Indian along with Pakistan and Bangladesh constitutes a geographical unit. Pakistan and Bangladesh are two sub continents of India. The geographical unit consisting of India, Pakistan and Bangladesh has distinctly stood apart from the main continent of Asia. This is because of the fact that Himalayan ranges are present in the North side while seas cover the other three sides. On the other hand, the Himalayan ranges are covered by other mountains such as in the west there is Karakoram and then Hindukush. In the south of the Hindukush is covered by Sufed Koh and the Sulaiman hills. And these are separating India from Afghanistan while the Kirthar hills separating India from Beluchistan. In the East side there are Himalayan spurs that forms the Patkoi, Lushai Hills and Naga hills, with their dense forests barring access to India from that quarter. There are several passes in the Western side. The prominent route is through the Khyber. The other route, which is also famous, starts from Heart to Kandahar and finally descends into the Indus Valley through the Bolan Pass. There is a third route that passes through the inhospitable Makran desert. These passes are the way in which different invaders and merchants tried to enter into the country. The same case happened with Indians, they maintained their commercial as well as cultural contact with the people of Western Asia, Europe, China, and Central Asia.
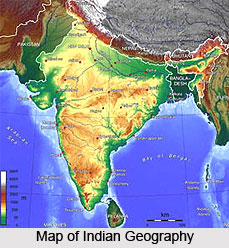 The Northeastern Mountains maintain a gap leaving the space for the river Brahmaputra. Though it is too difficult to pass through the dense forests but still some merchants and missionaries passed through them and entered India.
The Northeastern Mountains maintain a gap leaving the space for the river Brahmaputra. Though it is too difficult to pass through the dense forests but still some merchants and missionaries passed through them and entered India.
Because of all these reasons and mainly because of Himalayan range India was isolated from other countries of Asia but it has always maintained the cultural and commercial contacts with the countries as well.
In the South direction there is Indian Ocean, because of which India is protected from the foreign invasion. But it is also seen that the people of the ancient India also maintained cultural contacts with many of the islands and countries through the sea.
Thus it can be seen that the country was always isolated from the rest of the world but as a matter of fact it always tried to keep in touch with the outer part of the world. Indian subcontinent is not a country but it is actually a vast geographical region whose length from the east to west is about 4,000 km and from the north to south it is about 3,200 km. The vastness of India has resulted in a variety of conditions both geographical and sociological and that is the reason why it has all the variety of climates from the scorching heat of the desert of Rajasthan to the extreme arctic cold of the snow-covered peaks of the Himalayas. The rainfall varies from the peak to the plains while there is also variation in the flora and fauna. India`s vast and varied resources have been utilized for economic self-sufficiency and independence.















