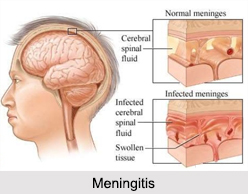
 Meningitis is a severe inflammation of the Meninges. This results from incursion of bacteria or virus into the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, which are collectively known as the "Meninges". The infection usually spreads from the base of the brain up over the surface and down the spinal cord. It appears to reach the inside from the throat and nose via the blood stream. It is one of the most serious of all the acute diseases. Epidemic meningitis sometimes occurs in densely populated areas during the cold season. It is also known as "Spotted Fever", as spots appear upon the face and body.
Meningitis is a severe inflammation of the Meninges. This results from incursion of bacteria or virus into the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, which are collectively known as the "Meninges". The infection usually spreads from the base of the brain up over the surface and down the spinal cord. It appears to reach the inside from the throat and nose via the blood stream. It is one of the most serious of all the acute diseases. Epidemic meningitis sometimes occurs in densely populated areas during the cold season. It is also known as "Spotted Fever", as spots appear upon the face and body.
Causes of Meningitis
Meningitis can be caused for several reasons. Meningitis usually follows an attack of Otitis Media (middle ear disease), or Mastoiditis (infection of bone projecting behind the ear), or brain abscesses or even tonsillitis. Any skull fracture or penetrating head wound may also result in meningitis. Sometimes tuberculosis may also spread to the brain and cause the disease. In case of epidemic meningitis, persons who have a mild sore throat or cold apparently spread the germs. Meningitis can be diagnosed by blood tests and imaging as well as lumbar puncture.
Symptoms of Meningitis
Symptoms of Meningitis start with an infection in most persons which develop from throat, nose, ear or lungs. But if they are subject to damp, cold and overcrowding, the organism is liable to pass into the blood stream. The incubation period is short, ranging between one and five days, and the onset is sudden. Persons with this disease usually have a high fever and stiffness in the neck and back. He becomes drowsy, confused and may become unconscious. There may also be a skin rash and an obstinate constipation. Vomiting is common in epidemic meningitis.
Types of Meningitis
Bacterial and viral are the two most common forms of meningitis. Viral and bacterial meningitis are contagious. They can be transmitted by coughing, sneezing, or close contact. There are actually 5 different types of meningitis:
•Bacterial
•Fungal
•Non-infectious
•Viral
•Parasitic
Treatment of Meningitis
Besides, conservative method, meningitis can be treated through alternative methods. Nature cure includes diet therapy. Diet plays an important role in treating meningitis. The emphasis should be on whole grain cereals, fresh fruits and raw or lightly cooked vegetables. Normal diet should be resorted to only after complete recovery. Water treatments have also proved to be beneficial as a remedy for meningitis. Cold compresses may be applied to the head in case the temperature rises above 103 Fahrenheit. Other alternative treatment includes home remedies such as warm water enema which is administered for a daily use that cleanse the bowels during the period when patients suffer from meningitis.




