 Jyotisa is the science of tracking and predicting the movements of astronomical bodies in order to keep time. Sometimes it is known as "Vedic Astrology". It refers to one of the 6 ancient Vedangas, or ancillary science connected with the Vedas - the scriptures of Hinduism. This field of study was concerned with fixing the days and hours of Vedic rituals. Through careful analysis of the cosmic influences, Jyotisa can help one to realistically evaluate the strengths and challenges in order to optimize full potential. It offers practical remedial measures to alleviate areas of difficulty, giving one the confidence to manifest the true destiny and create success, happiness and harmony on all levels.
Jyotisa is the science of tracking and predicting the movements of astronomical bodies in order to keep time. Sometimes it is known as "Vedic Astrology". It refers to one of the 6 ancient Vedangas, or ancillary science connected with the Vedas - the scriptures of Hinduism. This field of study was concerned with fixing the days and hours of Vedic rituals. Through careful analysis of the cosmic influences, Jyotisa can help one to realistically evaluate the strengths and challenges in order to optimize full potential. It offers practical remedial measures to alleviate areas of difficulty, giving one the confidence to manifest the true destiny and create success, happiness and harmony on all levels.
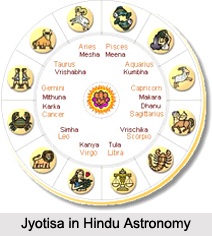
Etymology of Jyotisa in Hindu Astronomy
In Sanskrit, the word "Jyotisa" is translated as "Science of Light" which refers to the profound and mathematically sophisticated form of astrology originating in the ancient Vedic traditions of India. The term Jyotisa includes the study of astronomy, astrology and the science of timekeeping using the movements of astronomical bodies. It aimed to keep time, maintain calendar and predict auspicious times for Vedic rituals.
Difference between Jyotisa and Astrology
Jyotisa is distinctly different from Astrology. In Jyotisa, the sidereal zodiac is used which is based on the fixed, observable positions of the constellations as seen in the sky. Astrology, in contrast, uses what is called the tropical zodiac. The tropical zodiac is based, not on the fixed, observable positions of the constellations but rather on the relative and changeable position of the sun.
In Jyotish, people are not thought in terms of their sun sign, as done in tropical astrology. Instead, there is a chart through what is called the "ascendant", the constellation that is rising on the Eastern horizon at the time of a person"s birth. This sets up the relationship between the planets at the time of birth to the event of the birth and gives clues about an individual"s personality, physical body and the way the person presents themselves to the world. A person is first thought in terms of the ascendant.
This article is a stub. You can enrich by adding more information to it. Send your Write Up to content@indianetzone.com















