeal also failed to bring about any peace in the country. On the other hand, the His Majesty"s Government put forth the objective of obtaining a unitary Government for British India and the Indian States, if possible within the British Commonwealth. According to the British Government this aim was to be achieved by forming a Constituent Assembly that would be set up in accordance with the Cabinet Mission plan. Moreover, Lord Mountbatten was directed that the transfer of power from British in India must be in accordance with Indian defence requirements.
However, this appeal also failed to bring about any peace in the country. On the other hand, the His Majesty"s Government put forth the objective of obtaining a unitary Government for British India and the Indian States, if possible within the British Commonwealth. According to the British Government this aim was to be achieved by forming a Constituent Assembly that would be set up in accordance with the Cabinet Mission plan. Moreover, Lord Mountbatten was directed that the transfer of power from British in India must be in accordance with Indian defence requirements.
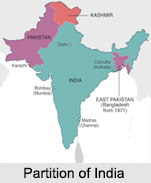 Thus, Lord Mountbatten was required to find an agreed solution for a united India on the basis of the Cabinet Mission plan. He held a meeting with the party leaders, particularly with Jinnah and his colleagues. However, the Viceroy was convinced that there was no prospect of an agreed solution. Thus, he decided for an alternative plan for the transfer of power and its implementation, in order to ease the growing political tension. This alternative plan by Lord Mountbatten provided that the members of the Legislative Assemblies of Bengal and the Punjab should meet separately in two parts, such as the representatives of the predominantly Muslim areas, and representatives of the predominantly non-Muslim areas. If both sections of each of these Assemblies voted for partition, then that province would be partitioned.
Thus, Lord Mountbatten was required to find an agreed solution for a united India on the basis of the Cabinet Mission plan. He held a meeting with the party leaders, particularly with Jinnah and his colleagues. However, the Viceroy was convinced that there was no prospect of an agreed solution. Thus, he decided for an alternative plan for the transfer of power and its implementation, in order to ease the growing political tension. This alternative plan by Lord Mountbatten provided that the members of the Legislative Assemblies of Bengal and the Punjab should meet separately in two parts, such as the representatives of the predominantly Muslim areas, and representatives of the predominantly non-Muslim areas. If both sections of each of these Assemblies voted for partition, then that province would be partitioned.
This was the first stage towards the transfer of power by Lord Mountbatten. The first proposed solution for the Indian subcontinent; known as the `May Plan` by Lord Mountbatten was rejected by Congress leader Jawaharlal Nehru. The May plan was postponed till June and another plan was formulated which came to be known as "June 3rd Plan" or "Mountbatten Plan".
Mountbatten Plan
On June 3, 1947, Lord Mountbatten put forward his plan which outlined the steps for the solution of India"s political problem. The outlines of the plan discussed below:
India to be divided into India and Pakistan.
Bengal and Punjab will be partitioned and a referendum in NEFP (North-East Frontier Province) and Sylhet district of Assam would be held.
There would be a separate constituent assembly for Pakistan to frame its constitution.
The Princely states would enjoy the liberty to join either India or Pakistan or ever remain independent.
August 15, 1947, was date fixed for handling over power to India and Pakistan.
The British Government passed the Indian Independence Act of 1947 in July 1947, which contained the major provisions put forward by the Mountbatten plan.
Salient Features of Mountbatten Plan
The Mountbatten Plan, with the following salient features, was sent for agreement of the three parties:
That the leaders agree to the procedure laid down for ascertaining the wishes of the people whether there should be a division of India or not;
That in the event of the decision being taken that there should only be one central authority in India; power should be transferred to the existing Constituent Assembly on a Dominion Status basis;
That in the event of a decision there should be two sovereign States in India, the central Government of each State should take over power in responsibility to their respective Constituent Assemblies, again on a Dominion Status basis;
That the transfer of power in either case should be on the basis of the Government of India Act of 1935, modified to conform to the Dominion Status position;
That the Governor-General should be common to both the Dominions and that the present Governor-General should be reappointed;
That a Commission should be appointed for the demarcation of boundaries in the event of a decision in favour of partition;
That the Governors of the provinces should be appointed on the recommendation of the respective central Governments;
In the event of two Dominions coming into being, the Armed Forces in India should be divided between them.
Thus, the actual division between the two new dominions took place according to the "3 June Plan" or "Mountbatten Plan". The border between India and Pakistan was determined by a British Government-commissioned report which was referred to as the "Radcliffe Line" after the London lawyer, Sir Cyril Radcliffe. Bangladesh (East Pakistan) and West Pakistan was geographically divided by India.






































