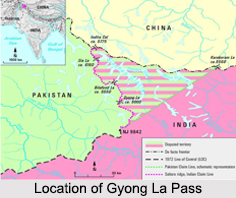
 Gyong La is a mountain pass, which is situated on the Saltoro Ridge at the southwest of the Siachen Glacier and is located 20 km north of map point NJ9842, where the 1972 line of control between India and Pakistan ends. Gyong La pass, with an elevation of 5686 meters, has been under the Indian control since 1989 while Pakistani forces control the Gyong and Chumik glaciers to the west. Dozens of Indian military tents and other equipments were visible on October 2013 by Google Earth imagery on both northeast and east-northeast of Gyong La pass.
Gyong La is a mountain pass, which is situated on the Saltoro Ridge at the southwest of the Siachen Glacier and is located 20 km north of map point NJ9842, where the 1972 line of control between India and Pakistan ends. Gyong La pass, with an elevation of 5686 meters, has been under the Indian control since 1989 while Pakistani forces control the Gyong and Chumik glaciers to the west. Dozens of Indian military tents and other equipments were visible on October 2013 by Google Earth imagery on both northeast and east-northeast of Gyong La pass.
Geopolitical Issues on Gyong La Pass
There have been major military actions on Gyong La pass, nearby Sia La pass and Bilafond La pass. The actions got its root from the 1983 Operation Meghdoot, the first military conflict of the Siachen Glacier, which was a part of the severe Kashmir conflict. In March 1989 Operation Ibex by the Indian Army attempted to seize the Pakistani post overlooking the Chumik Glacier. Indian army was unsuccessful in dislodging the Pakistani soldiers from their positions. Then again, Indian army launched an artillery attack on Kauser Base under the commands of Brig. R. K. Nanavatty. As a result of which, Pakistani troops vacate the Chumik posts. Thuse, Operation Ibex concluded.
Then finally in June 1999, the Indian Army under Brig. P. C. Katoch, Col. Konsam Himalaya Singh seized the control of point 5770 on the southern edge of the Saltoro defense line, about 4 km west of Gyong La, from Pakistan troops.















