 Malaria or intermittent fever is a mosquito-borne serious infectious disease caused by protozoa Plasmodium. The word malaria comes from the Italian "mala aria", meaning bad air as it was once supposed to be caused by bad air. It is one of the most widespread diseases in the world, especially in tropical and subtropical regions and people living in marshy areas are more prone to this disorder.
Malaria or intermittent fever is a mosquito-borne serious infectious disease caused by protozoa Plasmodium. The word malaria comes from the Italian "mala aria", meaning bad air as it was once supposed to be caused by bad air. It is one of the most widespread diseases in the world, especially in tropical and subtropical regions and people living in marshy areas are more prone to this disorder.
Symptoms of Malaria:
There are three main types of malaria and it is caused depending upon types of parasites, causing it, viz vivax, falciparum and malariae, commonly called tertian fever, quarten fever and the malignant tertian malaria. The most common symptom of all types of malaria is high fever, which may come every day, on alternate days or every fourth day. The malarial attacks may or may not have all the characteristic stages of rigour, high fever and profuse sweating, but the temperature goes as high as 41.5C. Violent chills, headache, vomiting, extreme thirst, shivering and pain in the limbs accompany the fever.
The most likely effects of the disease are the enlargement of liver and spleen and anaemia as the parasite mainly attacks the red blood cells. The temperature comes down after some time with profuse sweating. Other complications of the disease are kidney failure and dysentery. The diagnosis of the disease can be well confirmed by a thick blood smear. This blood testing shows various stages of the parasite.
Causes of Malaria:
Plasmodium, a tiny parasite causes Malaria. The parasites grow in the liver of a person for a few days and then enter the bloodstream where they invade the red blood cells. The disease is spread from a sick person to a healthy one by the female anopheles mosquito. She draws a small quantity of blood containing the parasites, when she bites a person who has malaria. These parasites then pass through several stages of development within the mosquito`s body and finally find their way to its salivary glands. There they lie in wait for an opportunity to enter the bloodstream of the next person the mosquito bites.
As in case of other infectious diseases, the reason for malaria is wrong feeding habits and faulty style of living, resulting in the system being clogged with accumulated systemic refuse and morbid matter. It is on this soil that the malaria germs breed. The liberal use of denatured foods of today such as white sugar, white flour and products made from them, as well as tinned foods, strong tea, coffee and alcoholic beverages, lower the vitality of the system and paves the way for the development of malaria.
Treatment of Malaria by Nature Cure:
Diet:
The patient should fast on orange juice and water for 7 to 15 days depending on the severity of the fever. The warm-water enema should be administered daily during this period to cleanse the bowels. After the fever has subsided, the patient should be placed on an exclusive fresh fruit diet for further three days. In this regimen, he should take three meals a day, at five-hourly intervals, of fresh, juicy fruits like oranges, grapes, grape-fruit, apple, pineapple, mango and papaya. Milk may be added to the fruit-diet after this period and this diet may be continued for a further few days.
Thereafter, the patient may gradually embark upon a well-balanced diet of natural foods consisting of seeds, nuts and grains, vegetables and fruits, with emphasis on fresh fruits and raw vegetables. The patient should avoid strong tea, coffee, refined and processed foods, fried foods, condiments, sauces, pickles, white sugar, white flour, and all products made from them. He should also avoid all meats, alcoholic drinks and smoking.
Water Treatments:
The best way to reduce temperature naturally, during the course of the fever, is by means of cold pack, which can be applied to the whole body. This pack is made by wringing out a sheet or other large square piece of linen material in cold water, wrapping it tight around the body and legs of the patient, (twice round would be best) and then covering completely with a small blanket or similar warm material. This pack should be applied every three hours during the day while temperature is high and kept on for an hour or so. Hot-water bottles may be applied to the feet and also against the sides of the body.
Home Remedies
Certain home remedies have been found beneficial in the treatment of malaria. A substance can be extracted from the grape fruits by boiling a quarter of the grapefruit and straining its pulp. Lime and lemon are beneficial in the treatment of quartan type of malarial fever. About three grams of lime should be dissolved in about 60 ml. of water and juice of one lemon added to it. This water should be taken before the onset of the fever.
Cinnamon is regarded as an effective cure for all types of colds, including malaria. It should be coarsely powdered and boiled in a glass of water with a pinch of pepper powder and honey. This can be used beneficially as a medicine in malaria. Alum is also useful in malaria. It should be roasted over a hot plate and powdered. It should be taken about four hours before the expected attack and every two hours after it. This will give relief.
Treatment of Malaria by Magnetic Therapy:
During the temperature fluctuations, i.e. cold and hot stages, the magnets should be applied to the palms of hands for 15 minutes and continued at least once during the intervening period between two attacks. Mixed magnetized water should be taken every two hours during the attack and every four hours during the feverless period.
Preventive Measures for Malaria:
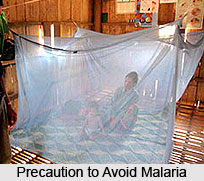
The preventive aspect in malaria is as important as the curative one. The best way to protect against malaria is to adopt all measures necessary for preventing mosquito bites. For this purpose, it is essential to maintain cleanliness of surroundings, environmental hygiene and to eradicate stretches of stagnant water with kerosene oil emulsion and use of mosquito nets in mosquito-infested areas. As the mosquito generally perches itself on the walls of the house, after biting a person, it would be advisable to spray the walls with insecticides.
The leaves of the holy basil (tulsi) are considered beneficial in the prevention of malaria. An infusion of some leaves can be taken daily for this purpose. The juice of about 11 grams of tulsi leaves mixed with three grams of black pepper, powder, can be taken beneficially in the cold stage of the malarial fever. This will check the severity of the disease.




