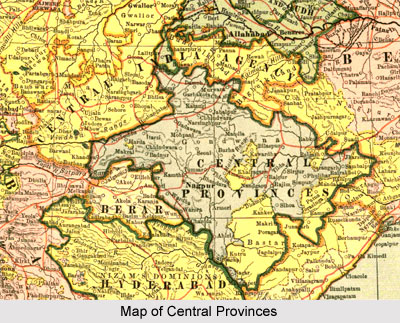
 The Central Provinces was an erstwhile province under the rule of the British Empire in India. The territory contained British occupations from the Mughal Empire and Maratha Empire in central India. It also included various parts of the present state of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh states. Nagpur was the capital of the province in British India. The Central Provinces was established by the unification of the Nagpur Province and the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories in the year 1861. The territory was bounded by several princely states of India like the princely state of Bhopal and Rewa state in the north; the princely state of Kalahandi and the Chota Nagpur state in the east; Berar state in the west; and Nizam`s territories of Hyderabad in the south. The region of Berar of the princely state of Hyderabad was annexed to the Central Provinces in 1903.
The Central Provinces was an erstwhile province under the rule of the British Empire in India. The territory contained British occupations from the Mughal Empire and Maratha Empire in central India. It also included various parts of the present state of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh states. Nagpur was the capital of the province in British India. The Central Provinces was established by the unification of the Nagpur Province and the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories in the year 1861. The territory was bounded by several princely states of India like the princely state of Bhopal and Rewa state in the north; the princely state of Kalahandi and the Chota Nagpur state in the east; Berar state in the west; and Nizam`s territories of Hyderabad in the south. The region of Berar of the princely state of Hyderabad was annexed to the Central Provinces in 1903.
The Legislative Council of the Central Provinces in British India was established on 8th November 1913. The Council continued for Chief Commissioner of the Central Provinces. The Central Provinces Legislative Council continued for the Governor of the Central Provinces between the period 1920 and 1936. Later, after the year 1936, the Legislative Assembly of Central Provinces and Berar was created. The territory became the new province of Central Provinces and Berar on 24th October 1936. After the country achieved independence and the withdrawal of the British Government of India on 15th August 1947, several former princely state of India were merged with the Central Provinces and Berar province. After the new Constitution of India went into effect in the year 1950, the erstwhile Central Provinces formed the new Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, which had Nagpur as its capital. In the year 1956, some of the regions of Madhya Pradesh, which included the Berar and Nagpur divisions, were incorporated as a part of Bombay state.
In 1960, the Bombay state was restructured, with the Gujarati-speaking regions becoming Gujarat and the Marathi-speaking regions forming Maharashtra. Later in the year 2000, the eastern part of the state of Madhya Pradesh was segregated in order to from the new Indian state of Chhattisgarh.






































