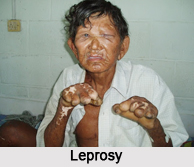
 Leprosy is an infectious disease that causes severe, disfiguring skin sores and nerve damage in the arms and legs. Leprosy primarily affects the skin and the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, called the peripheral nerves. It may also strike the eyes and the thin tissue lining the inside of the nose.
Leprosy is an infectious disease that causes severe, disfiguring skin sores and nerve damage in the arms and legs. Leprosy primarily affects the skin and the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, called the peripheral nerves. It may also strike the eyes and the thin tissue lining the inside of the nose.
The disease is mainly prevalent in Africa, the Indian sub-continent, the Far East, and Central and South America. Anyone can get leprosy, but children seem to be more susceptible than adults.
Cause of Leprosy
Leprosy is caused by a slow-growing type of bacteria called Mycobacterium Leprae. Leprosy is also known as "Hansen"s Disease", after the scientist who discovered M. Leprae in 1873.
Symptoms of Leprosy
When a person becomes infected with the bacteria that cause leprosy, the bacteria begin to multiply within the body. The main symptom of leprosy is disfiguring skin sores, lumps, or bumps that do not go away after several weeks or months. The skin sores are pale-colored. Nerve damage can lead to loss of feeling in the arms and legs and muscle weakness. The eyes may be affected, leading to total blindness. Ulcers may also occur in the mouth and the larynx. There are tragic cases of deformity when the fingers fall off at the joints, leaving only the palms over which the entire skin starts rotting.
After 3 to 5 years, symptoms of leprosy will usually begin. This period between becoming infected and the start of symptoms is the "Leprosy Incubation Period". Although the incubation period is typically between 3 to 5 years, it can range from 6 months to several decades. Once a person starts experiencing symptoms, they can range in type and severity. Symptoms can also vary based on the form of leprosy that a person has.
Types of Leprosy
 There are 2 distinct types of leprosy. These can be named as "Tuberculoid" and "Lepromatous". The differentiation is important since the former runs a relatively benign course and is often self-healing, whereas the latter is a steadily progressive form of the disease. The distinction cannot be always made because mixed symptoms are also found in many cases.
There are 2 distinct types of leprosy. These can be named as "Tuberculoid" and "Lepromatous". The differentiation is important since the former runs a relatively benign course and is often self-healing, whereas the latter is a steadily progressive form of the disease. The distinction cannot be always made because mixed symptoms are also found in many cases.
Ayurvedic Concept of Leprosy
According to Ayurveda, aggravation of all the 3 doshas of the body is the causative factor in Leprosy. The two main divisions of Leprosy or Kushta Roga can be named as "Mahakushta", which is of 7 types, and "Kshudra Kushta", which is of 11 types.
In the latter category are included leprous afflictions, which are confined only to the skin. Eczema, ecthyosis - where the skin resembles the scales of a fish, xerodermia pigmentosa - where the skin is dry and resembles the skin of an elephant, Psoriasis - in which the skin turns black and coarse, Rhagades - splitting of the skin on the hands and feet, Lichen - acute itch and boils, ringworm, Excoriation - destruction of small areas of the surface of the skin or mucous membrane, scabies, bullae, Erythemas - these are all the various forms of leprosy according to Ayurveda.
Prevention of Leprosy
The best way to prevent the spread of leprosy is the early diagnosis and treatment of people who are infected. For household contacts, immediate and annual examinations are recommended for at least 5 years after last contact with a person who is infectious. A doctor who is experienced in the field should treat patients with leprosy. Treatment for the disease is usually done with multiple drugs for 6 months to 2 years.