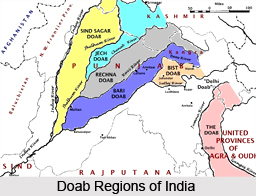
 The term Doab in Persian stands for two waters while the term in India or Pakistan connotes a "tongue"or tract of land lying between two confluent rivers. The Doab designates the flat alluvial tract between the Ganges and Yamuna rivers in western and southwestern Uttar Pradesh state, extending from the Shivalik Range to the rivers` confluence at Allahabad. This well-irrigated region is the greatest wheat growing area of the state.The Doab has an area of about 23,360 square miles (60,500 square km). It lies between the Ganges and Yamuna rivers. The doab is about 500 miles (800 km) in length and 60 miles (100 km) in width.
The term Doab in Persian stands for two waters while the term in India or Pakistan connotes a "tongue"or tract of land lying between two confluent rivers. The Doab designates the flat alluvial tract between the Ganges and Yamuna rivers in western and southwestern Uttar Pradesh state, extending from the Shivalik Range to the rivers` confluence at Allahabad. This well-irrigated region is the greatest wheat growing area of the state.The Doab has an area of about 23,360 square miles (60,500 square km). It lies between the Ganges and Yamuna rivers. The doab is about 500 miles (800 km) in length and 60 miles (100 km) in width.
When the Aryans moved from Punjab they first settled in the Doab along the Ganga river till Prayag. Prayag is situated at the confluence of the holiest rivers of the Hindus, the Ganga and the Yamuna The Doab was also the central location in the Vedic age . Although the focus of Rig-vedic culture was the Punjab area; in the later Vedic texts it was the Doab, the region between the Yamuna and Ganga (Ganges) rivers which became the heart of brahmanic civilization.In the Mahabharata ,Hastinapur the capital of the Kuru tribe was located in upper Ganges doab At present the following districts form part of the Doab:Dehradun, Rishikesh, Saharanpur, Muzaffarnagar, Meerut, Delhi, Ghaziabad, Gautam Buddha Nagar, Bulandshahar, Mathura, Aligarh, Etah, Agra, Mainpur, Etawah, Farrukhabad, Kanpur, Fatehpur, Kaushambi and Allahabad.



















