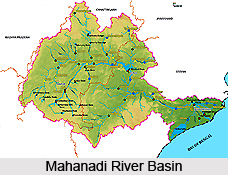
 Mahanadi River Basin extends over an area of 141589 sq km which is nearly 4.3 % of total geographical area of the country. The basin lies in the states of Chhattisgarh, Orissa, Bihar and Maharashtra. Mahanadi River rises from Raipur district of Chhattisgarh and flows for about 851 km before its outfall into the Bay of Bengal. Its main tributaries are Seonath, Jonk, Hasdeo, Mand, Ib, Ong, and Tel. Physiographically the basin can be divided into four regions namely the Northern Plateau, the Eastern Ghats, the Coastal Plain and the Erosional Plains. The first two are hilly regions. The coastal plain is the central interior region of the basin traversed by the river and its tributaries.
Mahanadi River Basin extends over an area of 141589 sq km which is nearly 4.3 % of total geographical area of the country. The basin lies in the states of Chhattisgarh, Orissa, Bihar and Maharashtra. Mahanadi River rises from Raipur district of Chhattisgarh and flows for about 851 km before its outfall into the Bay of Bengal. Its main tributaries are Seonath, Jonk, Hasdeo, Mand, Ib, Ong, and Tel. Physiographically the basin can be divided into four regions namely the Northern Plateau, the Eastern Ghats, the Coastal Plain and the Erosional Plains. The first two are hilly regions. The coastal plain is the central interior region of the basin traversed by the river and its tributaries.
The Mahanadi River marks the southern boundary of the Chhattisgarh district clearly. River Brahmani enters the district through Rengali reservoir passes through Talcher sub- division. Both these great rivers have too many tributaries, both large and small. Pallahara and Talcher Sub-Divisions and a major portion of Angul Sub-division form a part of Brahmani basin, which is also a part of Mahanadi River Basin. The Basin of Mahanadi River is spread over Athamallik Sub-division and some regions of Angul Sub-division.
There are some significant rivers in the Mahanadi River Basin some of them are as follows -
The Mahanadi River rises in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and then flows in the eastward direction, cutting a ravine in the Eastern Ghat. Before joining the Bay of Bengal at False Point through several channels, the river enters the plains of Orissa near Cuttack and forms a delta.
The Brahmani River originates in the vicinity of the Nagri village in the Dhenkanal district of Orissa at the confluence of the Sankh and the South Koel Rivers at an elevation of about 600 m. The river, with a total length of 480 km, winds around the south and southeast past Bonaigarh and Talcher and then turns towards the east to unite with the northern branches of the Mahanadi River.
Sankha River has its origin at the Chotanagpur region of Jharkhand and joins with the Koel River at Panposh near Rourkela of Sundargarh District. River Brahmani enters into Angul District through the Rengali Reservoir.
Drainage Density of Mahanadi River Basin
The river flows for 560 miles (900 km) and the drainage area of the river is estimated to be 51,000 square miles (132,100 sq km). The drainage density of the Mahanadi River Basin upto Manibhadra dam site works out to be 0.022, which is within the range of low drainage density value. It depicts that the basin has a high resistance with permeable soil under dense vegetative cover and low relief.















