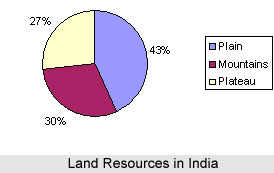
 Land Resources in India enclose approximately 1.3 million sq miles and is a cape, protruding into the Indian Ocean, in between the Bay of Bengal on the east and Arabian Sea on the west. Indian land resources are segmented into varied relief features, 43% of land area is plain region; Indian mountain region constitutes 30% of the area, where as plateaus account for 27 % of the total surface area on the nation.
Land Resources in India enclose approximately 1.3 million sq miles and is a cape, protruding into the Indian Ocean, in between the Bay of Bengal on the east and Arabian Sea on the west. Indian land resources are segmented into varied relief features, 43% of land area is plain region; Indian mountain region constitutes 30% of the area, where as plateaus account for 27 % of the total surface area on the nation.
In spite of sufficient accessibility of landed topography, population pressure in the country is excessive and that makes space for both food production and the real estate market. However, land resources in India are both essential and at shortage in present days.
Land resources in India are considered as non-renewable energy reserve. Further, they are associated with a host of several other elements such as agrarian base of rural as well as urban economy, accessibility of water, and other factors. Speedy urban expansion and the rising land usages have changed because of the increasing population growth and economic development in some selected landscapes is being observed in India. The monitoring of land use changes is essential to understand land use over different sequential or spatial time scales for successful land management.
Today, with increasing urbanisation as well as industrialisation, an increased pressure has been witnessed on land, water and other environment resources, mainly in big metropolitan cities.
In order to utilise available land resources in India effectively, the country is re-organising efforts in the areas of land resource management. Thus, there has been a growth in land resource companies as well as in other service providers across the country. India occupies a land area of around 3,287,263 sq km.
There are different types of land in India, of which 54.7 % of it is civilised land. The several types of land resources in India include agricultural land, farmland, barren land, real estate land, commercial land and residential land. Majority of the population of India are engaged in agricultural and allied activities and thus agricultural land accounts for near about 56.78 % of the total land area of the country. In India, the total cultivable area is 1,269,219 sq km. Moreover, land is also used in India for grazing and as permanent pastures.
Land resources in India also include vast barren lands. They are mostly found in states like Rajasthan, parts of Leh and Jammu as snowfall prevents any major cultivation here. Real Estate lands are growing at an incredible rate in India. With the people becoming mobile due to transferable jobs the growth of houses and apartments has increased hugely all over India. Havelis in Rajasthan Commercial land is becoming more expensive with passing years. There is a strong competition in acquiring the best of farmlands, as they can be nestled in the lap of picturesque valleys replete with streams, private piece of beach in Goa, Puducherry or private havelis in Rajasthan.
The trend of love for nature and due to less available space in city apartments, farm land is fast becoming the best option for land resources in India. Thus, land resources in India are crucial factors dealt by the Indian government and managed effectively according to the requirements. In order to make appropriate utilisation of obtainable land resources, the nation is making efforts to manage land resources effectively. Thus, there has been an increase in the number of land resource companies and service providers.















