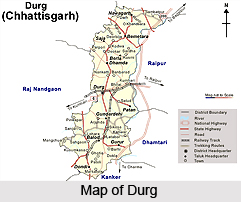
 Durg is located in the Southwestern part of Chhattisgarh State. It is located 317m above sea level. The geographical area of Durg is 8702 Sq km. The district occupies the southwestern part of the Chhattisgarh plain and possesses belts of hilly country in the south, southwest and northwest that are rich with mineral resources and forests. The District occupies the southwestern part of the Upper Sheonath-Mahanadi valley and the bordering hills in the south and southwest. Geographically, the district can be divided into two divisions as the Chhattisgarh plain and the Southern plateau. The Chhattisgarh plain occupies the largest area in the District. The slope of the district is towards west.
The major rivers of the district are Sheonath and Kharun. Sheonath river flows nearer to the western border of the district whereas river Kharun forms the eastern border of the district which ultimately joins Sheonath river. The three main seasons of Durg are summer, winter and rainy season. The average rainfall of Durg is 1071.16. Maximum, Average & Minimum Rain fall Of District Durg are 1477.2 mm, 1071.16 mm and 781.5 mm per year respectively.
Durg is located in the Southwestern part of Chhattisgarh State. It is located 317m above sea level. The geographical area of Durg is 8702 Sq km. The district occupies the southwestern part of the Chhattisgarh plain and possesses belts of hilly country in the south, southwest and northwest that are rich with mineral resources and forests. The District occupies the southwestern part of the Upper Sheonath-Mahanadi valley and the bordering hills in the south and southwest. Geographically, the district can be divided into two divisions as the Chhattisgarh plain and the Southern plateau. The Chhattisgarh plain occupies the largest area in the District. The slope of the district is towards west.
The major rivers of the district are Sheonath and Kharun. Sheonath river flows nearer to the western border of the district whereas river Kharun forms the eastern border of the district which ultimately joins Sheonath river. The three main seasons of Durg are summer, winter and rainy season. The average rainfall of Durg is 1071.16. Maximum, Average & Minimum Rain fall Of District Durg are 1477.2 mm, 1071.16 mm and 781.5 mm per year respectively.
History of Durg
Durg was part of Dahshina Kosala or Southern Kosala. In the epics, it is mentioned that King Dasharatha of Uttara Kosala married Kosalaya, the princess of Dakshnia Kosala. During the 4th century, Huien Tsang, the Chinese traveler visited Southern Kosala . However the name `Durg, came into existence in the 8th century A.D. through the stone inscriptions found in Durg. The first inscription mentions the name of a king Shiva Deva. The 2nd inscription associates the name of Sivapura with that of Shiva Durga, indicating thereby that during Shivadeva`s reign the town and the fort were separate.
The present name of the city "Durg" is evidently a contraction of the old Shivadurga, which he built. Durg stands on the banks of the "Shiva River."
In 1182 AD, there was the advent of Kalachuri dynasty in Durg. From then on it remained under the Kalachuries, till 1742 A. D, when the Marathas deposed them. In 1877, after the Marathas lost the third Anglo- Maratha War, the tract of Chhattisgarh passed into British hand. For the purpose of administration, Durg was attached to Bhandara District. In 1857 Durg was separated and made into a tehsil of Raipur district.
Ddurg became a separate district in 1906. During the freedom struggle, Durg was a center of nationallist activites. Prominent leaders including Mahatama Gandhi, Pt. Jawahalal Nehru and Dr. Rajendra Prasad visited Durg during the freedom struggle.
Culture of Durg
The people of Durg are fashionable and are interested in new trends and life styles. People from all over the world have come and settle here and hence it is a society having multi cultural people. Simplicity ,kind hearted ness and adaptability are the traits of the people of Durg.
The people are very fond of colors and they like wearing colorful dresses. Women wear sarees with Kardhani. In rural areas women wear mala made of one rupee coin. Durg is rich in its cultural heritage. The famous dances of Durg are Panthi and Soowa dance styles.
The different types of Scheduled tribes found at Durg are Gond, Kanver, Uraon, Korva, Kol, Bhariya, Binjhwar, Sawar, Dhanwar, Madiya. People of Durg celebrate dance, music, marriage and other cultural festivals like Navakhani, Ganga Dushhara, Sarhul Chherka, Dushara, Dipawali, Karma & Kartika. Durg`s most famous and popular folk plays are Chandaini-Gonda, Sonha-Bihan, Lorik-Chanda, Kari, Hareli, Gammatiha. Rahas is a modern folk drama of Durg.
Economy of Durg
The people of Durg are mainly farmers. Paddy is the major crop cultivated here. Other crops cultivated here are jowar and maize. The oil seeds cultivated here are l soyabean, gropundnut and sunflower. Iron ore is the major mineral product of Durg. There are 314 registered industries at Durg.
Divisions of Durg
The subdivisions of Durg are Dondi lohara, Balod, Patan, Saja, Bemetara and Durg.
Transportation of Durg
Durg is connected to other cities by means of air, rail and road. The nearest airport from Durg is at Mana (Raipur). The District is well connected by roads. The National Highway No. 6 traversing the district is the Mumbai-Calcutta G. E. Other important roads of district are Durg-Dhamdha-Bemetara Road. Kawardha-Bemetara- Simga Road, Kumhari-Patharia Road, Rajnandgaon-Antagarh Road, Durg-Utai Road etc. Durg town is favorably situated on the main line of the South Eastern Railway, whickh lies midway between Mumbai-Calcutta. The National Highway No. 6 is the major highway of the district and the train route is the main line of the South Eastern Railway midway between Mumbai-Calcutta. Nearest airport from the District Headquarter Durg is at Raipur.



















