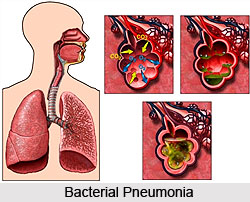
 The major causes of Pneumonia are said to be viruses, bacteria and in rare cases parasites or other micro organisms. However, medical tests have diagnosed particular causes for diverse age group. In adults, pneumonia is most primarily caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, and Legionella. Legionella bacteria are also responsible for causing a disease called Legionnaires` disease. Pneumonia in an immunocompromised malady and is associated with lung infection. This ailment occurs in a person who experiences significantly impaired infection-fighting mechanisms. This makes the persons more susceptible to infections by microorganisms that are present everywhere. Furthermore, immunosuppression is a result of HIV infection, leukemia, organ transplantation, bone marrow transplant, and medications to treat cancer.
The major causes of Pneumonia are said to be viruses, bacteria and in rare cases parasites or other micro organisms. However, medical tests have diagnosed particular causes for diverse age group. In adults, pneumonia is most primarily caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, and Legionella. Legionella bacteria are also responsible for causing a disease called Legionnaires` disease. Pneumonia in an immunocompromised malady and is associated with lung infection. This ailment occurs in a person who experiences significantly impaired infection-fighting mechanisms. This makes the persons more susceptible to infections by microorganisms that are present everywhere. Furthermore, immunosuppression is a result of HIV infection, leukemia, organ transplantation, bone marrow transplant, and medications to treat cancer.
In addition to that young children develop pneumonia from exposure to a virus that includes the parainfluenza and influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus, and adenovirus. Furthermore, chickenpox virus can also cause pneumonia in adults and children. Mycoplasma pneumonia is the cause of walking pneumonia which can occur in children as well as adults. The other major causes of Pneumonia can be Chlamydia psittaci which is found in bird droppings, specifically poultry. Pneumocystis carinii, is a parasite and a fungi which causes pneumonia in people with compromised immune systems, such as those with AIDS or patients undergoing cancer treatment.
Causes of Pneumonia are brilliantly described in Ayurveda. According to Ayurveda the lung is a kapha region of the body. It is a major organ vital to the continued running of the body and well-being of the person. Pneumonia occurs when there is a collision course between the kapha and the element of air (vita) in the Ayurvedic cosmosology. The elements in this collision result in an occurrence of trauma in the affected area and leads to the spread of infection and disease.
A wide spectrum of causes of Pneumonia is underlined. However, all reasons of pneumonia fall under two broad categories: infective pneumonia and aspiration pneumonia. Infective pneumonia includes inflammation and infection of the lungs and bronchial tubes that occurs when a bacteria (bacterial pneumonia) or virus (viral pneumonia) gets into the lungs and begins reproducing. Whereas, Aspiration pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs and bronchial tubes that is caused by inhaling vomit, mucous, or other bodily fluids. Aspiration pneumonia can be a result of inhaling certain chemicals. Pneumonia usually develops in a person when he inhales infected air particles into the lungs. Although, healthy lungs do not have any type of bacteria or virus because the body develops immunity to protect the lungs. Yet, these defend mechanisms can be besieged by exposure to a large number of the organisms causing pneumonia.
Other varied causes of pneumonia develop during or after a viral upper respiratory infection, such as a cold or the flu. Pneumonia also occurs as a complication of a viral illness such as measles or chickenpox. This disease can affect a person in most cases by breathing in small droplets so as to contain the bacteria or virus that can cause pneumonia. These droplets get into the air when a person infected with these germs coughs or sneezes. In other cases, pneumonia is caused when bacteria or viruses which are normally found in the mouth, throat, or nose inadvertently enter the lung. Individuals who suffer from emphysema, heart disease, and swallowing problems, as well as who are alcoholics, drug users and have suffered stroke or seizure are at higher risk for developing pneumonia.
The moment, the bacteria, virus or fungus have entered the lungs, they settle in the air sacs of the lung rapidly and multiply. This area of the lung then is filled with fluid and pus as the body attempts to fight off the infection. Respiratory viruses are thus the most common causes of pneumonia in young children, who are between the ages of 2 and 3. Other causes of pneumonia can develop while admitted in a hospital. There lies a greater possibility of infection with bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics. Even though most of the cases of pneumonia are results of a viral or bacterial infection, yet the disease is also caused by the obstruction of the bronchial tubes. The objects such as tumors, peanuts, hard candies, or small toys in the bronchial tubes can trap bacteria, viruses or fungi resulting in pneumonia. Pneumonia is a disorder that is the consequence of contract with the pneumonia causing viruses and bacteria. This disease is spread all over through coughs and sneezes, sharing drinking glasses and eating utensils with an infected person, and contact with used tissues or handkerchiefs.