 India is one of the richest sources of iron ore deposits in the world. Iron ore, which is also known as hematite, occurs in abundance in the country. Iron ore reserves account for almost two-third of the entire iron ore reserves in India. Interestingly, India holds a leading position in the list of leading iron ore reserve countries. Moreover, the iron ore reserves are easily accessible and also high grade. They are also good for smelting as they are free from impurities like phosphorous and sulphur. Iron ore is vastly distributed throughout the country but its huge deposits are concentrated only in a few selected districts.
India is one of the richest sources of iron ore deposits in the world. Iron ore, which is also known as hematite, occurs in abundance in the country. Iron ore reserves account for almost two-third of the entire iron ore reserves in India. Interestingly, India holds a leading position in the list of leading iron ore reserve countries. Moreover, the iron ore reserves are easily accessible and also high grade. They are also good for smelting as they are free from impurities like phosphorous and sulphur. Iron ore is vastly distributed throughout the country but its huge deposits are concentrated only in a few selected districts.
Of the total iron ore reserves in the country, Chikkamagaluru in Karnataka, Singhbhum in Jharkhand, Sundargarh and Kendujhar in Orissa, Bellary District, Shimoga and Goa accounts for a major portion. Further, in Bihar and Orissa, huge deposits of iron grade iron ore occur as huge masses that rise above the adjoining plains. Some of them are located within a close proximity to the coal fields. Iron ore generally occur near top of the hills and thus aerial roadways are used by the iron ore companies to bring down the ore and for pumping it directly into the railway carriages. Singhbhum district in Bihar and the neighbouring districts of Mayurbhanj, Sundargarh and Keonjhar constitute the richest high grade iron reserves.
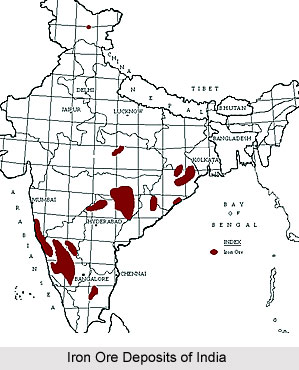 In India, the chief mining centres are Sulaipat and Badampur in Mayurbhanj District in Orissa and Gua and Noamundi in Singhbhum district in Jharkhand. The iron ore from these mines is supplied to the iron and steel works located at Jamshedpur, Durgapur, Asansol and Raurkela. The Rajhara and Dhali Hills located south of Bhilai Steel Works are other major sources of iron ore with huge iron content. These hills provide iron ore to the Bhilai Steel Works. Moreover, apart from these places, there is a large high-grade iron ore deposit at Kemmangundi in the Bababudan Hills of Chikmagalur district in Karnataka. This deposit is used for supplying iron ore to steel plant located at Bhadravati.
In India, the chief mining centres are Sulaipat and Badampur in Mayurbhanj District in Orissa and Gua and Noamundi in Singhbhum district in Jharkhand. The iron ore from these mines is supplied to the iron and steel works located at Jamshedpur, Durgapur, Asansol and Raurkela. The Rajhara and Dhali Hills located south of Bhilai Steel Works are other major sources of iron ore with huge iron content. These hills provide iron ore to the Bhilai Steel Works. Moreover, apart from these places, there is a large high-grade iron ore deposit at Kemmangundi in the Bababudan Hills of Chikmagalur district in Karnataka. This deposit is used for supplying iron ore to steel plant located at Bhadravati.
Interestingly, iron ore found in Goa is basically of high grade and is situated in close proximity to the port of Marmagao. Rich deposits are also found in other areas of the country. Like for instance, eastern region of Madhya Pradesh and adjacent districts of Maharashtra, rich deposits of iron ore or hematite occur at a number of places. Hematite occurring in regions like Rowghat and Bailadila in Bastar District and Lohara and Pipalgaon in Chandrapur District are generally very large. After the iron belt of Orissa and Bihar, Bailadila and Rowghat constitute the richest high grade iron ore area.
Mining of iron ore on modern lines has been started in the country. Mines in different places have been made fully mechanized and also export oriented. The mines are fully equipped with modern machinery. Other areas with sizeable deposits of iron ore occur are the Salem and Ratnagiri districts Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district. These regions consist of low grade magnetite iron ore. Iron ore mines in Kudremukh hills are very developed. Few places in Andhra Pradesh like Kurnool and Anantapur districts and Palamau in Bihar also produce small proportion of iron ore. Production of iron ore in the country has also increased with the passage of time.















