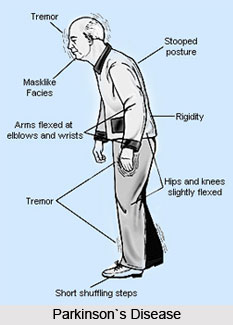
 Parkinson`s disease is caused by the progressive mutilation or deterioration of neurons (nerve cells) in an area of the brain known as the substantia nigra. When functioning normally, these neurons create a vital brain chemical known as dopamine. Dopamine serves as a chemical messenger thus allowing communication between the substantia nigra and another area of the brain called the corpus striatum. This communication coordinates smooth and balanced muscle movement. Absence of dopamine results in abnormal nerve functioning, causing a loss in the ability to control body movements.
Parkinson`s disease is caused by the progressive mutilation or deterioration of neurons (nerve cells) in an area of the brain known as the substantia nigra. When functioning normally, these neurons create a vital brain chemical known as dopamine. Dopamine serves as a chemical messenger thus allowing communication between the substantia nigra and another area of the brain called the corpus striatum. This communication coordinates smooth and balanced muscle movement. Absence of dopamine results in abnormal nerve functioning, causing a loss in the ability to control body movements.
Low levels of dopamine, a brain chemical (neurotransmitter) concerned with the controlling movement, cause symptoms of Parkinson`s disease. The shortage of this brain chemical occurs when nerve cells in a part of the brain (substantia nigra) that produces dopamine collapse or deteriorate. The exact cause of this deterioration is not known till date. The connections between Parkinson`s disease and factors such as genetics, ageing, toxins in the environment, and free radicals are all under study. Although these studies are beginning to provide some answers, experts do not know the particular cause of the disease. Studies are continuing to examine whether there is a genetic cause of Parkinson`s disease. Only a small percentage of people with Parkinson`s disease have a parent, brother, or sister who has the disease; however, strange genes do seem to be a cause in a few families where early-onset Parkinson`s disease is very common.
Although, the reason of Parkinson`s disease occurrence and how the neurons become impaired is not known, there is increasing evidence that Parkinson`s disease may be inherited (passed on genetically from family members). There is considerable argument surrounding the prospect of a genetic cause of Parkinson`s disease. In a small number of families, exact genetic abnormalities leading to the illness have been recognised. However, the enormous majority of people with Parkinson`s disease do not have one of these recognised genetic abnormalities. It is probable that in people who develop Parkinson`s disease early in life (young-onset Parkinson`s disease) there is a genetic factor. It is not yet understood about how Parkinson`s disease is inherited; the implications for children of people with Parkinson`s disease are vague.
 There is also some proof that certain toxins in the environment may cause Parkinson`s disease. Scientists have suggested that external or internal toxins may particularly destroy the dopaminergic neurons, causing Parkinson`s disease. Toxins that may cause Parkinson`s include manganese, carbon monoxide, carbon disulfide and some other pesticides. Also, it is believed that oxidative stress can cause Parkinson`s disease. Oxidation is a process in which free radicals (unstable molecules lacking one electron), in an attempt to replace the missing electron, react with other molecules (such as iron). Free radicals are normally formed in the brain and body, but usually the brain and body have mechanisms to get rid of free radicals. In people with Parkinson`s disease, the mechanisms may not be effectual or they may create too many free radicals. It is also probable that environmental toxins may donate to abnormal free radical formation and lead to Parkinson`s disease. Oxidation is believed to cause damage to tissues, including neurons. In most cases, antioxidants protect cells from free radical damage.
There is also some proof that certain toxins in the environment may cause Parkinson`s disease. Scientists have suggested that external or internal toxins may particularly destroy the dopaminergic neurons, causing Parkinson`s disease. Toxins that may cause Parkinson`s include manganese, carbon monoxide, carbon disulfide and some other pesticides. Also, it is believed that oxidative stress can cause Parkinson`s disease. Oxidation is a process in which free radicals (unstable molecules lacking one electron), in an attempt to replace the missing electron, react with other molecules (such as iron). Free radicals are normally formed in the brain and body, but usually the brain and body have mechanisms to get rid of free radicals. In people with Parkinson`s disease, the mechanisms may not be effectual or they may create too many free radicals. It is also probable that environmental toxins may donate to abnormal free radical formation and lead to Parkinson`s disease. Oxidation is believed to cause damage to tissues, including neurons. In most cases, antioxidants protect cells from free radical damage.
While the causes of Parkinson`s disease are not apparent, the abnormal nerve functions linked to Parkinson`s disease are associated with certain conditions and medications that can cause Parkinson`s disease-like symptoms. Certain drugs such as antipsychotics used to treat severe paranoia and schizophrenia can cause a person to experience symptoms that resemble Parkinson`s disease (Parkinsonism). Street drugs MPTP, a synthetic heroin contaminant, can cause severe Parkinson`s disease-like symptoms as well. Blood vessel disorders, although rare, stroke and atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) can cause symptoms similar to Parkinson`s disease. Shy-Drager syndrome is an uncommon degenerative condition that produces symptoms similar to Parkinson`s disease. Most researchers suggest that a combination of these factors may be the causes of Parkinson`s disease.




