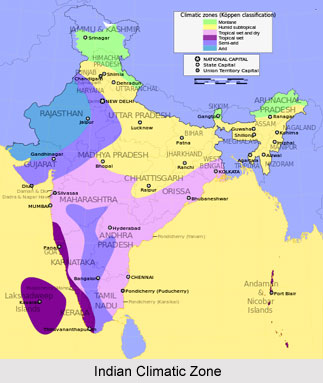
 Humid sub tropical climate group characterizes the temperature during the coldest months in its respective regions to fall between 18 and 0°C. It has one climatic subdivision in India, namely humid sub-tropical with dry winters.
Humid sub tropical climate group characterizes the temperature during the coldest months in its respective regions to fall between 18 and 0°C. It has one climatic subdivision in India, namely humid sub-tropical with dry winters.
The foothills of the Himalayas, Rajasthan east of the Aravalli range, Punjab-Haryana plain adjacent to the Himalayas, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and northern part of West Bengal and Assam experience this type of climate. The rainfall is received mostly in the summer and is about 65 cm in the west and increases to 250cm annually to the east and near the Himalayas. The winters are mainly dry due to the land derived winter winds which blow down the lowlands of north India towards the Bay of Bengal. The summers are hot and temperatures can reach 46°C in the plains. May and June are the hottest months. Winter months are usually dry with feeble winds. The difference in rainfall between the east and the west regions is responsible for a wide difference in the natural vegetation and crops.
The Himalayan Alpine climate varies according to the elevation. It gets colder as the elevation increases and gets wetter as the elevation drops. As a result the temperature and climatic changes in the Himalayan regions alter very quickly. All of a sudden, these areas can experience monsoons, floods, high winds, snowstorms and other types of precipitation, which makes the climate, quiet an unpredictable and dangerous one. The two major seasons of this climatic tract are winter and summer. During the winter the region receives the maximum snow with very icy temperatures. Summers are quiet mild over here, making the places over here quiet good summer holiday hideouts. Usually throughout the year the Alpine Himalayan region receives snow.
Some specific regions like Ladakh and Zanskar that lie to the North of the main tract experiencing humid sub tropical climate often escape the full impact of the monsoon. Humidity is always low in these regions, and receives only a few centimeters of rainfall every year. These regions also experience some of the coldest temperatures anywhere in the world, and it doesn`t get any warmer till the spring season in late April or early May.
In June, daytime temperatures frequently rise to the mid 200Cs, the snow on the passes melts and most of the treks can be undertaken from then on until the middle of October. Heavy rainstorms can occasionally be experienced during July and August, and river crossing should be undertaken with great care at this time. By September the conditions are ideal, and they normally remain so until late October even though nigh-time temperatures often fall below freezing. By November, the early winter snows fall on the passes closest to these regions. In winter the villagers experience intense cold, to follow the valley floors where river crossings are no longer a problem.
After October the daytime temperatures of this climatic belt drops, but the weather is generally moderate until the middle of November when the first of the heavy winter snows fall on the high mountain passes. Winter months from December to March are often miserable. April and May months bring about heavy precipitation, which falls as snow in the mountains, precluding trekking over the passes until the spring snows melt in June. Places like Darjeeling and Sikkim are subject to the Indian monsoon that sweeps up from the Bay of Bengal, bringing heavy rainfall from early June until the end of September. The post-monsoon months of October and November provide matured conditions, with clear views of the landscape, although night time temperatures above 3,500m frequently fall below freezing point.
These regions have a harsh environment therefore few animals and plants can survive over here. The few plants that do inhabit these regions consist of rhododendrons, the tea plant and shrub type plants. They have to adapt to the freezing temperatures, high winds and to a short growing season. That is why most of the plants grow low to the ground. One of the most interesting and accessible areas are the forests on the ridge line that form the Indo Gangetic watershed on which lie Shimla, Narkanda and the most beautiful forests of silver Fir starting from Narkanda. From the plains to the snow covered mountains, one goes through fine forests of Pine, Deodar, Fir, Oak, Rhododendron, Birch and finally between the tree line and the snows, rich alpine pastures.
The mountain fauna that are found in the humid sub tropical climatic belt are similar to the mountain animals found in the surrounding areas of the region. Some animals that have adapted the Himalayan climate include the mountain goat, which has a thick coat for warmth and strong hooves for climbing up the rocky slopes.















