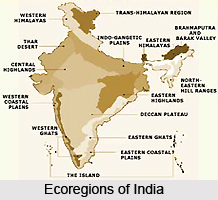
 Eco-region is a vast piece of land or water with no fixed and distinct boundaries. The region has a collection of species, natural communities and environmental conditions that can be called geographically distinct. The Indian subcontinent is also blessed with a great diversity of eco-regions, which ranges from land covered with snow and ice to the tropical rainforests. Some of these eco-regions are given below.
Eco-region is a vast piece of land or water with no fixed and distinct boundaries. The region has a collection of species, natural communities and environmental conditions that can be called geographically distinct. The Indian subcontinent is also blessed with a great diversity of eco-regions, which ranges from land covered with snow and ice to the tropical rainforests. Some of these eco-regions are given below.
Tropical and Subtropical Moist Broadleaf Forests
The first variety of eco-region found in India is the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests. Under this category, several forests have been classified.
Andaman Islands Rain Forests
Andaman Islands Rain Forests belong to the category of Tropical and Subtropical Moist Broadleaf Forests.
Brahmaputra Valley Semi Evergreen Forest
Brahmaputra Valley Semi Evergreen Forest is found in eastern India and southern Bhutan. It encompasses an area of about 56,700 square kilometers.
Chin Hills Arakan Yoma Montane Forests
Chin Hills Arakan Yoma Montane Forests are spread over an area of about 29,700 square kilometers and includes many Himalayan species and many endemic species.
Eastern Highlands Moist Deciduous Forests
Eastern Highlands Moist Deciduous Forests were the home to the Asian elephants, which have become extinct from the region.
Himalayan Subtropical Broadleaf Forests
Himalayan Subtropical Broadleaf Forests are spread over India, Nepal and Bhutan.
These forests encompass an area of about 38,200 square kilometers.
Lower Gangetic Plains Moist Deciduous Forests
Lower Gangetic Plains Moist Deciduous Forests are spread over Bangladesh and eastern India.
Malabar Coast Moist Forests of Southwestern India
Malabar Coast Moist Forests of Southwestern India have been largely cleared for agriculture, grazing and teak plantations.
Meghalaya Subtropical Forests of Eastern India
Meghalaya Subtropical Forests of Eastern India have rich and abundant wildlife.
North Western Ghats Moist Deciduous Forests
North Western Ghats Moist Deciduous Forests are positioned in the southwestern part of India and spread over an area of 48,200 square kilometers.
South Western Ghats Moist Deciduous Forests
South Western Ghats Moist Deciduous Forests covers the southern portion of the Western Ghats range and the Nilgiri Hills.
North Western Ghats Montane Rain Forests
North Western Ghats Montane Rain Forests are dominated by the trees of the laurel family.
South Western Ghats Montane Rain Forests
South Western Ghats Montane Rain Forests are the home to numerous endemic species.
Odisha Semi Evergreen Forests
Odisha Semi Evergreen Forests lie in the coastal plains of Odisha covering an area of about 22,300 square kilometers.
Sundarbans Freshwater Swamp Forests
 Sundarbans Freshwater Swamp Forests are spread over an area of about 14,600 square kilometers.
Sundarbans Freshwater Swamp Forests are spread over an area of about 14,600 square kilometers.
Tropical and Subtropical Dry Broadleaf Forests
Tropical and Subtropical Dry Broadleaf Forests are another variety of eco-region found in India. Under this category, several forests have been classified.
Central Deccan Plateau Dry Deciduous Forests
Central Deccan Plateau Dry Deciduous Forests belong to the category of Tropical and Subtropical Dry Broadleaf Forests and occupy an area of about 240, 200 square kilometers.
Chota Nagpur Dry Deciduous Forest
Chota Nagpur Dry Deciduous Forest is located in the Chota Nagpur Plateau covering the states of Jharkhand, Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
East Deccan Dry Evergreen Forests
East Deccan Dry Evergreen Forests are located in the southeastern region of India and spread over an area of about 25,500 square kilometers. It is a home to two important wetlands namley, the Kaliveli Lake in Viluppuram district of Tamil Nadu and Pulicat Lake in the north of Chennai.
Kathiawar Gir Dry Deciduous Forest
Kathiawar Gir Dry Deciduous Forest is a home of top predatory animals like Asiatic lion, Bengal tiger, leopard and Indian wolf.
Narmada Valley Dry Deciduous Forest
Narmada Valley Dry Deciduous Forest lies mostly in the state of Madhya Pradesh and is a home to 76 species of mammals.
Northern Dry Deciduous Forests
Northern Dry Deciduous Forests extend across the Indian states of Bihar, Odisha and Madhya Pradesh.
South Deccan Plateau Dry Deciduous Forest
South Deccan Plateau Dry Deciduous Forest is characterized by tall trees that drop their leaves during the dry winter and spring months.
Tropical and Subtropical Coniferous Forests
Tropical and Subtropical Coniferous Forests are the third variety of eco-region found in India.
Himalayan Subtropical Pine Forests
Himalayan Subtropical Pine Forests are characterized by the drought resistant chir pine.
Northeast India - Myanmar Pine Forests
Northeast India - Myanmar Pine Forests are dominated by the Tenasserim Pines at lower elevations and Khasi Pines and Blue Pines at higher elevations.
Temperate Broadleaf and Mixed Forests
The next variety is the Temperate Broadleaf and Mixed Forests. They are spread over an area of about 83, 100 square kilometers and are characterized by diverse and abundant wildlife. The eco-region has two predominant forest types namely, the Evergreen Forests and the Deciduous Forests.
Evergreen Forests
Evergreen Forests are characterized by oaks.
Deciduous Forests
Deciduous Forests are dominated by Betula alnoides, Juglans regia and Betula utilis.
Western Himalayan Broadleaf Forests
Western Himalayan Broadleaf Forests also belong to the category of Temperate Broadleaf and Mixed Forests.
Temperate Coniferous Forests
Eastern Himalayan Sub-Alpine Conifer Forests and the Western Himalayan Sub-Alpine Conifer Forests belong to the category of Temperate Coniferous Forests.
Tropical and Subtropical Grasslands, Savannas and Shrublands
Under the category of Tropical and Subtropical Grasslands, Savannas and Shrublands comes the Terai-Duar Savanna and Grasslands.
Montane Grasslands and Shrublands
Montane Grasslands and Shrublands include the Eastern Himalayan Alpine Shrub and Meadows, Karakoram-West Tibetan Plateau Alpine Steppe, Northwestern Himalayan Alpine Shrub and Meadows and the Western Himalayan Alpine Shrub and Meadows.















