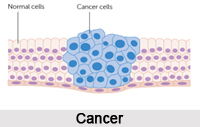
 Cancer is a class of diseases characterized by out-of-control cell growth. The medical term of cancer is malignant neoplasm, and it is actually a class of diseases in which a group of cells display uncontrolled growth, invasion and sometimes metastasis. The uncontrolled growth is defined by division beyond the normal limits; invasion means violation and destruction of adjacent tissues; and metastasis is spreading to other locations in the body via lymph or blood. The cancer cells can multiply and spread to other parts of the body.
Cancer is a class of diseases characterized by out-of-control cell growth. The medical term of cancer is malignant neoplasm, and it is actually a class of diseases in which a group of cells display uncontrolled growth, invasion and sometimes metastasis. The uncontrolled growth is defined by division beyond the normal limits; invasion means violation and destruction of adjacent tissues; and metastasis is spreading to other locations in the body via lymph or blood. The cancer cells can multiply and spread to other parts of the body.
The branch of medicine involved with the study, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of cancer is called "Oncology". Cancer can affect all kinds of living beings in the world, including human and animals. People of all ages, even foetuses, can be affected by cancers. However, generally, for most types of cancers, the risk increases with age.
Causes of Cancer
Many causes have been identified behind the development of cancer. Though the prime cause of cancer is not known, certain cancer-promoting substances have been identified, which increase the chances of the disease. These substances are known as "Carcinogens". The major causes of cancers include; mutation due to chemical carcinogens; mutation due to ionising radiation; the viral or bacterial infection; hormonal imbalances; having immune system dysfunction and also heredity. A majority of cancers are caused by abnormalities in the genetic material of the transformed cells. These abnormalities may happen due to the effects of different substances like tobacco smoke, radiation, chemicals, or infectious agents, etc. Even certain environmental factors are identified as potential causes of cancer.
Some other genetic abnormalities can also promote cancers. These abnormalities may be randomly acquired through errors in DNA replication, or may be inherited, and thus they are present in all cells from birth. Apart from these, new aspects of the genetics of cancer pathogenesis like DNA methylation and micro RNAs are also recognised as important factors behind developing cancers. 
Symptoms of Cancer
There are several symptoms that help to identify cancers. The symptoms of cancers can be classified in 3 major groups like the local symptoms, the symptoms of metastasis (spreading), and the systemic symptoms. The local symptoms include unusual lumps or swelling (tumour), haemorrhage (bleeding), pain and/or ulceration, etc. The symptoms of metastasis include the enlarged lymph nodes, cough and haemoptysis, hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), bone pain, fracture of affected bones, etc. and also the neurological symptoms. On the other hand, the systemic symptoms include weight loss, poor appetite, fatigue and feebleness, excessive sweating, anaemia and specific para-neoplastic phenomena, etc.
Types of Cancers
Several types of cancers have been identified so far, and most of them form a tumour. However, some cancers like leukaemia do not form any tumour. The classification of cancers can be done depending on the organ they affect. Some of the most commonly found cancers include;
•Blood Cancer,
•Breast Cancer,
•Cervical Cancer,
•Liver Cancer,
•Brain Cancer or Brain Tumour,
•Leukaemia,
•Bladder Cancer,
•Bone Cancer,
•Lung Cancer,
•Pancreatic Cancer,
•Skin Cancer, etc.
 Treatments for Cancer
Treatments for Cancer
Many methods are used for the treatment of cancers. In India, cancer is treated following different traditional methods like Ayurveda, Homoeopathic, Unani, etc. and Yoga is also used sometimes for the treatment of cancers. The most common treatments for cancers include surgery, hormone therapy, radiation, etc. However, cancers can also be treated by using nature care, magnetic therapy, etc.
Prevention of Cancer
Taking different preventive actions is another effective way to avoid the development of cancers. Different preventive actions include;
•Not smoking;
•Not drinking too much alcohol;
•Limiting red meat consumption;
•Eating fruits and vegetables;
•Maintaining a controlled diet or reaching a healthy weight;
•Being physically active;
•Protecting skin from sunlight;
•Avoiding second hand tobacco smoking;
•Avoiding exposure to pesticides and dioxins; etc.




