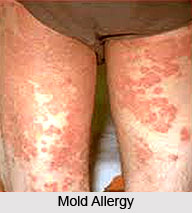
 Contact dermatitis or contact allergy is a localised rash or irritation of the skin caused by contact with a foreign substance. Only the superficial regions of the skin are affected in contact allergy. Inflammation of the affected tissue is present in the epidermis that is the outermost layer of skin and the outer dermis, which is the layer beneath the epidermis. Unlike contact urticaria, in which a rash appears within minutes of exposure and fades away within minutes to hours, contact dermatitis takes days to fade away. Even then, contact allergy fades only if the skin no longer comes in contact with the allergen or irritant. Contact allergy results in large, burning, and itchy rashes, and these can take anywhere from several days to weeks to heal. Chronic contact dermatitis can develop when the removal of the disturbing agent no longer provides expected relief.
Contact dermatitis or contact allergy is a localised rash or irritation of the skin caused by contact with a foreign substance. Only the superficial regions of the skin are affected in contact allergy. Inflammation of the affected tissue is present in the epidermis that is the outermost layer of skin and the outer dermis, which is the layer beneath the epidermis. Unlike contact urticaria, in which a rash appears within minutes of exposure and fades away within minutes to hours, contact dermatitis takes days to fade away. Even then, contact allergy fades only if the skin no longer comes in contact with the allergen or irritant. Contact allergy results in large, burning, and itchy rashes, and these can take anywhere from several days to weeks to heal. Chronic contact dermatitis can develop when the removal of the disturbing agent no longer provides expected relief.
Contact allergy is an allergic skin reaction from contact with a substance that is usually harmless to others. The most common manifestation is an itchy rash that develops over a few days, after skin contact with a substance. The affected area first becomes itchy, then red and swollen with vesicles (water bubbles). Occasionally the rash is more chronic, manifesting as an itchy patch that does not heal for weeks or even months. This usually occurs when there is frequent contact with the substance. The rash resulting from contact allergy is called allergic contact dermatitis.
A substance that can cause contact allergy is called a contact allergen and the most common ones are metals like nickel in watch straps, chrome in cement, skin care products like fragrances, lanolin and medication like flavine, neomycin. Skin test called patch test is used to confirm contact allergy. Usually the upper back is used as a test site. A small amount of the suspected contact allergen in diluted to a non-irritant concentration is applied onto the skin in an aluminium chamber and sealed with hypoallergenic tape. Usually, several suspected allergens are tested all together. They are left on the skin for 48 hours and read after 96 hours. A positive reaction indicates that he patient is allergic to the test substance.
Treatment of contact allergy at the first place suggests removing the cause i.e. the allergen from skin contact results in cure. Usually, once allergy to a substance has developed, it remains for lifetime. That is to say, future contact with the substance will result in aggravated allergic contact dermatitis. This resembles the steps of a drug allergy. It is advisable for patients to carry a card to remind themselves and their doctors of their contact allergy. Irritant dermatitis is the most common type of contact allergy that involves inflammation resulting from contact with acids, alkaline materials such as soaps and detergents, solvents, or other chemicals. The reaction of this kind of contact allergy often resembles a burn. The second most common type of contact allergy is caused by exposure to a material to which the person has become hypersensitive or allergic. The skin inflammation varies from mild irritation and redness to open sores, depending on the type of irritant, the body part affected, and the contact allergy of the individual. Over treatment dermatitis is a form of contact allergy that occurs when treatment for another skin disorder causes irritation.
 Maintaining a history is equally important after patch testing of contact allergy. Only history and questioning can determine whether the materials to which a patient is allergic are partly or wholly responsible for the current dermatitis.
Maintaining a history is equally important after patch testing of contact allergy. Only history and questioning can determine whether the materials to which a patient is allergic are partly or wholly responsible for the current dermatitis.
The prime symptoms of contact allergy are as follows -
•Red rash appears immediately in irritant contact dermatitis. In case of allergic contact dermatitis, the rash sometimes does not appear until 24-72 hours after exposure to the allergen.
•Blisters or wheals often form in a pattern where skin was directly exposed to the allergen or irritant.
•Itchy, burning skin tends to be more painful than itchy, while allergic contact dermatitis often itches.
Irritant contact dermatitis often affects the hands, which have been exposed by resting in or dipping into a container like sink, pail, tub, Sun, Swimming Pools with high chlorine containing the irritant. Self-care can be taken at home to prevent contact allergy.
Some of the methods are as follows
•Immediately after exposure to a known allergen or irritant, one should wash the body with soap and cool water to remove or inactivate most of the offending substance.
•Weak acid solutions like lemon juice or vinegar can be used to neutralise the effects of dermatitis contracted by exposure to basic irritants.
•Oral antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl, Ben-Allergin) can also relieve itching.
•If blistering develops, cold moist compresses can be applied for 30 minutes 3 times a day that can offer relief.
•Calamine lotion, neem paste, mint paste and cool colloidal oatmeal baths may relieve itching.
•One should avoid scratching, as this can cause secondary infections.
Medicinal treatment for contact allergy is required if the rash does not improve or continues to spread after 2-3 of days of self-care, or if the itching or pain is severe, the patient should consult a dermatologist or other physician or physician assistant. Medical treatment usually consists of lotions, creams, or oral medications. Since contact allergy relies on an irritant or an allergen to initiate the reaction, it is important for the patient to identify the responsible agent and avoid it. Having patch tests can solve this problem or a method commonly known as allergy testing. The patient must know where the irritant or allergen is found to be able to avoid it. It is important to also note that chemicals sometimes have a series of different names.