 Clams are an immense group of edible bivalves widely distributed in all coastal waters. There are many kinds of clams belonging to different families. These include Venerid clams, Surf-clams, Giant clams, Wedge-shells and Soft-shelled clams. The flesh of all clams is valued as food. Their shells are of intrinsic beauty, variety. Clams are far more developed bivalves than the primitive Arks. India has a wealth of different genera of clams both along the seashores and in the backwaters.
Clams are an immense group of edible bivalves widely distributed in all coastal waters. There are many kinds of clams belonging to different families. These include Venerid clams, Surf-clams, Giant clams, Wedge-shells and Soft-shelled clams. The flesh of all clams is valued as food. Their shells are of intrinsic beauty, variety. Clams are far more developed bivalves than the primitive Arks. India has a wealth of different genera of clams both along the seashores and in the backwaters.
Venerid clams form the largest bulk of sea clams. Their feet are comparatively short and compressed and are free or partly united. They live below half-tide mark, buried a few inches deep in sand beds and mud-flats. They are more or less localized and do not make any long excursions in search of food. They dwell on minute plant and animal organisms washed back and forth by the waves. Seashore birds feed on them at low tide, and those living near rocks are eaten by carnivorous Whelks.
 There are several genera of Venerid clams: Circe, Gafrarium, Venus, Paphia, Kaielysia, Tapes, Dosinia, Pitar, Sunetta, etc. All these genera are alike in their internal structure, habits and habitat. They are however remarkable for their shells which are well-known for their varied shape, concentric grooves, radial bands, elegant sculpture, delicate colours and chevron designs. It is because of the exquisite beauty of these shells that their entire family is named Veneridae after Venus the Goddess of Beauty. They are also called Tapestry shells because of the elaborate network and chevron designs on many of the shells. Of all the species, special mention may be made of Pitarerycina which occurs in large numbers near Adam`s Bridge and the north coast of Sri Lanka. Shells of this species fetch a high price in the booths in front of Rameshwaram Temple. The shell is very large, 8 cm long and 7 cm high, thick, with its apex inclined forwards. There are concentric grooves over the shell and the surface colour is orange brown. Several broad radial bands of chestnut tinge diverge from the apex margin wards.
There are several genera of Venerid clams: Circe, Gafrarium, Venus, Paphia, Kaielysia, Tapes, Dosinia, Pitar, Sunetta, etc. All these genera are alike in their internal structure, habits and habitat. They are however remarkable for their shells which are well-known for their varied shape, concentric grooves, radial bands, elegant sculpture, delicate colours and chevron designs. It is because of the exquisite beauty of these shells that their entire family is named Veneridae after Venus the Goddess of Beauty. They are also called Tapestry shells because of the elaborate network and chevron designs on many of the shells. Of all the species, special mention may be made of Pitarerycina which occurs in large numbers near Adam`s Bridge and the north coast of Sri Lanka. Shells of this species fetch a high price in the booths in front of Rameshwaram Temple. The shell is very large, 8 cm long and 7 cm high, thick, with its apex inclined forwards. There are concentric grooves over the shell and the surface colour is orange brown. Several broad radial bands of chestnut tinge diverge from the apex margin wards.
Surf-clams or Mactrids are shallow burrowers in sandy shores, among the surf. The common Indian species belong to genus Mactra. They vary in size from 2 to 6 cm. The shells have their two valves similar; in shape triangularly oval. A shell with closed valves, when viewed from above, looks bulging and roomy. In habits and structural details Mactrids agree with Venerids but their shells are very thin and fragile. Their siphons are united and the foot tongue-shaped, both adapted to live buried in sand with the tips of their siphons alone exposed above the surface. They feed on minute organisms contained in the surf, i.e. the thick white foam of crashing waves. Soon after storms one can see these clams dislodged from their burrows and scattered along the shore. These molluscs are considered tastier than Venerid clams.
The two large clams of Indian shores are Mactra turgida and M. violacea, both 6 to 7 cm long and 5 cm high. The shell of the former is yellowish cream in colour and finely concentrically grooved; while the latter is smooth-surfaced and violet and is tinted with white blotches. There is a Mactra mera, of smaller size, straw-coloured and with a number of white radial bands.
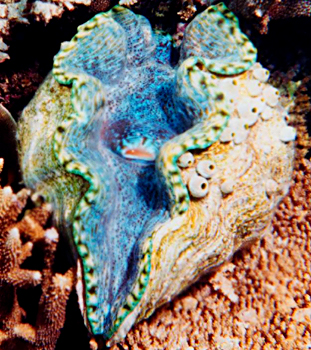
Among the sea clams, the Giant clams (Tridacna gigas) are the largest and heaviest of living bivalves. The shell surface is ornamented with thick, broad, crested, radiating ridges and the margin deeply indented. The interior is thickly enamelled and polished. The animal grows to about a metre in length and weighs 100 kg or more. The mantle of this animal has wide openings. Its foot is short but it attaches itself with strong byssus threads to dead coral or rocks. It has only one adductor muscle connecting the two valves but its pulling power is so great that anything caught between the valves can scarcely be pulled out.
In Indian seas giant clams occur here and there, chiefly attached to coral reefs in the Gulf of Mannar and in larger numbers around Lakshadweep. These clams, living a stationary life among coral reefs, rival their surroundings by the brilliance of their colour: the edges of the fleshy mantle appearing between the gaping valves resemble aster brilliantly coloured in shades of red, blue and green.
All the- backwaters and saline creeks along both coasts of India abound in this clam. In Cochin backwaters and Vembanad Lake members of the species Meretrix ovum grow so abundantly that they form regular beds or layers over the bottom. These shells are dredged in boatloads for the manufacture of quicklime and cement. The flesh is widely eaten. The shell can easily be distinguished by its heart-like shape, smooth grey surface and two broad rays running from the umbo to the lower margin. An adult clam measures about 4 cm long and 3 cm high.
There is another species of backwater clam, Meretrix meretrix, which is very large, 8 cm 5 cm, called the Great clam. The shell exhibits considerable variation in colouring and at least five well-defined colour varieties are known. It is found at the mouths of rivers and creeks opening into the sea, irregularly along both the east and west coasts. These Great clams do not form regular beds. Their flesh is a delicacy.



















