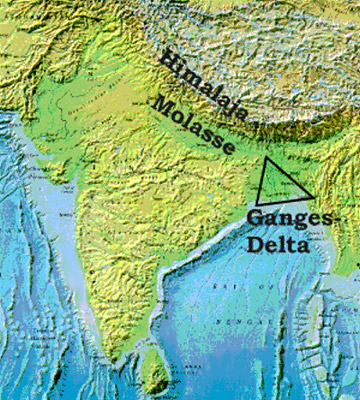
 The Ganges Delta is also called the Sunderban Delta or the Bengal Delta. The Delta of River Ganges is one of the largest river deltas in the South Asia region of Bengal, comprising Bangladesh and the state of West Bengal, India. It is the world`s largest delta, and flows into the Bay of Bengal. The Ganges delta is also one of the most fertile regions in the world and is thus called The Green Delta. The delta, also known as the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, since it extends from the Hoogli River on the west to the Meghna River on the east. The length of this delta is approximately 220 miles or 350 km across at the Bay of Bengal. Kolkata and Haldia in India and Mongla in Bangladesh are the major seaports on the delta. The Ganges Delta arises from the confluence of Padma or the Lower Ganges, Jamuna or Lower Brahmaputra and Meghna.
The Ganges Delta is also called the Sunderban Delta or the Bengal Delta. The Delta of River Ganges is one of the largest river deltas in the South Asia region of Bengal, comprising Bangladesh and the state of West Bengal, India. It is the world`s largest delta, and flows into the Bay of Bengal. The Ganges delta is also one of the most fertile regions in the world and is thus called The Green Delta. The delta, also known as the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, since it extends from the Hoogli River on the west to the Meghna River on the east. The length of this delta is approximately 220 miles or 350 km across at the Bay of Bengal. Kolkata and Haldia in India and Mongla in Bangladesh are the major seaports on the delta. The Ganges Delta arises from the confluence of Padma or the Lower Ganges, Jamuna or Lower Brahmaputra and Meghna.
The Shape and composition of Ganges Delta -
The Ganges delta resembles the shape of a triangle, and is considered to be an "arcuate" delta or the arc-shaped one. The delta covers more than 105,000 km², and although the delta lies mostly in Bangladesh and India, majority of the rivers from Bhutan, China, India and Nepal flow into it from the north. Approximately two-thirds of the delta lies in Bangladesh. Most of the delta is made up of alluvial soils, with red and red-yellow leterite soils. The concentration of leterite soil gets higher as one heads farther east. The soil, minerals and nutrients are good for agriculture.
The Ganges delta is composed of a maze of waterways, lakes, swamps and flood plain sediments, called the Chars. The Ganges delta is divided into two parts, namely the eastern or the active region and the western or the less active part.
The Ganges delta is populated between 125 and 143 million inhabitants. These people live on the delta, in spite of risks from floods caused by monsoons, heavy overflow from the melting snows of the Himalayas, and tropical cyclones. A large portion of the nation of Bangladesh lies in the Ganges Delta, and most of the country`s people depend on the delta for their survival.
It is believed that more than 300 million people lives and earns in the Ganges Delta and approximately 400 million people permanently reside in the Ganges River Basin, making it the most densely inhabited river basin in the world. Most of the Ganges Delta has a population density of more than 520 people per square mile. Thus the River Ganges delta is considered as one of the most densely populated area on earth.
Agriculture and fishing in Ganges Delta -
 Roughly, two-thirds of the Bangladesh population work in the sector of agriculture, and grow crops on the fertile floodplains of the Ganga delta. The major crops that are grown in the Ganges Delta include tea, jute and rice. Fishing is also a significant activity in the delta region, where fish is a major source of food for many of the people in the region.
Roughly, two-thirds of the Bangladesh population work in the sector of agriculture, and grow crops on the fertile floodplains of the Ganga delta. The major crops that are grown in the Ganges Delta include tea, jute and rice. Fishing is also a significant activity in the delta region, where fish is a major source of food for many of the people in the region.
Cyclones and flooding dangers in Ganga Delta -
In November 1970, the most dangerous tropical cyclone of the 20th century hit the Ganges Delta region. The 1970 Bhola cyclone was the most disastrous one, killing almost 500,000 people with another 100,000 missing. The Guinness Book of World Records anticipated the total loss of human life from the Bhola cyclone to be around 1,000,000. There was another cyclone hit in the delta of 1991 that killed about 138,000 people. This cyclone was popularly known as the 1991 Bangladesh Cyclone.
Since then, the people have been careful while building houses or any other construction on the river delta. The severe flooding is also a problem in the delta. In 1998, the Ganges flooded the delta and killed about 1,000 people, leaving more than 30 million people destitute. The Bangladesh government asked for an aid of around $900 million to help supply the people of the region, as the entire rice crop was demolished.
Climate of Ganges Delta -
The climate of Ganges Delta is the tropical wet climate type and receives between 60 and 80 inches (1.5 to 2 m) of rainfall every year in the western part. Around 80-120 inches (2 to 3 m) rainfall is received in the eastern part. The coolest month of the year is usually January, with April and May being the warmest months among others. Average temperatures in January usually range from 14 to 25 °C and average temperatures in April range from 77 to 95 °F (25 to 35 °C). July is the wettest month in the Ganges delta on average, when over 13 inches of rain falls on the delta and the temperature averages from the zone of Kolkata.
Flora and fauna of Ganges Delta
 Three terrestrial eco zones encompass the delta region of Ganga. The Lower Gangetic plains feature the moist deciduous forests and the eco region covers most of the Gangetic delta region. However, most of the forests have mostly been cleared for agriculture and only small enclaves remain. Thick grove of tall grass, known as canebrakes, grows in wetter zones of the delta. The Sundarbans freshwater swamp forests or the Ecoregions lies very close to the Bay of Bengal. This Ecoregions is often flooded with faintly salty water during the dry season and fresh water during the monsoon season. These forests are often used for intensive agriculture, with only 130 km² of the eco-region`s 14,600 km² protected. Here the delta meets the Bay of Bengal; Sundarbans mangroves form the world`s largest Mangrove eco-region, this area covering an area of 20,400 km² in a long chain of 54 islands. These islands derive their name from the principal mangrove species, Heritiera fomes, which are known locally as sundri or sundari plant. Trees found in the delta include sundari, bamboo, garyan, mangrove palm (Nypa fruticans), and mangrove date palm or the Phoenix paludosa.
Three terrestrial eco zones encompass the delta region of Ganga. The Lower Gangetic plains feature the moist deciduous forests and the eco region covers most of the Gangetic delta region. However, most of the forests have mostly been cleared for agriculture and only small enclaves remain. Thick grove of tall grass, known as canebrakes, grows in wetter zones of the delta. The Sundarbans freshwater swamp forests or the Ecoregions lies very close to the Bay of Bengal. This Ecoregions is often flooded with faintly salty water during the dry season and fresh water during the monsoon season. These forests are often used for intensive agriculture, with only 130 km² of the eco-region`s 14,600 km² protected. Here the delta meets the Bay of Bengal; Sundarbans mangroves form the world`s largest Mangrove eco-region, this area covering an area of 20,400 km² in a long chain of 54 islands. These islands derive their name from the principal mangrove species, Heritiera fomes, which are known locally as sundri or sundari plant. Trees found in the delta include sundari, bamboo, garyan, mangrove palm (Nypa fruticans), and mangrove date palm or the Phoenix paludosa.
Animals in the delta are of diverse nature and include the rare Bengal tiger, the Indian python, Asian elephant, Clouded leopard and crocodiles, which live in the Sundarbans. Approximately 1,020 Bengal tigers dwell in the Sundarbans.
 It was once estimated that 30,000 spotted deer inhabits the Sundarbans part of the delta. Birds found in the delta are the kingfishers, eagles, swamp partridges, woodpeckers, shaliks, and the doel or the magpie robin. Two species of dolphins can also be found in the delta: the Irrawaddy dolphin, and the Ganges River Dolphin. The Irrawaddy dolphin is not actually a river dolphin, but enters the delta from the Bay of Bengal. The Ganges River Dolphin is an extremely rare, true river dolphin.
It was once estimated that 30,000 spotted deer inhabits the Sundarbans part of the delta. Birds found in the delta are the kingfishers, eagles, swamp partridges, woodpeckers, shaliks, and the doel or the magpie robin. Two species of dolphins can also be found in the delta: the Irrawaddy dolphin, and the Ganges River Dolphin. The Irrawaddy dolphin is not actually a river dolphin, but enters the delta from the Bay of Bengal. The Ganges River Dolphin is an extremely rare, true river dolphin.
The people living on the Ganges Delta may face in coming years, the threat of rising sea levels because mostly by submergence in the region and partly by climate change. An increase of half a meter of the water level could result in around six million people losing their homes in Bangladesh. Higher temperatures related to climate change can also bring about harsher flooding of the delta, due to increased melting of snow and glaciers in the Himalayas.
Important gas reserves have been exposed in the delta, which could play a vital role in the future of the region, and hopefully help to lift many of the poor people living in the delta amidst poverty. Several major oil companies have invested in developing the Ganges delta region.



















