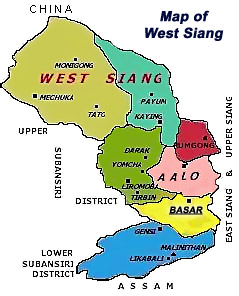
 Basar is a census town situated in the administrative district of West Siang in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India. Standing at an elevation of 578 metres, Basar is a popular town since it is the abode of the Galo tribe. The language spoken by the Galo people in Basar is Galo which is also known as Lare, it is related to the Chinese and Tibetan languages. The town of Basar is subdivided into 5 zila segments and adjudicating such facts it lies along the central part of Arunachal Pradesh. The different tribal groups of the district are the Adi, the Memba and Khamba. A famous Tibetan Buddhist temple, Mechuka Gompa is positioned in the western part of the Mechuka district of West Siang.
Basar is a census town situated in the administrative district of West Siang in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India. Standing at an elevation of 578 metres, Basar is a popular town since it is the abode of the Galo tribe. The language spoken by the Galo people in Basar is Galo which is also known as Lare, it is related to the Chinese and Tibetan languages. The town of Basar is subdivided into 5 zila segments and adjudicating such facts it lies along the central part of Arunachal Pradesh. The different tribal groups of the district are the Adi, the Memba and Khamba. A famous Tibetan Buddhist temple, Mechuka Gompa is positioned in the western part of the Mechuka district of West Siang.
Demographics of Basar
As per the reports of the Census India 2011, the Basar town has a total population of about 12,224 people. Out of which 6,237 are males while 5,987 are females. In 2011, there were total 2,512 families residing in the Basar Circle. The average sex ratio of Basar circle is 960. Out of the total population, 35% people lives in urban areas while 65% lives in the rural areas. The average literacy rate in the urban areas is 88% while that in the rural areas is 68percnt; and the sex ratio of urban areas in Basar circle is 880 while that of rural areas is 1,006. The population of children between the ages 0 to 6 years is 1,523 which is 12% of the total population. The number of male children is 766 while the female is 757. Thus as per the Census 2011, the child sex ratio of this region is 988 which is greater than the average sex ratio of Basar, which is 960. The total literacy rate of Basar circle is 75% out of which the male literacy rate is 70% and the female literacy rate is 60% in this region.
Cultivation in Basar
The Galo people of the Basar region practise slash-and-burn agriculture. The plains of the Basar valley are famous for wet rice cultivation and thus the staple crop of the Galo people are rice and maize. Fruits like oranges and pineapples are grown in abundance while kiwi and apple are grown in the higher ridges of the mountainous ranges.
Festivals in Basar
An agricultural festival called Mopin, is the mother of all festivals in the Basar region and is performed before or after the sowing of seeds for bumper crops. Poppyir song and dances of Mopin are performed during this festival.
The majority of Galo people practise the religion known as Donyi-Polo, which involves the chanting of rhymes to appease the ancestors to invoke the blessings of the sun and the moon, where the priest called Nyibu plays a crucial role as intermediary between the Donyi-polo and the people.
Visiting Information on Basar
The nearest airport to Basar is at Dibrugarh in Assam, which is about 150 km away. The Dibrugarh railway station is the closest to the town of Basar.



















