Introduction
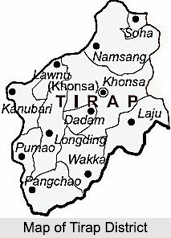 Located in the south –eastern part of the state of Arunachal Pradesh, the Tirap district shares an international state border with Nagaland and Assam. The Tirap district derives its name from the river Tirap which originates in this district and flows through Changlang district. The entire area of this district is covered with high hills and deep valleys. Khonsa is the district headquarters.
Located in the south –eastern part of the state of Arunachal Pradesh, the Tirap district shares an international state border with Nagaland and Assam. The Tirap district derives its name from the river Tirap which originates in this district and flows through Changlang district. The entire area of this district is covered with high hills and deep valleys. Khonsa is the district headquarters.
History of Tirap District
 History of Tirap district includes a number of administrative developments that resulted in the formation of this district. The beginning of the administration of Arunachal Pradesh is traced back to the Scheduled Districts Act of 1874 of the Government of India. This act provided a schedule of districts where the Local government could decide as to which of the enactments of the Government of British India are in force and which are excluded. As a result, several Hill Tracts (territories) were placed under the Chief Commissionership of the state of Assam as local government. Following this, again in the year 1880, Assam Frontier Tracts Regulation was passed that provided for removal of certain frontier tracts in Assam inhabited or frequented by semi-civilized tribes from the operation of enactments of British Government to be in force. This power was vested in the Chief Commissioner of Assam.
History of Tirap district includes a number of administrative developments that resulted in the formation of this district. The beginning of the administration of Arunachal Pradesh is traced back to the Scheduled Districts Act of 1874 of the Government of India. This act provided a schedule of districts where the Local government could decide as to which of the enactments of the Government of British India are in force and which are excluded. As a result, several Hill Tracts (territories) were placed under the Chief Commissionership of the state of Assam as local government. Following this, again in the year 1880, Assam Frontier Tracts Regulation was passed that provided for removal of certain frontier tracts in Assam inhabited or frequented by semi-civilized tribes from the operation of enactments of British Government to be in force. This power was vested in the Chief Commissioner of Assam.
In the year 1914, the notifications of the Government of India, Foreign and Political Department, it was mentioned that the Assam Frontier Tracts Regulation of 1880 would extend to the hills inhabited by the Abors, Miris, Mishmi tribe, Singhpho tribe, Naga tribe, Khamti tribe, Bhutias, Aka tribes and Nishing tribe. It meant that the Chief Commissioner of Assam was hereafter free to leave out any of these areas from any of the enactments of the government and also employ officers for smooth administration of the region. These notifications also approved boundaries of two units which would henceforth consist of the North-East Frontier Tract.
These were named as -
•The central and eastern section, North East Frontier Tract
•The Western Section, North East Frontier Tract
The Indian Penal Code was extended to both sections in the year 1916. The Central and Eastern Section had its headquarters at Sadiya. In the year 1919, this section was renamed as `Sadiya Frontier Tract.` In the year 1937, these two tracts, along with the Lakhimpur Frontier Tract of Assam came to be jointly known as `Excluded Areas of province of Assam` under the provisions of Government of India Act, 1935. It specified that the legislative or administrative control of the regional Government of Assam was excluded from these areas. Thus, the actual administration of the Frontier Tracts was hence carried out by the Governor of Assam. The secretariat was formed in the year 1937 and the expenses were borne by the state government.
Further, the history of Tirap district makes it clearly evident that the occupation of tribal territories all over India was marked by a series of disciplinary measures by the British Government. In the year 1943, these areas were brought under standard administration through gradual penetration of organizational machinery. Consequently, the post of Adviser to the Governor of Assam was accordingly formed in the year 1943. Under the International Administration Regulation 1943 of the North Eastern Frontier Tract, a new administrative unit was created by merging certain areas of the Sadiya and the Lakhimpur Frontier Tracts and was named as Tirap Frontier Tract. It was placed under a separate political officer with its headquarters at Margherita in Assam.
After the independence of the country in 1947, the Governor was divested from of his discretionary powers in respect of the North-East Frontier Tracts and subsequently the administrative control was passed on to the Government of Assam by provisions of the Indian Independence Act of 1947. This arrangement continued till the year 1950 when the Government of Assam was reassured of its responsibility of administration of North-East Frontier Agency and the discretionary power was re-invested in the Governor of Assam. Further, in 1951, the plains portions of Tirap Frontier Tract were transferred to the administrative jurisdiction of Government of Assam. The remaining hill areas of the frontier tracts were cooperatively renamed as North-East Frontier Agency. Under the regulation of 1954, Tirap Frontier Tract was renamed as Tirap Frontier Division with its headquarters at Khela that was later shifted to Khonsa in the year 1956. Again, in 1965, the Frontier Division was renamed as Tirap District and the classification of Political Officer was changed to that of Deputy Commissioner under the North East Frontier Agency (Administration) Regulation of 1965.
The history of Tirap district also suggests that in the year 1987, this district was divided into two districts - Tirap and Changlang district with its headquarters at Khonsa. The name of Tirap district was derived from river Tirap.
Geography of Tirap District
 Geography of Tirap district comprises mostly hilly and mountainous regions including several deep valleys. This district is positioned between the latitudes 26 degrees 38 minutes North and 27 degrees 47 minutes North and the longitudes 96 degrees 16 minutes East and 95 degrees 40 minutes East. Tirap district is covered by Myanmar towards South, by Changlang District of the state of Arunachal Pradesh towards the east, by Dibrugarh in Assam towards North and by Sibasagar District in Assam and Mon (Nagaland) districts in the West. The entire area of Tirap district is enclosed with high hills. There are hardly a few plots of plain land available in the villages lying close to the plains of Assam. Khonsa that is the district headquarters is situated at an altitude of around 4200 feet.
Geography of Tirap district comprises mostly hilly and mountainous regions including several deep valleys. This district is positioned between the latitudes 26 degrees 38 minutes North and 27 degrees 47 minutes North and the longitudes 96 degrees 16 minutes East and 95 degrees 40 minutes East. Tirap district is covered by Myanmar towards South, by Changlang District of the state of Arunachal Pradesh towards the east, by Dibrugarh in Assam towards North and by Sibasagar District in Assam and Mon (Nagaland) districts in the West. The entire area of Tirap district is enclosed with high hills. There are hardly a few plots of plain land available in the villages lying close to the plains of Assam. Khonsa that is the district headquarters is situated at an altitude of around 4200 feet.
The physiographical regions of Tirap district are as follows -
Namchik-Tirap River Valley: It is a shared valley of Tirap and Namchik rivers, both of which have their source at the top of Patkai Hills or Purvanchal Ranges. The region covers an area of near about 1300 sq. kms. It basically spreads over the Lazu circle and also in some parts of Khonsa circle of Tirap District, and the rest of it is covering Changlang District. The region is bounded by Tirap River and Assam in the North, Myanmar in the south and Namsang and Wakka circles in the west and south-west. The entire area is covered with dense tropical forests.
Namsang-Dirak River Valley: This valley covers an area of approximately 640 sq. kms. It largely expands over Khonsa and Namsang circles of Tirap and parts of Changlang District. It is covered by Burhi-Dirang River and Assam in the North, Lazu circle in the south and Khonsa circle towards the east and the west.
Tissa River-valley: This valley of the Tirap district forms a part of Patkai ranges. It covers an area of around 1214 sq. kms. The region spreads over Kanubari, Longding, Pongchao and Wakka circles and parts of Khonsa circle. It is bounded by Assam in the north, Myanmar in the south, Nagaland in the west and by Lazu, Deomali and Lower Shivalik Hills group classification. The entire area is covered with thick tropical forests.
The climate of Tirap district is hugely influenced by the topography that is marked with high hills, deep gorges and valleys through which the streams and rivers flow. In general, the elevation of land varies from around 200 feet above sea-level in the north-west to around 5000 feet over the mountains. The climate of this district varies considerably from one place to another due to its mountainous nature. Usually, the climate of Tirap district is cold and extremely moist in the lower elevations and in the valleys. The cold season prevails from the later part of the month November to February and is followed by common thunderstorms in the pre-monsoon season from the month of March to May. Very heavy and frequent monsoon showers continue from the month of May to around mid of October. Thus, it is evident from the geographical facts of Tirap district that this area is rich with valleys and has a pleasant weather that adds charm to its natural beauty.
Demography of Tirap District
 Demography of Tirap district includes a huge density of population. This district is one of the smallest districts of the state of Arunachal Pradesh as far as its area is concerned. However, it is the most thickly populated (density of 42 persons per sq. km). Moreover, Khonsa that is the district headquarters is also the most heavily populated administrative unit. Major portion of the people residing in the district are the indigenous tribal groups which constitute more than 70 per cent of the total population of Tirap district. The major tribes inhabiting in the district are the Nocte tribe, Wancho tribe and the Tutsa tribes. Among the tribal groups, Noctes form near about 45 per cent, Tutsas about 5 per cent and Wanchos almost 50 per cent of the total tribal population of the Tirap district.
Demography of Tirap district includes a huge density of population. This district is one of the smallest districts of the state of Arunachal Pradesh as far as its area is concerned. However, it is the most thickly populated (density of 42 persons per sq. km). Moreover, Khonsa that is the district headquarters is also the most heavily populated administrative unit. Major portion of the people residing in the district are the indigenous tribal groups which constitute more than 70 per cent of the total population of Tirap district. The major tribes inhabiting in the district are the Nocte tribe, Wancho tribe and the Tutsa tribes. Among the tribal groups, Noctes form near about 45 per cent, Tutsas about 5 per cent and Wanchos almost 50 per cent of the total tribal population of the Tirap district.
Further, the demography of Tirap district also suggests that each of these three tribes inhabits a separate geographical area and has its own social norms, traditions, customs, beliefs and practices. They have rich native cultures and live in social accord with each other. All these tribes are martial Naga tribe who at one time vigorously engaged in head-hunting. However, the practice is now extinct. Most of the people of this district live in the villages and the life-style of the people is entirely community based. The main occupation of the people of Tirap district is agriculture and farming. Although agriculture is the main occupation of the villagers, it is of a survival nature only. Some people earn their livelihood through other activities such as government employment, government contract works, trade in local products and agricultural labour, contract works in forest products, etc. Here, people generally practice shifting type of agriculture or jhoom cultivation though slowly people have started adopting terrace farming too.
Chieftainship is an important feature of the tribal communities of Tirap district. Both Nocte tribe and the Wancho tribe have chiefs in their villages. There exist the major chiefs above the village chiefs who receive honours from the subsidiary villages within the district. However, with the introduction of Panchayati Raj system, the role of the head has changed to a great extent but still they still enjoy a place of pride and a very high status in their community. Each and every village has a well-organized council for the proper administration of law and order. Each tribal group has its own usual laws and most of the divergence decision is done through village councils.
Flora and Fauna of Tirap District
 Flora and Fauna of Tirap district is really vast and extensive. Flora of this region like the other districts of the state of Arunachal Pradesh is rich in diversity and extent. The plants of the Tirap district mostly comprise tropical as well as sub-tropical evergreen forests with combined grasslands and moderate forests in the high hills. Most of the wooded areas are of secondary nature due to the frequent destruction of forests by shifting cultivation practiced by the local people. Primary forests are limited to relatively less accessible areas.
Flora and Fauna of Tirap district is really vast and extensive. Flora of this region like the other districts of the state of Arunachal Pradesh is rich in diversity and extent. The plants of the Tirap district mostly comprise tropical as well as sub-tropical evergreen forests with combined grasslands and moderate forests in the high hills. Most of the wooded areas are of secondary nature due to the frequent destruction of forests by shifting cultivation practiced by the local people. Primary forests are limited to relatively less accessible areas.
Like in all the tropical rain forests, the vegetation in Tirap district too presents a tiered sequence. The forest covering is Golden-Backed Woodpecker by the spreading branches of tall trees of diverse range particularly Diterocarpus Vesque, Terminalia Heurck and Muell. Scattered and less tall trees and other middle-sized species outline the second tier. In somewhat open areas, clusters of the fan-leaved palm Livistonia Kurz, and the fish tailed palm Wallichi Anders can be seen occasionally. Other palms like the slender stemmed Pinanga gracilis the stout, fan-leaved Licuala spinosa and the spiny large-leaved Zalacca Griff also occur. Further, large masses of giant Bamboos are also not infrequent. Large woody climbers, frequently interrelating adjoining trees, entangle the trees and forming entwined garlands of branches hanging loosely from the top. Interestingly, the climbers are chiefly of the families named Menispermaceae, Annonaceae, Vitaceae, Connaraceae and Cucurbitaceae. Amid all these a particularly vicious member is the climbing palm, the cane or Calamus. There are a number of species in these forests, some with heavy stems extending to abnormally long distances, and others with slim stems. These canes are largely used by the local tribal people of Tirap district.
Similarly, like the flora, the fauna of Tirap district is also rich and diverse. It consists of some unusual species of wild animals. The region is frequented by few local Palaearctic species and migratory species of birds that breed around the Sino-Himalaya Mountains area. The resident waterfowls that are commonly found in river waters and pools are the Spotbill Duck, the Comb Duck, the Lesser Whistling Teal, the large Whistling Teal and Cotton Teal. Varieties of birds can be found in the evergreen jungle on the plains and the lower slopes. In the denser part of the forests that has tall trees laden with epiphytes, birds that are usually found are the Fairy Drongos such as the Crowbilled Drongo and the Greater Racket-Tailed Drongo, the Mountain Thrush, the streaked spider hunter, the Lesser Golden-Backed Woodpecker, etc.
The conditions are frequently changing as shifting terrace cultivation is extensively practiced by the people. As a result, may portion of the slopes once covered with intense forests are now covered with dense secondary growth of shrubs, grass interspersed with scattered trees of Bombax, Zizyphus etc. Such secondary shrub jungles are the home of Bulbuls, such the Red Whiskered Bulbul, Babblers, Chats and several species of Warblers, Spotted Dove and Quails, such as the Manipur Bush Quail, the Bustard Quails and the Malabar Pied Hornbill, the Red-headed Trogon, the Malabar Whistling Thrush and the Indian roller. The other birds that are frequently found are the Black-naped Green Woodpecker, Rufousneck Hornbill, Maroon Oriole, Minivets etc. Moreover, the mountain forests of the Tirap district contain some characteristic high altitudinal birds, such as the Common Hill Partridges, Blyth`s Tragopan and more.
During the winter season, migrating birds from Northern Asia have their momentary quarters in this region. Thus, the rich and vast range of flora and fauna of Tirap district is considered as one of the main attractions for the tourists.
Festivals in Tirap district
 The festivals of Tirap district reflect the distinct cultural and ethnic identity of the people. The state of Arunachal Pradesh is the land of charming and captivating natural beauty which is inhabited by a number of tribes. The festivals of the different tribal people residing in this are considered as one of the main attractions for the tourists. Interestingly, the travellers will be really amazed at the sight of the various colourful cultural festivals that are celebrated separately by each of the tribal groups of Tirap district. In Arunachal Pradesh, the tribal folks celebrate a number of festivals. They celebrate these festivals to pacify the malevolent and benevolent deities who would protect their crops and yield good harvest. The main festivals of the three major tribes, which are Nocte tribe, Wancho tribe and Tutsa tribe, celebrated in Tirap district are:
The festivals of Tirap district reflect the distinct cultural and ethnic identity of the people. The state of Arunachal Pradesh is the land of charming and captivating natural beauty which is inhabited by a number of tribes. The festivals of the different tribal people residing in this are considered as one of the main attractions for the tourists. Interestingly, the travellers will be really amazed at the sight of the various colourful cultural festivals that are celebrated separately by each of the tribal groups of Tirap district. In Arunachal Pradesh, the tribal folks celebrate a number of festivals. They celebrate these festivals to pacify the malevolent and benevolent deities who would protect their crops and yield good harvest. The main festivals of the three major tribes, which are Nocte tribe, Wancho tribe and Tutsa tribe, celebrated in Tirap district are:
Festivals of Nocte Tribe
The major festival of Nocte tribe is the Loku festival. Loku literally means to drive out the old season of the year. It is celebrated during the month of July or August. However, in some villages it is celebrated during the month of October or November. The date of the festival is fixed after calculating the digits of the waxing moon. The date is fixed by the elders of the community. Every Nocte village is echoed by the declaration of the date for celebration of Loku. This festival is celebrated with immense zeal and fervour.
Festival of Tutsa Tribe
The people belonging to the Tutsa tribal community mainly celebrate two festivals and these are Pongtu Kuh festival and Ronghun Kun. These celebrations are considered as an integral part of the socio cultural life of the Tutsa tribe. They are celebrated usually in April every year for obtaining the blessings for proper Jhoom cultivation. The elders of the village fix the date of the celebration. People celebrate them for continuous ten days immediately after collection of all the festival materials.
Festival of Wancho Tribe
Ojiyele Festival is regarded as the major festival of the Wancho tribe residing in the Tirap district. People celebrate this festival generally in the months of March and April every year. According to the calendar of the Wanchos they celebrate the Ojiyele festival during the month of Dinglik Let (March) and Saniyak Let (April). The festival date fixed by the village chief. However, the celebration date differs from one village to another.
These festivals of Tirap district have their own charm and truly replicate the indigenous culture of the people.
Administration of Tirap District
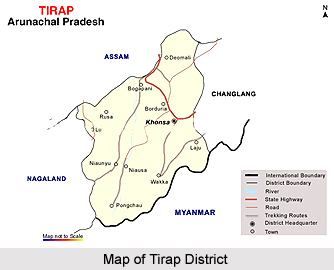 The administration of Tirap district is headed by the Deputy Commissioner. Like other districts of the state of Arunachal Pradesh, the administrative head of Tirap district is in charge of all the departments of the administration. However, he is assisted by various District heads of various departments in the overall discharge of duties. The overall in charge of the Police Force of the Tirap district is the Superintendent of Police who assists the Deputy Commissioner in maintenance of law and order. The headquarters of this district is at Khonsa, which is a picturesque town of the state, situated at a height of around 1300 metres above the sea level.
The administration of Tirap district is headed by the Deputy Commissioner. Like other districts of the state of Arunachal Pradesh, the administrative head of Tirap district is in charge of all the departments of the administration. However, he is assisted by various District heads of various departments in the overall discharge of duties. The overall in charge of the Police Force of the Tirap district is the Superintendent of Police who assists the Deputy Commissioner in maintenance of law and order. The headquarters of this district is at Khonsa, which is a picturesque town of the state, situated at a height of around 1300 metres above the sea level.
Interestingly, in the state of Arunachal Pradesh, only the districts are defined as territorial units. The territory of administrative units below the level of district is not clearly defined. In this state, a sub-division is a group of circles and a circle is a group of villages, whereas a village is a group of houses. The lowest administrative unit in Tirap district is a circle, which is under the control of a Circle Officer. Tirap district is separated into four sub-divisions, each of which is headed by a sub-divisional officer. The administration of Tirap district is divided into several circles. These are -
•Khonsa Circle
•Kanubari Circle
•Lazu Circle
•Namsang Circle
•Pongchau Circle
•Pumao Circle
•Wakka Circle
Currently, Longding sub-division has recently been upgraded to headquarter, which gives the administrative head, some supplementary financial and establishment related powers.
The various administrative departments of Tirap district are as follows -
•Account
•Adult Education
•Agriculture
•Arunachal Pradesh State Transport
•Art and Cultural
•Economic and Statistics
•Education
•Electrical
•Establishment Branch
•Food and Supply
•Horticulture
•Information and Public Relation
•Inner Line Permit Branch
•Khonsa Forest Division
•Labour and Employment
•Legal Metrology and Consumer Affair
•Library
•Medical Department
•Police
•Public Works Department - Khonsa Division
•Relief Rehabilitation
•Research
•Rural Works Department, Khonsa Division
•Textile and Handicraft
•Urban Development and Housing Department
The administration of Tirap district is entirely committed towards the progress and expansion of the area and the people residing here.
Sports in Tirap District
 Sports in Tirap district are quite popular among the tribal people. The various sports of Tirap district include Kiko-Khoam, Sakchin Tam and Jaam. Among them the most popular is the Kiko-Khoam that means stilt walk. This game of the district is very popular among the youths and is specifically meant for the men folks. Kiko Khoam is the game basically played by the lower belt Nocte tribe of the state of Arunachal Pradesh. Interestingly, the upper belt Nocte tribe people call this game Daki-Ko. For playing this game, the branches of bamboo are used as a foot hold. When a person mounts on the foothold, he balances himself and walks. In this game, the level of potentiality of the players of balancing on two pieces of bamboo above the ground is analyzed.
Sports in Tirap district are quite popular among the tribal people. The various sports of Tirap district include Kiko-Khoam, Sakchin Tam and Jaam. Among them the most popular is the Kiko-Khoam that means stilt walk. This game of the district is very popular among the youths and is specifically meant for the men folks. Kiko Khoam is the game basically played by the lower belt Nocte tribe of the state of Arunachal Pradesh. Interestingly, the upper belt Nocte tribe people call this game Daki-Ko. For playing this game, the branches of bamboo are used as a foot hold. When a person mounts on the foothold, he balances himself and walks. In this game, the level of potentiality of the players of balancing on two pieces of bamboo above the ground is analyzed.
There is no specific season for playing the game of Kiko Khoam, however, the players prefer the winter season. There is no association of the game with any ritual or festival. This is chiefly a game to test the level of balance that an individual has. As a part of this sport, sometimes fights are organised among the players where each player hits the other and tries to get the opponent player down while still balancing on the bamboo. One who gets dismounted as a result of the strike is declared as the looser. Another game includes jumping with one bamboo on single leg. The players jump with only single stick on one leg. The player who performs the maximum jump is declared the winner. Moreover, the sport of Kiko Khoam is considered to be the legacy from their forefathers. Further, this sport has been the most popular amongst the youths till date.
In Arunachal Pradesh, there are various sports that are played by the Wancho tribe of the Tirap District. Sakchin Tam is one such popular sport that literally means `arm grip.` This is very popular among the men folk. In general, this sport is played by a youth when he attains maturity. Normally this is an event to measure strength of an individual. The sport of Sakchin Tam also analyzes the strength, force and gripping capacity of the individuals. In this sport, two individuals hold a piece of wooden stick close to each other as like arm wrestling and tries to grab the stick by applying force. Finally, the one who is able to possess the stick after certain period is declared as the winner. Interestingly, like the game of Kiko Khoam, in this game too there is no connection with any kind of ritual or festival. Generally, this game is being played four to five days before the Oriah festival of the Wanchos.
Another most popular game of the Tirap district is Jaam. Mostly the men folks play it. Jaam means wrestling and it is played by the Wancho tribe. This game is almost similar to that of Sakchin Tam. It puts to test the level of one`s power, patience and stamina. In this game, two individuals try to dominate each other by applying tremendous force or certain techniques. The wrestling continues till one throw the rival and makes him fall on the ground. There is no specific occasion for conducting Jaam.
Places of Attraction in Tirap District
The places of interest in the Tirap district are quite few and listed below are some of the places of attraction in this region.
Khonsa: It is the headquarters of the Tirap district and is a small hill station in a valley surrounded by the Himalayas. Created during the British period, it is one of the 5 earliest districts of the state. Surrounded by panoramic views of thick forests fringed by hills, Khonsa is a paradise to the visitor"s eye. The forests around Khonsa host wild beings from tigers, leopards, white gibbon monkeys, jackals, wild boars, bears, barking deer, red panda, musk deer, mithun and numerous species of rodents. A spectacular attribute of this place lies in the ethnicity of the tribes and their festivals, fairs and flawless artworks which are created with intense dedication.
Khonsa Museum: Built in the year 1956, the Khonsa museum houses some of the amazing artefacts which represent the diverse culture of the district. Swords and other weapons are on display here. Apart from that, the museum houses handlooms and artefacts collections that represent the culture of various parts of India. Different types of cane and bamboo works can also be seen here.
Visiting Information on Tirap District
There is no direct train service to Tirap. The nearest railway stations are at Dibrugarh, Tinsukia or Naharkatia in Assam. The closest airport is Dibrugarh at a distance of approximately 119 km and is well connected to Guwahati.



















