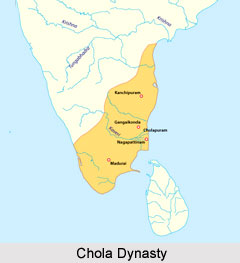
 Chola dynasty was founded by Vijayalaya around 850 AD apparently by starting off as a vassal of the Pallava king. With the conflict between Pallavas and Pandyas, Vijayalaya occupied Tanjore and made his capital. Their home land was called Cholamandalam which included modern Tanjore, Trichinopoly and the Pudukottai state. Kaveri River was the heartland of the Chola dynasty. Uraiyur, presently known as Tiruchirapalli was one of its oldest capital. The Chola chronology is difficult. They ruled from later half of the 9th century till the beginning of the 13th century.
Chola dynasty was founded by Vijayalaya around 850 AD apparently by starting off as a vassal of the Pallava king. With the conflict between Pallavas and Pandyas, Vijayalaya occupied Tanjore and made his capital. Their home land was called Cholamandalam which included modern Tanjore, Trichinopoly and the Pudukottai state. Kaveri River was the heartland of the Chola dynasty. Uraiyur, presently known as Tiruchirapalli was one of its oldest capital. The Chola chronology is difficult. They ruled from later half of the 9th century till the beginning of the 13th century.
History of Chola Dynasty
The origin of Chola Dynasty is shrouded in mystery. Historians have had various views regarding its origin. The most accepted theory is that Cholas is the name of a ruling family or clan of ancient times. The Tamil literature of the Sangam period has information regarding the Cholas of the early period. Cholas have had a mention in the Ashokan pillars too. There are four periods attributed to the history of the Cholas. They are the early Cholas of the Sangam literature, the period between the decline of Sangam Cholas and rise of medieval Cholas, and later Chola dynasty of Kulothunga Chola I.
Administration of Chola Dynasty
The entire kingdom of Cholas was administered under one government. The highest commander of the kingdom was the king. He was a kind dictator. He issued oral commands to responsible officials. The king was assisted by a strong officialdom in implementation of orders. There was no legislative system as such. Every village was an entity governed by itself. Minor disputes were settled by the village heads. Crimes were punished by fining the offenders or property confiscation. Through royal courts, village Panchayats justice was governed. The feudal chiefs were kept away from governmental activities. The Cholas possessed a competent navy and army. The coasts were controlled by its navy. The army had many trained soldiers to protect its borders. Local self government played an important role in the administration set up of the Chola kingdom. Certain amount of autonomy was enjoyed by the villages.
Economy of Chola Dynasty
As the villages were self governing the economy was also prosperous. The villagers made their own clothes and produced their own food. There were other professionals to cater to extra requirements of the village. Lands were based on ownership and its tax was paid by the entire village. The manufacturers of the Chola kingdom produced high quality textiles, metals, pottery, spices, precious stones, pearls and ivory were exported to foreign countries. Chola kingdom had greater access to the sea and was the centre for sea trade as they were located in South India. The merchant guilds were an important part of the economy and operated from major towns. They specialized in procurement of goods and its distribution. They formed a vital part of the economy as there was an increase in internal and external demand for goods.
Society Under Cholas
Stability characterized the kingdom of the Chola dynasty. The people, thus, led a contented life. However, famines were common accompanied with other natural disasters during the rule. According to the inscriptions it is indicated that indicates the people were educated and literacy was a part of the society. The father passed on his skills to his sons; this was the available vocational education. The masses conversed in Tamil language.
Art and Culture Under Cholas
South India reached new heights under the control of Cholas. Majestic temples and stone sculptures were made. Cholas also contributed to Dravidian style of building temples.
Airavateswara temple at Darasuram was built during the rule of the Cholas. Even the temples of Thanjavur and Gangaikondacholapuram are examples of architecture of the Cholas. The temple at Gangaikonda Cholapuram was the creation of Rajendra Chola. Many temples of Lord Shiva and Lord Vishnu were built during this time.
Literature of Chola Period
The age of the Cholas was the golden age of Tamil literature. Devotional literature was widespread especially pertaining to Lord Shiva and Lord Vishnu. Jain and Buddhist authors also thrived during this rule. Jivaka Chintamani by Tirutakkatevar and Sulamani by Tolamoli are among famous authors. Kamban`s Ramavatharam is a great epic in Tamil literature. Devotional religious literature was a major characteristic of the Chola period.
Religion of Chola Period
Cholas were mainly followers of Hinduism. They were not influenced by the augment of Hinduism and Jainism. Cholas did build the largest temple dedicated to Lord Shiva. Cholas did build many temples of Lord Shiva which does make us believe that they were followers of Shaivism. However many temples of Lord Vishnu had also been constructed. In fact, Chola king Sundara was a devotee of Lord Vishnu. Parantaka I and Sundara Chola built temples for both Shiva and Vishnu and also gave many endowments. However Rajaraja Chola I patronised Buddhists, and did provide the requirements for the construction of Buddhist monastery in Nagapattinam. It can be conclude that Shaivism was the most popular faith practiced during their rule.
Rulers of Chola Dynasty
In the 7th century, a Chola kingdom thrived in Andhra Pradesh. Vijayalaya found this dynasty. Vijayalaya captured Thanjavur and established the majestic row of the medieval Cholas. The second Chola King Aditya I, who caused the demise of the Pallavas, defeated the Pandyas of Madurai thereby occupying large parts of the Kannada region. Rajaraja Chola I and Rajendra Chola I extended the Chola kingdom to the island of Sri Lanka in the south to the Godavari-Krishna basin in the north, up to the Konkan coast in Bhatkal, the entire Malabar Coast in addition to Lakshadweep, Maldives and vast areas of Chera territory. The kingdoms of Deccan and the eastern coast were subordinates of the Cholas. The Western Chalukyas were one of the main enemies of the Cholas. They always controlled the Chalukyas successfully in the western Deccan. Chola rulers like Kulothunga I, Vikrama Chola were also capable in keeping the bast Chola empires intact. The wars against the Chalukyas were mainly fought in Karnataka, Vengi, Kakinada and Anantapur. Cholas had to deal with Kadambas, Hoysalas, Kalachuris, and the Chalukyas. The Cholas under Kulothunga Chola III even had alliance with Hoysalas. Marital and political alliances with the Eastern Chalukyas began during Rajaraja`s rule following his invasion of Vengi. The later Chola dynasty saw rulers like Kulothunga Chola I, his son Vikrama Chola, other successors like Rajaraja Chola II, Rajadhiraja Chola II and the great Kulothunga Chola III. The Cholas lost Srilanka to the Sinhalas. The decline of the Chola power began with the rise of Pandyan Empire in 1215 AD -1216 AD. The Pandyas routed out the Cholas completely. Thus the Chola empire was completely surpassed by the Pandyan empire and they declined by the end of the 13th century.
Overall it can be ascertained that the rule of the Cholas had brought about a major change in all spheres of life. It had introduced new rules in administration and economy. Architecture was given a new shape in this age with many majestic temples being built of Lord Shiva and Lord Vishnu. Tamil literature gained a major importance during the reign of the Chola rulers.



















