 The Great Nicobar Islands is an integral part of the entire bio-diversity of India and is located in the Indian Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The Great Nicobar Island is the southern most island of Andaman & Nicobar archipelago and is also the southernmost part of India. The Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve is situated about 482 kms south of Port Blair and is dominating most of the Great Nicobar Island. The reserve is the home of one of the most primitive tribes of India, the Shompens. The most endangered species in India, the Megapode and the Edible-Nest Swiftlet, also reside in this reserve. The total geographic area of the reserve is 885 sq. km. and is surrounded by a 12km-wide "forest buffer zone". It presents a varied natural panorama covered with virgin lush evergreen dense tropical forests, which extend from seacoast to the tip of the hills.
The Great Nicobar Islands is an integral part of the entire bio-diversity of India and is located in the Indian Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The Great Nicobar Island is the southern most island of Andaman & Nicobar archipelago and is also the southernmost part of India. The Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve is situated about 482 kms south of Port Blair and is dominating most of the Great Nicobar Island. The reserve is the home of one of the most primitive tribes of India, the Shompens. The most endangered species in India, the Megapode and the Edible-Nest Swiftlet, also reside in this reserve. The total geographic area of the reserve is 885 sq. km. and is surrounded by a 12km-wide "forest buffer zone". It presents a varied natural panorama covered with virgin lush evergreen dense tropical forests, which extend from seacoast to the tip of the hills.
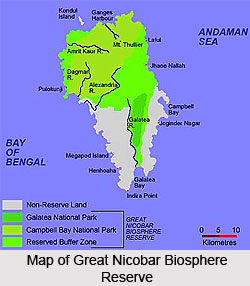
The Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve was established in January, 1989 with a view to achieve certain aims and objectives. The main objective behind its formation was to preserve biological diversity. The other principal objectives include conservation of the representative samples of ecosystem; provision of long-term conservation of genetic diversity in situ; promotion of basic and applied research work and its monitoring; and dissemination of experience for education and training. The reserve incorporates two National parks of India, which were gazetted in 1992; the larger amongst which is the Campbell Bay National Park on the northern part of the island. The other National Park is the Galathea National Park in the southern interior. Apart from agriculture, forestry and settlements, the non-Biosphere portions of the island are confined to the southwestern and southeastern coastal reaches.
The environment of the Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve is classified by the World Wide Fund for Nature as Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome, and it is located in the Indomalaya ecozone. The reserve represents the tropical rain forests in Andaman & Nicobar Islands bio-geographic region. About 85% of the forest in this Biosphere Reserve is still in its virgin state and they are rich in their species composition. Some of the most important species that are found in the reserve include the 5 species of Ficus, 2 species of Terminallia, Pandanus tanctoria, Pynanga coastata, Sterculia alata, Ipomea spp., Casaurina sp., Nipa Palm, Albizia procera, Canarium euphyllum, Callophyllum spp., Syzizium Cuminii, Eliocarpus gangestrus (Rudraksha tree), Malinkara litoris, Rhizophora spp., Brugeria spp., Ceriops tagal, the Canes etc. However, the characteristic tree fern (Cyathea albosetacea) and the beautiful ornamental ground orchid (Phalaenopsis speciosa) are endemic to this reserve and they can only be found in this southern most island.
Apart from the rich flora, the Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve also houses several species of fauna that attracts a large number of visitors, every year. The most unique fauna of this Biosphere Reserve include the Crab Eating Macaque, Salt Water Crocodile, Giant Leather Back Turtle, Malayan Box Turtle, Nocobar Tree Shrew, Nicobar Megapode, Reticulated Python and the Giant Robber Crab. There are also several other important species found in this reserve that include the Andaman Wild Pig, Palm Civet, Fruit Bat, Nicobar Pigeon, White Bellied Sea Eagle, Nicobar Serpent Eagle, Parakeets, Nicobar Parakeets, Water Monitor Lizard etc. This reserve is well known for its unique bio-diversity and also for housing rich genetic germ plasm resources.











