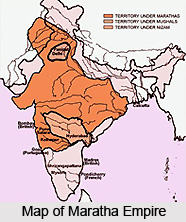
 Maratha Empire was also known as `Maratha Confederacy` and was amongst the renowned royal dynasties of India which remained under administrative control from 1674 till 1818. Their empire was spread over 208 square million kilometers and is believed to have catapulted the decline of the Mughal Dynasty in the nation. Maratha Empire rose to imperial supremacy during the regime of the Great king Chhatrapati Shivaji Bhonsle who made Raigad his royal capital after defeating the Mughals and Bijapur Sultanate. There existed several Maratha rulers and Peshwas who conquered vast stretches of territories, especially following the death of the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb. It extended from Peshawar (current-day Pakistan) in the north till Tamil Nadu towards extreme south, and till Andaman Islands and Bengal in the eastern India.
Maratha Empire was also known as `Maratha Confederacy` and was amongst the renowned royal dynasties of India which remained under administrative control from 1674 till 1818. Their empire was spread over 208 square million kilometers and is believed to have catapulted the decline of the Mughal Dynasty in the nation. Maratha Empire rose to imperial supremacy during the regime of the Great king Chhatrapati Shivaji Bhonsle who made Raigad his royal capital after defeating the Mughals and Bijapur Sultanate. There existed several Maratha rulers and Peshwas who conquered vast stretches of territories, especially following the death of the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb. It extended from Peshawar (current-day Pakistan) in the north till Tamil Nadu towards extreme south, and till Andaman Islands and Bengal in the eastern India.
After the defeat of the Marathas to the Afghans at the Third Battle of Panipat, Madhavrao Peshwa reinstalled Maratha governance over northern India. The influential Maratha rulers were recognised as the Bhonsles of Nagpur, Scindias of Gwalior, Gaekwads of Baroda, Holkars of Malwa and Indore. The Anglo-Maratha battles which were fought against the British East India Company eventually led to the decline of the Maratha power after 1775.
History of Maratha Empire
Shivaji Bhonsle was capable of establishing himself as the leader of the Hindu Maratha kingdom after he became victorious against Aurangzeb and the Adil Shahi Dynasty of Bijapur during 1674. He made Raigad his capital and died during 1680. Though the Maratha Empire again was compelled to defend their kingdom against the repeated onslaughts of the Mughals from 1681 till 1707, the Marathas were successful in safeguarding their territories.
 Shivaji`s grandson Shahu was the king till 1749 followed by the very first Peshwa who was appointed as the head of government. From 1749 to 1761, following the demise of Shahu, the Peshwas continued to rule the kingdom with their base in Satara. However, the Peshwas lost against the Afghans at the Third Battle of Panipat, 1761 and therefore gradually started losing their administrative control of their state.
Shivaji`s grandson Shahu was the king till 1749 followed by the very first Peshwa who was appointed as the head of government. From 1749 to 1761, following the demise of Shahu, the Peshwas continued to rule the kingdom with their base in Satara. However, the Peshwas lost against the Afghans at the Third Battle of Panipat, 1761 and therefore gradually started losing their administrative control of their state.
Meanwhile the military chiefs like Pandit of Bhor, Pant Pratinidhi, Holkar, Shinde Patwardhan and Bhosale made attempts to rebel against the Peshwas and establish their own independent rule. Madhavrao Peshwa was a skilful ruler under whose rule Maratha authority was reinstated but after his death it became a faulty Confederacy as Maratha power was classified under Bhonsles, Holkars, Peshwas of Pune and Gaekwads. Frequent enmity with the Holkars and Scindias and also the conflicts with the British East India Company during the three Anglo-Maratha battles further weakened the Maratha Empire in the 19th century. The British defeated Peshwa Baji Rao II during the Third Anglo-Maratha War in 1818 and gradually majority of the erstwhile Maratha territories were captured by British Raj. Some Maratha states remained as bondsmen of the British till Indian Independence.
 Rulers of Maratha Empire
Rulers of Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire has been a silent spectator of the reign of various powerful rulers. The rulers of Maratha Empire have been discussed in brief below:
Shivaji: The founder of Maratha Empire, Shivaji, belonged to the Bhonsle clan. His brave efforts enabled the restoration of `Hindavi Swarajya` or independent rule of the Hindus, after he won against the Mughals. His subjects crowned him as `Chhatrapati` or `sovereign` of Maratha kingdom during 1674.
Sambhaji: Sambhaji was the elder son of Shivaji who was credited for defeating Chikka Deva Raja of Mysore and the Portuguese. This ruler safeguarded the Maratha Empire against Aurangzeb who had attacked the kingdom equipped with 5,00,000 soldiers in 1681. Aurangzeb aimed to conquer the Sultanates of Golconda, Bijapur besides crushing the Marathas. Till 1689, Sambhaji prevented Aurangzeb in his ambitious efforts but was attacked by Mughal troops in an ambush while he was engaged in a meeting.
Rajaram: Rajaram, the half-brother of Sambhaji ascended the throne soon after the death of Sambhaji. He had confronted the Mughal forces when they laid siege to Raigad, the nerve-centre of Maratha Empire. He had retreated to Vishalgad and next to Gingee to assault the Mughal territories and restore several forts from them. Rajaram died at Sinhagad during 1700.
 Tarabai: Tarabai, the widow of Rajaram crowned herself the next ruler of Maratha Empire in the name of Ramaraja who was her son. Tarabai was appreciated particularly for the bravery exhibited by her at the battle of Marathas against Mughals. The Maratha troops were motivated by her courage and they made a grand entry in Malwa after crossing Narmada River. The Mughals were robbed of their imperial power in the subcontinent after this battle, which was a strong foundation of the Peshwas as the main Maratha power.
Tarabai: Tarabai, the widow of Rajaram crowned herself the next ruler of Maratha Empire in the name of Ramaraja who was her son. Tarabai was appreciated particularly for the bravery exhibited by her at the battle of Marathas against Mughals. The Maratha troops were motivated by her courage and they made a grand entry in Malwa after crossing Narmada River. The Mughals were robbed of their imperial power in the subcontinent after this battle, which was a strong foundation of the Peshwas as the main Maratha power.
Shahuji: Bahadur Shah I had released Shahuji, Sambhaji`s son during 1707 after Aurangzeb`s death but was made a complete dependent of the Mughals. His mother was held as hostage in the Mughal court to make Shahuji follow the conditions of his release. Following his release Shahuji revolted against the rule of his aunt Tarabai and her son. He became the new ruler of Maratha Empire. This instigated the formation of Kolhapur and Satara during 1707.
Peshwa Baji Rao I: Baji Rao I or Baji Rao Vishwanath (Bhat) Deshmukh was confirmed as the Peshwa in April 1720 after the death of Balaji Vishwanath by Chhatrapati Shahu and worked as an impressive general for Shahuji. He had fought fearlessly in more than 41 battles with victory in all of them. On 28th February, 1728 he fought against Nizam-ul-Mulk of Hyderabad near Palkhed village of Nashik, Maharashtra and defeated the Nizam. Baji Rao I is also greatly admired for his warfare techniques in the Battle of Vasai, against the Portuguese rulers. The Maratha troops were led by the brother of Baji Rao I, named Chimaji Appa.
Balaji Baji Rao or Nanasaheb: He was the son of Baji Rao, who was proclaimed Peshwa by Shahuji. During 1740, under his leadership the Marathas captured Arcot and defeated Dost Ali, the Nawab of Arcot. His brother, Raghunath Rao played an important role in defeating the Afghan troops in August, 1757 in the Battle of Delhi.
 Mahadaji Shinde: The central parts of India were controlled by Mahadaji Shinde, the king of Gwalior State who played a significant role in re-establishing Maratha Empire following the Third Battle of Panipat during 1761. The landlords of Bundelkhand, Rajput kingdoms of Rajasthan and Malwa `sardars` refused to pay taxes to Mahadaji Shinde which resulted in conquests of the kingdoms of Gohad, Datiya, Salbai, Chanderi, Narwar and Bhopal. Mahadaji laid siege to the Gwalior Fort in 1783 and transferred the rule of Gwalior to Khanderao Hari Bhalerao. Shah Alam II was placed at the Mughal throne by Mahadaji Shinde, as a puppet king.
Mahadaji Shinde: The central parts of India were controlled by Mahadaji Shinde, the king of Gwalior State who played a significant role in re-establishing Maratha Empire following the Third Battle of Panipat during 1761. The landlords of Bundelkhand, Rajput kingdoms of Rajasthan and Malwa `sardars` refused to pay taxes to Mahadaji Shinde which resulted in conquests of the kingdoms of Gohad, Datiya, Salbai, Chanderi, Narwar and Bhopal. Mahadaji laid siege to the Gwalior Fort in 1783 and transferred the rule of Gwalior to Khanderao Hari Bhalerao. Shah Alam II was placed at the Mughal throne by Mahadaji Shinde, as a puppet king.
Maharaja Yashwantrao Holkar: Yashwantrao Holkar was made the official authority of the Government of Maratha following the Battle of Poona and he proceeded towards Indore after appointing Amrutrao as his Peshwa on 13th March, 1803. He entered into a treaty with the British Raj during 1805. Yashwantrao was capable of solving the arguments with Madhavrao Peshwa and Scindia. It is believed that he is amongst the most well-known rulers in the military history of the country.
Anglo-Maratha Wars
The British East India Company had interfered in a succession issue in Pune during 1775, representing Raghunathrao which sowed the seeds of the First Anglo-Maratha War. It concluded during 1782. The British lost against Mahadaji Shinde and Tukojirao Holkar in the battle of Vadgaon. The British again intervened during the year 1802 when they signed a treaty with the new king, promising them freedom from the Maratha Empire in return for his surrender to the British Raj in India. The event took place in Baroda.
Peshwa Baji Rao II signed a similar treaty with the British in the Second Anglo-Maratha War (1803 to 1805). Yashwantrao Holkar revolted against the rules of Peshwa Baji Rao II and he proceeded to Pune in May 1802. Consequently the Battle of Poona followed in which Madhavrao Peshwa was defeated. Though Yashwantrao tried his level best to unite the Maratha Empire, he failed. Finally the Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817 to 1818) occurred which threw open the majority of Indian territories to the British powers in India.
Decline of Maratha Empire
Madhavrao Peshwas was made a pensioner of the British and exiled to Bithoor, Uttar Pradesh. The Maratha kingdoms of Nagpur, Indore and Gwalior all slipped into the administrative powers of the British. They all became princely states and all the Maratha powers had no other chance to succeed so they surrendered to the British. This gave rise to the Treaty of Gwalior (5th November, 1817). The Treaty of Mandeswar was signed by Holkar on 6th January, 1818 and it required the Holkar state to remain as subsidiary to the British. The British East India Company seized the Nassak Diamond as part of the war spoils, apart from large quantities of land which were governed by the Maratha Empire. This led to the decline of the Maratha Empire.



















