About Mandir Vastu
 Agni Purana believes that a temple should be constructed with a lot of precision and care. A lot of things should be kept in mind while erecting the structure of a temple. Lord Agni has described in a perfect manner the Vastu that is involved in the construction of a temple. Adhyaya ninety three of the Purana gives an account of the temple Vastu.
Agni Purana believes that a temple should be constructed with a lot of precision and care. A lot of things should be kept in mind while erecting the structure of a temple. Lord Agni has described in a perfect manner the Vastu that is involved in the construction of a temple. Adhyaya ninety three of the Purana gives an account of the temple Vastu.
The description begins saying that the plot of land on which the divine edifice will be erected should be square in shape and should be divided into sixty-four rectangular chambers. Poles of Bamboo should be driven into the four cardinal points of the ground and the strings should be laid down across the eight angular points thereof. The gods respectively occupying the two and six chambers of the ground should be jointly worshipped jointly with the Vastudevata. At the time of worship, the preceptor should meditate upon the Vastudevata in the sacrificial fire receptacle.
It is advised in Agni Purana that the thighs and knee-joints of the god should be considered lying towards the north-west and the southern corner of the chequered ground. The soles of his feet lie towards the south and his head is towards the north-west. The two of his palms lie blended in the attitude of prayer on his heart. It is believed that all the gods should be worshipped as located in the Vastu and only then the worshipper would be able to attain bliss.
Vastu in the Puran states that the Rishis such as Marichi should occupy six chambers of the diagram counted from the east and four such chambers in the middle of the ground should be assigned to and set apart for Lord Brahma, while the rest of the gods should respectively occupy a single chamber. Every god should be offered with a sacrificial porridge while the construction of a temple in the form of oblation.
Lord Agni narrates that a divine place or a temple which is erected also with a purpose of sacrifice, in that the diagram should be divided into hundred and thirty-four square-shaped chambers or divisions. Sixty four out of which shall be dedicated to Brahma and the Rishis. The gods such as Isana should have nine chambers assigned to each of them; the gods such as Skanda should have eight chambers. The demonesses such as Charaki should also have eight chambers dedicated to them. The rite of Nyasa is a necessity to be performed in the erection of a divine space. It is advised that the rectangular diagram may be inscribed within a triangle, a hexagon or a circle and the Nyasa should be performed in the excavation encircling the same as on the stone slab known as Bramha-shila.
The Fire-God while describing the Vastu of a temple states that the diagram should measure five cubits in the absence of any specific measurement. It is believed that this particular measurement is the most recommended one for a divine mansion.
Vastu Shastra for Temple Interiors
 In the modern world of today, knowledge of Science and Nastikavada is increasing rapidly. At the same time, the construction of temples, religious associations, Pithas or centres of spiritual teachings and of astrology are also growing, as modern science can provide man only with physical comfort and not spiritual happiness. More and more people are getting interested in the scriptures and philosophy as they are struggling for the achievement of spiritual happiness and peace.
In the modern world of today, knowledge of Science and Nastikavada is increasing rapidly. At the same time, the construction of temples, religious associations, Pithas or centres of spiritual teachings and of astrology are also growing, as modern science can provide man only with physical comfort and not spiritual happiness. More and more people are getting interested in the scriptures and philosophy as they are struggling for the achievement of spiritual happiness and peace.
There is a close relationship between the planers and idols according to ancient Hindu tradition. Planet (graha) means that which receives. Idol means that which transmits power that has been received from Graha. According to Hindu Astrology, the nine planets rule the eight directions. It is proved that each idol, which receives power from its concerned planet, radiates only the concerned directional power. The combined power of the idol in the eight directions is called Akhilandeswari or Adi-para-sakti.
The shape of the Adi-para-sakti is that of an elliptical atom or dirghanda-vritta. The shape of each idol, as ruler of a particular direction, is that of one sub-atom. The rectangle and square in geometry have an important place in Vastu Shastra. The atom-shaped ellipse can be inscribed in a rectangle. So the rectangle is the form of Asta-padma or Octagonal lotus, and the sign of the power of eight directions. The square is the form of sub-atom, in the Octagonal lotus, or asta-dala-padma and it is the sign of power of one direction. As per the above theory, it is proved that the house-site which is the shape of the complete Octagonal lotus and the sign of an atom should be in the form of a rectangle.
The temple site which is the shape of only a petal of the Octagon and the sign of only a sub-atom should be in the form of a square. Site area or Aydma means the house-site or temple-site which is correctly marked as per the mariner`s compass. Both the sanctum sanctorum of the temple, and the Mandapa constructed before it, should be in the shape of squares. Then only does the temple completely radiate the sub-atom power of that direction.
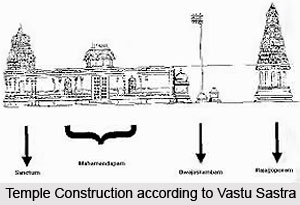
According to Vastu Shastra the sanctum sanctorum should be in the shape of a square, inner length and breadth of which is six feet. The width of the wall of the sanctum sanctorum must be two feet each only, and it should be the same on all the four sides. The construction of a Mandapa before the sanctum sanctorum is a must.
The whole temple, i.e. the sanctum sanctorum and the Mandapa, should be constructed in the correct direction using magnetic compass. The idol of 6 feet height should be installed in the middle of the sanctun sanctorum or garbhagriha. If the height of the idol is less, the pedestal should be raised sufficiently to obtain this height. The Dhwaja Stambha should be perpendicular and directly opposite the idol. The base of the idol and the Dhwaja should be of equal height. At the same height as the middle point between the eyebrows of the idol, there should be carved on the Dhwaja three vertical marks or the middle point between the eyebrows of a bowing man. A line making an angle of 22.5 degrees with the normal sight line of the idol should cut exactly the top of the Dhwaja. Thus, the height of Dhwaja is fixed. A hole should be made in the roof of the Mandapa where the line of the above angle touches the roof. The middle point between the eyebrows of the idol, the hole in the roof and the top of the Dhwaja should be in the same line. The above angel line when extended should reach the top of the Kalasa the Gali-Gopuram. Thus, the Gali-Gopuram should be constructed at a convenient distance. As the earth axis makes an angle of 22 degrees with the Sun, the small hole, the top of the Dhwaja and the top of the Gali-Gopuram should be in a line making an angle of 22 degrees with the normal sight line of the idol for the correct powerful radiation of the directional power.
The idol of God enjoys sixteen phases completely when the temple is constructed in the right direction. So the idols should be installed exactly towards the middle point of the concerned direction. Even if the idol is installed to the left side (ascending direction) of the mid-point of the concerned direction, nothing happens. But is the idol is installed to the right side of the mid-point (descending direction) of the concerned direction, the installation is completely useless and the idol has no power at all. In the former situation the Sun`s directional power reaches the middle point, between the eye-brows of the idol, which relates its power-on the Prasadam. In the latter situation even if the Sun`s directional power reaches the mid-point between the eye-brows of the idol, it is of no use as the idol does not radiate its power on the Prasadam.
Finally in conclusion it has been said that unless the principles of Vastu are followed in the interiors of the temple the lord of the temple will not receive regular worship and the donors of the temple will suffer from illness.
Vastu Shastra of Karnataka Temples
 Vastu Shastra includes all types of constructions, including palaces, public buildings, halls, tanks, etc., the majority of surviving structures of ancient days are temples. Hence Vastu-Shilpa generally means the study of temple architectures. Devalaya Vastu is the appropriate word to indicate temple and its architecture. It partly includes sculpture as iconographic details also form part of temple construction.
Vastu Shastra includes all types of constructions, including palaces, public buildings, halls, tanks, etc., the majority of surviving structures of ancient days are temples. Hence Vastu-Shilpa generally means the study of temple architectures. Devalaya Vastu is the appropriate word to indicate temple and its architecture. It partly includes sculpture as iconographic details also form part of temple construction.
Prasada and its construction are dealt with in architecture, and Pratima is the study of iconography. The word `Shilpa` is often used synonymously with sculptural studies, but it has a different meaning altogether. Sashtra and Shilpa are the two faces of the same coin; the former represents theory and the latter refers to the practice or technique. A systematic study of temples essentially include origin and evolution of temple structures, differentiation of traditions and styles, ornamentation and its archaic types, etc.
In Karnataka Prapa is also known as Prapanga. It is without Adhisthana. It is raised above the foundation. The topmost member of the foundation is Homa. Khatapada or Homastambhas are pegged in the Homa structure. These pillars may be wooden or of bamboo with thatched coconut leaves stretched to cover the top. The whole structure may be made out of stone. Thus the description available is about the structure that provides shelter.
Chatuska is four pillared. It may be an independent structure also. It stands in between Prapa and Mandapa. Chatuska gained importance when it occupied central portion in structures, especially Sabha, which will be described later. Chatuska may be opened or closed. When closed it is covered by Bhitti on all the sides. The Mandapa structure that is seen in Puskarini in Mahdkuta, the Nandi Mandapa in Jyotirlinga group of temples at Aihole is to be identified as Chatuska. Though these structures are generally called Mandapas, they are Chatuskas, the early phase in the development of structures; the Prastara above the pillars is not fully evolved.
Mandapa is next to Chatuska. Mandapa is that which protects the decoration. While describing Mandapa the basic aspect of Vastu, i.e. providing shelter or protection to living beings is lost as it protects decoration. The structure of Mandapa is known as Trivarga.
 The growth and development of Mandapa structure, further, is in two directions, vertical and horizontal. The same is known as Urdhva-krama and Tiryak-krama, respectively. In the Urdhvakrama, Chaturvarga structure is known as Lupakara, Panchavarga is Sabha and Sadvarga is Vimana. The details regarding ancient Lupa and Sabha structures are irretrievably lost and presently available features are also scattered. By virtue of the textual explanation Lupa is identified as Chaturvarga.
The growth and development of Mandapa structure, further, is in two directions, vertical and horizontal. The same is known as Urdhva-krama and Tiryak-krama, respectively. In the Urdhvakrama, Chaturvarga structure is known as Lupakara, Panchavarga is Sabha and Sadvarga is Vimana. The details regarding ancient Lupa and Sabha structures are irretrievably lost and presently available features are also scattered. By virtue of the textual explanation Lupa is identified as Chaturvarga.
Lupa temples have sloppy roof which is the Sikhara portion. They are found in western coastal area. Such temples with modern terminology are built even today in Kerala region. The Sikhara portion is mostly made of wooden structure.
Sabha is known as Panchavarga structure according to southern texts wherein the description is not available. Northern texts like the Aparajita-procha and the Samardngana-sutradhdra, however, have descriptions of Sabha. Before the temples took a definite shape, public buildings were utilised to house gods and goddesses, and Sabha is one such structure which is evident from Ladh Khan Temple of Aihole. This temple has stood as a landmark in Karnataka in the origin and development of temple structure.
Ladh Khan Temple is a larger structure with four massive pillars in the middle to form a Chatuska. It is surrounded by Alinda in two stages. The pillars of outer Alinda are smaller than those of the inner Alinda, The sloppy roof extends over the Alinda structure. The outer pillars are inter-connected by Bhitti-palaka or Jalandra. Kudya-stambhas are seen at the corner. Mukhamandapa with Kaksasana is seen in front which provides entrance through Sopana or steps.
The word Vimana is applied to mean Sikhara and above portion of the temple by some scholars. However, it is evident from the above that it refers to the structure from bottom to top in Sadvarga structures.
The southern texts usually refer to Garbhagriha as Vimana, whereas the northern texts identify them as a Prasada. Several scholars name them as southern Vimana and northern Prasdda, respectively. Vimana is pyramidical and Prasada is curvilinear in outline. The Sadvargas of the Vimana are Adhisthana, Pada, Prastara, Kantha, Sikhara and Stupa.
Constructions of Religious Temples
 Vastu Shastra, the ancient science of architecture has also laid some basic rules for the construction of the temples. Some of them are as follows:
Vastu Shastra, the ancient science of architecture has also laid some basic rules for the construction of the temples. Some of them are as follows:
Site for Temple Construction: It is very important to choose a proper site for building religious Vastu temples. A plot where there is a sea, river, tank, lake etc. in the east or the north direction. Such a plot is the best place as there is natural slope in the east or the north directions.
Plot for Temple Construction: The plot of the temple should be square or rectangular in shape. The magnetic north-south poles of the plot should be parallel. This means that the four major directions, the east, the west, the north and the south should meet the plot in parallel and not in the corner.
Division of Plot for Temple Construction: By dividing this place into four equal parts the main structure of the temple with "Sabha Mandap" or lecture-hall should be in the south-west part. Go-downs and shops should be in the north-west part. Water storage tanks, wells etc. should be in the north-east part. Kitchen, rest houses etc. should be in the south-east portion as well.
The slope of the land that surrounds the temple in the east and the north direction should be in the north-east corner. Presence of compound wall around the temple in all the four directions is very essential.
Entrance for Temple Construction: Entrance gate should be placed on the east side of the compound wall and that is the best position. Entrance gate on the north side is tolerable. It is very auspicious to have four entrance gates to the main temple building. If there are two gates, at least one of them should be placed in the east and the other one should be in the north side. On the other hand, if there is only one gate it should be in the east direction. But the gate should never be in the south direction. The main entrance gate should be taller than other doors and should be decorated.
There are also many other points which should be decided carefully to establish a temple. These can be mentioned as the sanctuary, the height of the idol, kind of stone of which the idol is made and its colour, the height of the lap from the ground on which the idol is placed, the height of the pinnacle and the metal used for the pinnacle, the height of the discourse hall, no of pillars used for this hall, their colours etc. should be carefully studied from the viewpoint of Vastu Shastra.
On the left side of the outside temple, the victory tower should be situated in front of the idol. It should not be in the north-east direction.
"Deepa Stambh" i.e. pillar for light, "Agni Kund" i.e. earthen pot in which the fire is built and "Homa Kund" i.e. Pit for sacred fire etc. should be in the southeast corner.
There should be no fan in the sanctuary of the idol. The presence of any fan actually spoils the magnetic environment.
There should be a window to the east of the temple such that sunrays fall unobtrusively on the idol from 6 a.m. to 9 a.m.
Marriage ceremony and any other ceremony should be performed in the open space around the temple in the west or in the south side.
Charity boxes or pots in the temple should be in the east or the north side. The divine gift place should be in the east or the north-east corner.
The bell should not be present in the temple. It should be placed somewhere outside the temple.
After the construction of the temple is completed with due regards to the favourable constellations, time and day; the idol should be installed. The installation of the idol and the raising of the pinnacle should be done simultaneously.




















