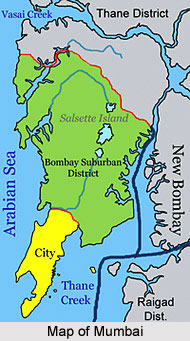
 Mumbai lies in the west coast of Indian state Maharashtra facing the Arabian Sea. As per the geography of the city, one fourth of the city lies under the sea. It is located on Salsette Island lying at the mouth of Ulhas River off the western coast of India in the coastal region known as the Konkan Coast. Mumbai covers an area of 440 sq km. Mumbai is actually an amalgamation of seven islands namely Colaba, Mazagaon, Old Woman`s Island, Wadala, Mahim, Parel, Matunga and Sion. The city`s geographical co-ordinates are 18.96° degree North and 72.82° degree east.
Mumbai lies in the west coast of Indian state Maharashtra facing the Arabian Sea. As per the geography of the city, one fourth of the city lies under the sea. It is located on Salsette Island lying at the mouth of Ulhas River off the western coast of India in the coastal region known as the Konkan Coast. Mumbai covers an area of 440 sq km. Mumbai is actually an amalgamation of seven islands namely Colaba, Mazagaon, Old Woman`s Island, Wadala, Mahim, Parel, Matunga and Sion. The city`s geographical co-ordinates are 18.96° degree North and 72.82° degree east.
Hills in Mumbai
The seven islands of Mumbai consisted of twenty hills. Some of them are Malabar Hill, Cumbala Hill, Antop Hill, Sewri Hill, Gilbert Hill, Worli Hill, Pali Hill, Mazgaon Hill, Sion Hill, Mahakali Hill, Pulshachi Dongri, Golanji Hill and Salamati Hill. Within the city limit there are three hill ranges. Malabar hill is considered to be the highest point of the city area having 180 feet above the sea level. The Ghatkopar Hill range lies parallel to the central railway track.
Lakes in Mumbai
In Mumbai there are three lakes. Vihar Lake and Tulsi Lake are well known for contributing part of city`s drinking water. They are located within the Borivali National Park. The location of Powai Lake is at the southern part of the previous two.
Rivers in Mumbai
Mumbai has five important rivers. They are Dahisar River, Mithi River, Oshiwara River, Poisar River and Ulhas River. Dahisar is originated from Tulsi Lake and is a river of the Northern suburbs of Mumbai. Several Bollywood movies were shot during the 1955-56 at the bank of this river. One branch of Ulhas River flows around Mumbai. The Mithi River is in the Salsette Island, the island of Mumbai. Oshiwara River is a river in Mumbai, India. It starts in the Aarey Milk Colony. Poisar River begins in the Sanjay Gandhi National Park in Mumbai and empties into the Marve Creek and finally into the Arabian Sea.
Islands in Mumbai
The islands were merged in the 18th century. But islands are still doted. The islands are Thane Creek. Elephanta Island, Butcher Island, Oyster Rock, Cross Island and Middle Ground are present here. The Oyster Rock, Cross Island and Middle Ground are now owned by the Indian Navy.
Bays in Mumbai
In Mumbai the largest bay is Black Bay. Black Bay`s coast line is like an "inverted C" scaling 4 kilometres in length. Marine Drive is located along with this stretch. There is Worli Bay at the North of Marine Drive. Mahim Bay is the second largest in the city.
Creeks in Mumbai
There are several creeks in Mumbai. The Vasai creek and Thane creek separates Mumbai from the Salsette Island. Other creeks in Mumbai are Malad creek, Gorai Creek, Mahul creek and Mahim Creek. They are equally important forming the geography of Mumbai.



















