 Forest Resources in India relate to the distinctive topography, terrain, wildlife, climate and vegetation of the country. Forest resources in India have always been one of the richest resources. Forests provide renewable natural resources and contribute considerably to the economic development of the nation. Forest plantations comprise a vital part of the forest resources. Most of the wood produced in India is obtained from the forest reserves. The forest resources of the country are ancient in nature and composition, since the nation was once covered with dense forests. The history of forest resources in India is evident in the ancient texts all of which have some mention of these forests. The people honoured the forests and a large number of religious ceremonies focused on trees and plants. Their early reference dates back to around 4000 years. Agni Purana states that man should protect forest resources to have material gains and religious blessings. Around 2500 years ago, Lord Buddha preached that man should plant a tree every 5 years.
Forest Resources in India relate to the distinctive topography, terrain, wildlife, climate and vegetation of the country. Forest resources in India have always been one of the richest resources. Forests provide renewable natural resources and contribute considerably to the economic development of the nation. Forest plantations comprise a vital part of the forest resources. Most of the wood produced in India is obtained from the forest reserves. The forest resources of the country are ancient in nature and composition, since the nation was once covered with dense forests. The history of forest resources in India is evident in the ancient texts all of which have some mention of these forests. The people honoured the forests and a large number of religious ceremonies focused on trees and plants. Their early reference dates back to around 4000 years. Agni Purana states that man should protect forest resources to have material gains and religious blessings. Around 2500 years ago, Lord Buddha preached that man should plant a tree every 5 years.
History of Forest Resources in India
In the year 1806, Captain Watson was appointed as the commissioner of forest resources in India. He was responsible for organising the production of teak and other timber appropriate for the building of ships. Forest management in the country was chiefly aimed at producing commercial products like teak timber. Even nowadays, huge territories of forest resources in the country are enclosed with teak plantations. Further, in the year 1855, Lord Dalhousie outlined regulations for protection of forest resources in India. In Malabar hills, Teak plantations were raised and in the Nilgiri Hills, Acacia and Eucalyptus were raised. From 1865 to 1894, forest resources in India were established for protecting material for imperial needs. From the 18th century, scientific forest management systems were engaged to regenerate and yield the forest resources in India to make it sustainable.
Importance of Forest Resources in India
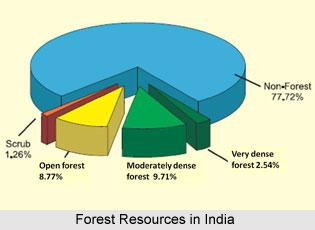
During the early 1990s about 17% of forest resources in India land were dense forestland. However, as around 50 % of this land was infertile, total region under productive forests was nearly 35 million hectares that is around 10 % of the total land area of the country. With the increasing demand of the growing population of the country the requirement of forest resources also increased. All these resulted in the continuing demolition of forests around the 1980s, taking a serious toll on the soil. Moreover, around 1990`s several forest resources experienced heavy rainfall, and many forests were in regions with a high altitude and some of them were inaccessible. Around 20% of the total area under forests is in the state of
Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Orissa, Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh. Forest vegetation is diverse and really large in the country. Like for instance, there are nearly 600 species of hardwoods, Sal and teak. These are the principal species.
National Forest Policy of 1988, concentrated on the importance of forest resources as a significant part of the economy and ecology of the nation. This policy particularly focused on ensuring stability of the environment, maintaining ecological balance and preserving the forests. Further, the Forest Conservation Act of 1980 was also amended in the year 1988 for facilitating stricter protection measures in the country.
Uses of Forest Resources in India
Wood is the main product obtained from Forest resources in India. Wood is generally utilised as fuel and as raw material of different manufacturing sectors like furniture items, paper, plywood, musical instruments, packing materials and crates, sports items, toys, vehicle parts, boats, railway sleepers, buildings, bridges, fodder for cattle etc. Bamboo, another type of wood, is extensively used for various purposes. There are also various by-products of Forest resources in India like Rubber, Gums, Tannins, Resins, Camphor, Canes, Fibres, Dyes, Medicines, Essential Oils, Medicines, Flocs and Spices etc. Moreover, various types of products are also obtained from various types of insects and wildlife that take shelter in the forests. Forest resources in India are also a major source of food items.
Forest Resources in India provides protection to environment and wildlife. It also enhances water holding capacity of soil and rainfall, helps in gaseous cycles of atmosphere, maintains the soil fertility, checks soil erosion, reduces flood disaster etc. Eventually, people have realised the significance of forests resources and the fact that deforestation threatens the ecology. Thus, people have become more interested and involved in conservation of forest resources in India.



















