 Indian demography entails the population living in different states of the nation. India is a country of great diversity, with a wide range of landforms (like mountain ranges, hilly jungle regions, deserts and coastal plains), which affect the lives of the citizen. The demography of India is remarkably diverse. It includes various aspects of the population like population density, education level, economic status, religious affiliations, health, etc. Diversity is evident in the geographical distribution of India`s linguistic groups. Great variation occurs across the Indian population on social parameters such as income, which is also a part of Indian demography. Some of the aspects of Indian demography are described below.
Indian demography entails the population living in different states of the nation. India is a country of great diversity, with a wide range of landforms (like mountain ranges, hilly jungle regions, deserts and coastal plains), which affect the lives of the citizen. The demography of India is remarkably diverse. It includes various aspects of the population like population density, education level, economic status, religious affiliations, health, etc. Diversity is evident in the geographical distribution of India`s linguistic groups. Great variation occurs across the Indian population on social parameters such as income, which is also a part of Indian demography. Some of the aspects of Indian demography are described below.
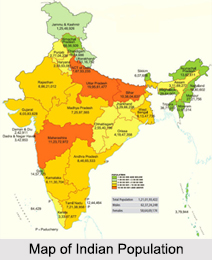
Indian Population
India occupies 2.41 percent of the world`s land area. According to the 1991 national census, Indian population was approximately 846.3 million. Around 38 percent of all Indians were officially listed as living below the poverty line in 1991. This percentage represented an increase from the low mark of 26 percent in the fiscal year 1989. India has more arable land area than any country in the world, except the United States. The lifestyle of the people of India therefore revolves mostly around agriculture and associated activities in small villages. The annual population growth rate from 1981 to 1991 was 2 percent. Every sixth person in the world during the early 1990s was an Indian. In July 1995, the population in India was estimated to be 936.5 million. The 2001 census reported that 72.2 percent of the population of India lived in about 638,000 villages and the remaining 27.8 percent lived in about 5,100 towns and about 380 urban settlements.
In 2008, India"s population was 1.197 billion, growth rate was 1.578 percent, birth rate was 22.22 births/1,000 population, death rate was 6.4 deaths/1,000 population, life expectancy was 69.25 years (for male-66.87 years and for female- 71.9 years) and fertility rate was 2.76 children born/ woman. As of 2017, India`s population of 1.34 billion is almost 17.85 percent of the world`s population. It is important to note that more than 50 percent of India"s population is below the age of 25 and more than 65 percent of its population is below the age of 35. Considering the fact that India is the second most populous country in the world, family planning programs are vital. Although family planning programs have become integrated with the programs of urban and rural health clinics, no official birth control programs have received widespread support in India.
Indian Languages
1,652 languages and dialects are spoken in India. There are two major families of languages in India namely, the Indo-Aryan and Dravidian languages. Other families are Indo-European, Austro-Asiatic, Tibeto-Burman languages, etc. A language of India namely, the Nihali language is called a language isolate, spoken in parts of Maharashtra. 40 percent of the Hindus are known to speak Hindi, while the rest speak Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada and other languages. Almost 70 percent of the Muslims speak Urdu while the rest speak Kashmiri, Telugu, Malayalam, Bengali, Tamil, Gujarati and other languages.
Indian Education System
Improvements in the education system in India have been substantial since independence in 1947. In the mid-1990s, only about 50 percent of children between the ages of six and fourteen were enrolled in schools. Important achievements were obtained in the domain of education in India with the implementation of non-formal education system and adult education programs. As mentioned in the Indian constitution, free and compulsory education is provided to children between the ages of six and fourteen, as a fundamental right. According to the census of 2011, the national literacy rate in India is 74.07 percent. About 152 central universities, 316 state universities and 191 private universities in India take care of the higher education system.
Indian Religions
Indian population is representative of different religions. 79.8 percent of the Indians are Hindus and 14 percent of the population follow Islam, making India home to the third-largest Muslim population in the world.















