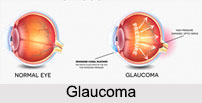
 Glaucoma is a serious eye disorder characterized by an increase of pressure within the eyeball, called "Intra-Ocular Pressure" (IOP). The condition of glaucoma generally refers to high blood pressure of the eyes. The condition is, therefore, also known as hypertension of the eye. It causes damage to the eye"s optic nerve and gets worse over time. A certain amount of intra-ocular pressure is considered necessary, but too much can cause damage to the eye and may result in vision loss. Glaucoma is the major cause of blindness among adults today and far-sighted persons are more prone to develop this disease than the nearsighted ones.
Glaucoma is a serious eye disorder characterized by an increase of pressure within the eyeball, called "Intra-Ocular Pressure" (IOP). The condition of glaucoma generally refers to high blood pressure of the eyes. The condition is, therefore, also known as hypertension of the eye. It causes damage to the eye"s optic nerve and gets worse over time. A certain amount of intra-ocular pressure is considered necessary, but too much can cause damage to the eye and may result in vision loss. Glaucoma is the major cause of blindness among adults today and far-sighted persons are more prone to develop this disease than the nearsighted ones.
Types of Glaucoma
There are two major types of glaucoma; Open-Angle Glaucoma (OAG) and Closed-Angle Glaucoma. The "angle" in both cases refers to the drainage angle inside the eye that controls the outflow of the watery fluid that is continually being produced inside the eye.
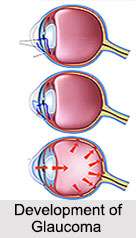
•Open-Angle Glaucoma: This is the most common type of glaucoma. It happens gradually; where the eye does not drain fluid well. As a result, eye pressure builds and starts to damage the optic nerve. This type of glaucoma is painless and causes no vision changes at first.
•Closed-Angle Glaucoma: This type happens when someone"s iris is very close to the drainage angle in their eye. The iris can end up blocking the drainage angle. When the drainage angle gets completely blocked, eye pressure rises very quickly. This is called an Acute Attack. It is can cause blindness if not treated right away.
Causes of Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a highly toxic condition of the system due to dietetic errors, a faulty life style and the prolonged use of suppressive drugs for the treatment of other diseases. Even severe eyestrain or prolonged working under bad lighting conditions is the contributory causes of glaucoma. Glaucoma is also caused by prolonged stress and is usually a reaction of adrenal exhaustion. Glaucoma has also been associated with giddiness, sinus conditions, allergies, diabetes, hypoglycaemia, arteriosclerosis and an imbalance of the autonomic nervous system.
Symptoms of Glaucoma
Glaucoma has been called the silent thief of sight. The first symptom of glaucoma is the appearance of coloured rings round distant objects, when seen at night. In this condition, the iris is usually pushed forward, and the patient often complains of constant pain in the region of the brow, near the temples and the cheeks. Another common symptom is headaches. There is also a gradual impairment of vision as glaucoma develops, and this may ultimately result in blindness if proper steps are not taken to deal with the disease in the early stages.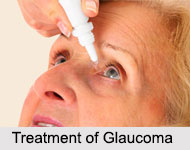
Diet Therapy for Glaucoma
The diet of the patient suffering from glaucoma should be based on three basic food groups, namely, seeds, nuts and grains; vegetables and fruit, with emphasis on raw vitamin C-rich foods. The patient should not take excessive fluids, whether it is juice, milk or water at any time, but he should drink small amounts several times with at least one-hour intervals.
Treatment of Glaucoma
Treatment of Glaucoma can involve glaucoma surgery, lasers or medication, depending on the severity. Eye drops with medication aimed at lowering IOP usually are tried first to control glaucoma. Because glaucoma often is painless, people may become careless about strict use of eye drops that can control eye pressure and help prevent permanent eye damage.
The patient should undertake various methods of relaxing and strengthening the eyes. He should avoid emotional stress and cultivate a tranquil, restful life style. He should also avoid prolonged straining of the eyes such as excessive TV or movie watching and excessive reading. The use of sunglasses should be avoided. Proper treatment of glaucoma often leads to normal eyesight after a considerable time.




