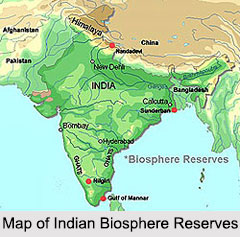
 Indian biosphere reserves have been established for the protection of large areas providing natural habitats to wildlife in the country. Such areas include one or more national parks as well as buffer regions. In these reserves, protection is granted not only to the flora and fauna, but also to the human communities of the region. A biosphere integrates all living beings, their relationships in the world and their interactions with the elements of the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere. A biosphere reserve is an ecosystem in which plants and animals of unusual scientific interest exist. The term "biosphere reserve" is an international conservation designation given to different areas under the UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) Man and the Biosphere (MAB) programme, operating since 1971. Around 18 biosphere reserves have been established by the Government of India. These reserves cover the East Himalayas, West Himalayas, Ganges delta, Western Ghats, Indian coasts, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, etc. In today`s world, where global warming is becoming a huge threat to the entire human civilization, Indian biosphere reserves are providing a scope to study the biosphere and share knowledge on new ideas.
Indian biosphere reserves have been established for the protection of large areas providing natural habitats to wildlife in the country. Such areas include one or more national parks as well as buffer regions. In these reserves, protection is granted not only to the flora and fauna, but also to the human communities of the region. A biosphere integrates all living beings, their relationships in the world and their interactions with the elements of the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere. A biosphere reserve is an ecosystem in which plants and animals of unusual scientific interest exist. The term "biosphere reserve" is an international conservation designation given to different areas under the UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) Man and the Biosphere (MAB) programme, operating since 1971. Around 18 biosphere reserves have been established by the Government of India. These reserves cover the East Himalayas, West Himalayas, Ganges delta, Western Ghats, Indian coasts, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, etc. In today`s world, where global warming is becoming a huge threat to the entire human civilization, Indian biosphere reserves are providing a scope to study the biosphere and share knowledge on new ideas.
Criterions for Establishing Indian Biosphere Reserves
Indian biosphere reserves have been established by fulfilling all the required criterions. India is one of the biggest contributors of the programme of biosphere reserve. According to the Statutory Framework of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves, biosphere reserves are created with an intention `to promote and demonstrate a balanced relationship between humans and the biosphere`. Another objective of biosphere reserves is to conserve in the original place, all forms of life and the support system, so that it can serve as a referral system for monitoring and evaluating changes in natural ecosystems. Article 4 of the Statutory Framework states that biosphere reserves must `encompass a mosaic of ecological systems`, and thus should consist of combinations of terrestrial, coastal or marine ecosystems. The conservation of these ecosystems and their biodiversity is sought to be maintained through appropriate zoning and management. 
Different Indian Biosphere Reserves
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve is located in the Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka. It is the first biosphere reserve in India and it was established in the year 1986. Other Indian biosphere reserves include the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve in Tamil Nadu, the Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve in West Bengal, the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve in Uttarakhand, the Nokrek Biosphere Reserve in Meghalaya, the Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve in Madhya Pradesh, the Simlipal Biosphere Reserve in Odisha, the Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Achanakmar Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve in Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh and the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve in Kerala. The above mentioned biosphere reserves are parts of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves. Eight remaining Indian biosphere reserves are the Dihang-Dibang Biosphere Reserve in Arunachal Pradesh, the Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve in Sikkim, the Dibru Saikhowa Biosphere Reserve in Assam, the Manas Biosphere Reserve in Assam, the Great Rann of Kutch Biosphere Reserve in Gujarat, the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve in Himachal Pradesh, the Seshachalam Hills Biosphere Reserve in Andhra Pradesh and the Panna Biosphere Reserve in Madhya Pradesh.











