The name `lanka` means `island`. In the Hindu mythology, it is found that Lanka is the name given to the island bastion capital of the King Ravana in the Hindu epics Ramayana and Mahabharata. As per Ramayana, the fortress was situated in a plateau between three mountain peaks known as the Trikuta Mountains.
The name `lanka` means `island`. In the Hindu mythology, it is found that Lanka is the name given to the island bastion capital of the King Ravana in the Hindu epics Ramayana and Mahabharata. As per Ramayana, the fortress was situated in a plateau between three mountain peaks known as the Trikuta Mountains.
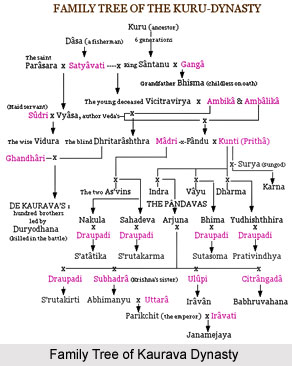
After Rama killed Ravana, Ravana`s brother Vibhisana ruled the kingdom of Lanka. His descendants ruled Lanka even during the time of the Pandavas.
As it is found in Ramayana, a Rakshasha, Sumali, ruled Lanka. Visarvana (kubera), who was a Yaksha, later took it and then from him, Rakshasa Ravana took the kingship of Lanka.
Moreover, it appears in Ramayana that Ravana ruled Lanka as the king of the Rakshasas and was a powerful king. When Surpankha, the sister of Ravana went to assault Sita, the wife of Rama, Laxmana, the brother of Rama cut off her nose. To take the proper revenge, Ravana carried off Sita to his kingdom. Then Rama, along with the monkey king Sugriva and his monkey army marched to liberate Sita. After great fighting, the monkey host prevailed and Sita was liberated from Ravana`s captivity. Rama slew Ravana in the battle.
In Mahabharata also, the reference to Lanka has been found in Book III (Varna Parva) of Section 271. Here sage Markandeya is found to narrate the story of Rama and Sita to king Yudhishthira.