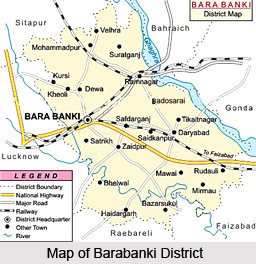
 Barabanki District is an administrative district of Uttar Pradesh located in Awadh region. Barabanki District is situated about 29 kms in the east direction of Lucknow. Barabanki District lies between latitudes 26 degree 30 minutes north and 27 degree 19 minutes north and longitudes 80 degree 58 minutes east and 81 degree 55 minutes east. Barabanki District is surrounded by Faizabad District in the east, districts Gonda and Bahraich in the north east, Sitapur District in the north-west, Lucknow District in the west, district Rae Bareli in the south and district Sultanpur in the south east. Ghaghara River forms the north eastern boundary separating Barabanki from Bahraich and Gonda.
Barabanki District is an administrative district of Uttar Pradesh located in Awadh region. Barabanki District is situated about 29 kms in the east direction of Lucknow. Barabanki District lies between latitudes 26 degree 30 minutes north and 27 degree 19 minutes north and longitudes 80 degree 58 minutes east and 81 degree 55 minutes east. Barabanki District is surrounded by Faizabad District in the east, districts Gonda and Bahraich in the north east, Sitapur District in the north-west, Lucknow District in the west, district Rae Bareli in the south and district Sultanpur in the south east. Ghaghara River forms the north eastern boundary separating Barabanki from Bahraich and Gonda.
History of Barabanki District
Barabanki District of Uttar Pradesh is known for its rich heritage and glorious past. Barabanki District was known as Dariyabad with its headquarters at Dariyabad town. It remained the district headquarter till 1858 AD. The district headquarter was shifted to Nawabganj in 1859 AD now known as Barabanki. This was done during the expansion of the district by the British, when Kursi from district Lucknow and Haidergarh from district Rae Bareli were added to it.
Geography of Barabanki District
Barabanki District can be topographically divided into three main regions - Tarai region, Gomti Par region and Har region. The entire tract of Barabanki District is gently undulating land. The main rivers of Barabanki District are Ghaghara River, Gomti River and Kalyani River. Geography of Barabanki District includes a typical climate that means it is extremely hot in the summer season, cold in the winters and humid in the rainy season.
 Mainly alluvial soil is found in the district.
Mainly alluvial soil is found in the district.
Administration of Barabanki District
Barabanki is one of the four constituent districts of Faizabad Division. Administration of Barabanki District is headed by Divisional Commissioner. Barabanki District has been divided into seven sub-divisions, popularly known as tehsils. The District Revenue Administration is headed by the District Collector, with office at the collectorate, and these tehsils are under the charge of sub-divisional Magistrates. The six tehsils are Nawabganj, Fatehpur, Ramsanehi Ghat, Haidergarh, Ram Nagar and Sirauli Ghauspur. The district level developmental activities are coordinated by the Block Development Officers, who head each of the Development Blocks into which the district is sub-divided. Barabanki encompasses 15 development blocks. The 15 development blocks are Banki, Siddhaur, Masauli, Pure Dalai, Dewa, Nindura, Harakh, Trivediganj, Fatehpur, Ram Nagar, Haidergarh, Sirauli Ghauspur, Dariyabad, Banikodar and Suratganj. The Law and Order administration is jointly coordinated by the District Magistrate and the Superintendent of Police. The district is sub divided into 22 Police Stations. Further, Barabanki District has 14 urban administrative bodies for the administration and provision of civil amenities in towns.
Tourism in Barabanki District
Barabanki District is known for its historical relevance. Thus, tourism in this district offers visits to various historically significant places. Dewa Sharif Shrine, Mahadeva Temple, Siddheshwar Temple, Badosarai, Kotwa Dham temple, Masauli, Rafi Ahmad Kidwai Memorial, Kintur, Satrikh, Bhitauli and Kunteshwar Temple are some of the main attractions of Barabanki District.
Barabanki District since its inception has been the place for numerous saints and ascetics, sanctum sanctorum of `Sadhna` for the literary intellectuals and battlefield for the freedom fighters.






